NVP: How to perform FLR using nonroot user on Linux VMs
Summary: This KB provides information about requirements that must be met to perform File Level Restores (FLR) on Linux Virtual Machines (VM) using the NetWorker VMware Protection (NVP) vProxy appliance. ...
This article applies to
This article does not apply to
This article is not tied to any specific product.
Not all product versions are identified in this article.
Instructions
NOTE: The NetWorker VMware Integration Guide contains information about performing FLR as nonroot users. See FLR Agent installation on Linux platforms. NetWorker version-specific guides are available through: Support for NetWorker | Manuals & Documents.
In order to perform FLR of a Linux Virtual Machine (VM) using the NetWorker VMware Protection (NVP) vProxy appliance, root credentials, or a user with sudo access must be used to mount the FLR. The following steps must be followed.
Configuring a Non-Root User for FLR on RHEL
- Create a Non-Root User (if one does not exist already)
Run the following commands to create a new user and set a password:useradd <username> passwd <username>
- For the user created, no
requirettyandNOPASSWDsettings must be configured. There are two options:- Create a
sudoersfile for the user account and allow globalNOPASSWDaccess to all commands (less secure but optional depending on environment):cat >/etc/sudoers.d/USERNAME-flr <<'EOF' Defaults:USERNAME !requiretty USERNAME ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL EOF
- Create a
sudoersfile for the user and only allowNOPASSWDaccess to the commands required for FLR (more secure):
- Create a
cat >/etc/sudoers.d/USERNAME-flr <<'EOF' Defaults:USERNAME !requiretty USERNAME ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /bin/rpm, /usr/bin/rpm, /opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/postinstall.sh, /opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/preremove.sh, /opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/vflrbrowse, /opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/vflrcopy EOF
- Overview of these settings:
!requiretty:sudoallowed from scripts/non‑TTY sessions. This is required to start the FLR mount remotely from the vProxy appliance and VMware API.USERNAME ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: Defines what commands can be run without prompting thesudouser for a password. Setting this toALLmeans that thesudouser can run any system command without a password prompt. Setting specific binaries or commands means that the user can only run those commands without a password prompt; all other commands prompt for a password. Once the FLR process has started through remote API, it would not be possible to interactively enter thesudouser's password, so the above settings must be used to ensure that the user can run the FLR commands on the host from remote API.
- Example of configuring these settings for user "
admin"
[root@rhel-client01 ~]# cat >/etc/sudoers.d/admin-flr <<'EOF' Defaults:admin !requiretty admin ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /bin/rpm, /usr/bin/rpm, /opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/postinstall.sh, /opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/preremove.sh, /opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/vflrbrowse, /opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/vflrcopy EOF [root@rhel-client01 ~]#
- Restrict permissions to the
sudoersfile:chmod 440 /etc/sudoers.d/USERNAME-flr - Validate that the required FLR permissions were applied:
su USERNAME -c 'sudo -l'
Example:
[root@rhel-client01 ~]# su admin -c 'sudo -l'
Matching Defaults entries for admin on rhel-client01:
!visiblepw, always_set_home, match_group_by_gid, always_query_group_plugin, env_reset, env_keep="COLORS DISPLAY HOSTNAME HISTSIZE KDEDIR LS_COLORS", env_keep+="MAIL PS1 PS2
QTDIR USERNAME LANG LC_ADDRESS LC_CTYPE", env_keep+="LC_COLLATE LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_MEASUREMENT LC_MESSAGES", env_keep+="LC_MONETARY LC_NAME LC_NUMERIC LC_PAPER
LC_TELEPHONE", env_keep+="LC_TIME LC_ALL LANGUAGE LINGUAS _XKB_CHARSET XAUTHORITY", secure_path=/sbin\:/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin, !requiretty
User admin may run the following commands on rhel-client01:
(ALL) NOPASSWD: /bin/rpm, /usr/bin/rpm, /opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/postinstall.sh, /opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/preremove.sh, /opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/vflrbrowse,
/opt/emc/vproxyra/bin/vflrcopy
- The VM's sudo file must have (
r-x) permissions.- Determine the sudo binary used:
which sudo - Validate permissions:
ls -l sudo_path(typically/usr/bin/sudo) - If
sudodoes not haver-xpermissions, set permissions using:chmod 4755 sudo_path
- Determine the sudo binary used:
Example:
[root@rhel-client01 ~]# which sudo /usr/bin/sudo [root@rhel-client01 ~]# ls -ltr /usr/bin/sudo ---s--x--x 1 root root 185304 Jun 26 2025 /usr/bin/sudo [root@rhel-client01 ~]# chmod 4755 /usr/bin/sudo [root@rhel-client01 ~]# ls -ltr /usr/bin/sudo -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 185304 Jun 26 2025 /usr/bin/sudo
Alternatively, you can leave the sudo permissions as they are and create the following symbolic link instead: ln -s /usr/bin/sudo /usr/local/sbin/sudo
NOTE: If
sudo does not have execute permissions, then it cannot be run. If sudo does not have read permissions for "users" and "others," then the VMware API used to start the FLR mount fails to find it. This results in an FLR mount failure, "Unable to get sudo path."
- Perform FLR Using the Non-Root user from the NetWorker Web User Interface (NWUI). The Run With Elevated Privileges option must be selected:
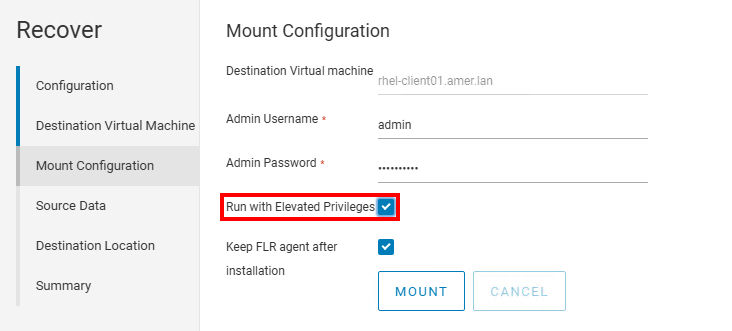
NOTE: It is only possible to perform FLR as a nonroot user from NWUI. There is no "run with elevated privileges" option in the NetWorker Management Console (NMC). For more information, see: NetWorker: How to Perform a VMware FLR from the NetWorker Web User Interface
Additional Information
Affected Products
NetWorker FamilyArticle Properties
Article Number: 000306157
Article Type: How To
Last Modified: 16 يناير 2026
Version: 4
Find answers to your questions from other Dell users
Support Services
Check if your device is covered by Support Services.