Data Domain: Managing Host Certificates for HTTP and HTTPS
Resumo: Host certificates allow browsers and applications to verify the identity of a Data Domain system when establishing secure management sessions. HTTPS is enabled by default. The system can use either a self-signed certificate or an imported certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). This article explains how to check, generate, request, import, and delete certificates for HTTP/HTTPS on Data Domain systems. ...
Este artigo aplica-se a
Este artigo não se aplica a
Este artigo não está vinculado a nenhum produto específico.
Nem todas as versões do produto estão identificadas neste artigo.
Instruções
Certificates may expire or become invalid. If no certificate is imported, the system uses a self-signed certificate, which may not be trusted by browsers or integrated applications.
1. Check Existing Certificates.
On the Data Domain (DD-CLI), run the following command to view installed certificates:
adminaccess certificate show
If certificates are expired or nearing expiration:
-
- If self-signed, regenerate using DD-CLI.
- If imported, follow the CSR and import steps below.
2. Generate Self-Signed Certificates.
To regenerate the HTTPS certificate:
adminaccess certificate generate self-signed-cert
To regenerate HTTPS and trusted CA certificates:
adminaccess certificate generate self-signed-cert regenerate-ca3. Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
Use DD System Manager:
-
- Set a passphrase, if not done already:
system passphrase set - Navigate to Administration > Access > Administrator Access.
- Select HTTPS > Configure > Certificate tab > Add.
- Click Generate the CSR for this Data Domain system.
- Complete the CSR form and download the file from:
/ddvar/certificates/CertificateSigningRequest.csr
- Set a passphrase, if not done already:
CLI alternative: (Example)
adminaccess certificate cert-signing-request generate key-strength 2048bit country "CN" state "Shanghai" city "Shanghai" org-name "Dell EMC" org-unit "Dell EMC" common-name "ddve1.example.com" subject-alt-name "DNS:ddve1.example.com, DNS:ddve1"4. Import Signed Certificate
- Use DD System Manager:
- Select Administration > Access > Administrator Access
- In the Services area, select HTTPS and click Configure
- Select the Certificate tab
- Click Add
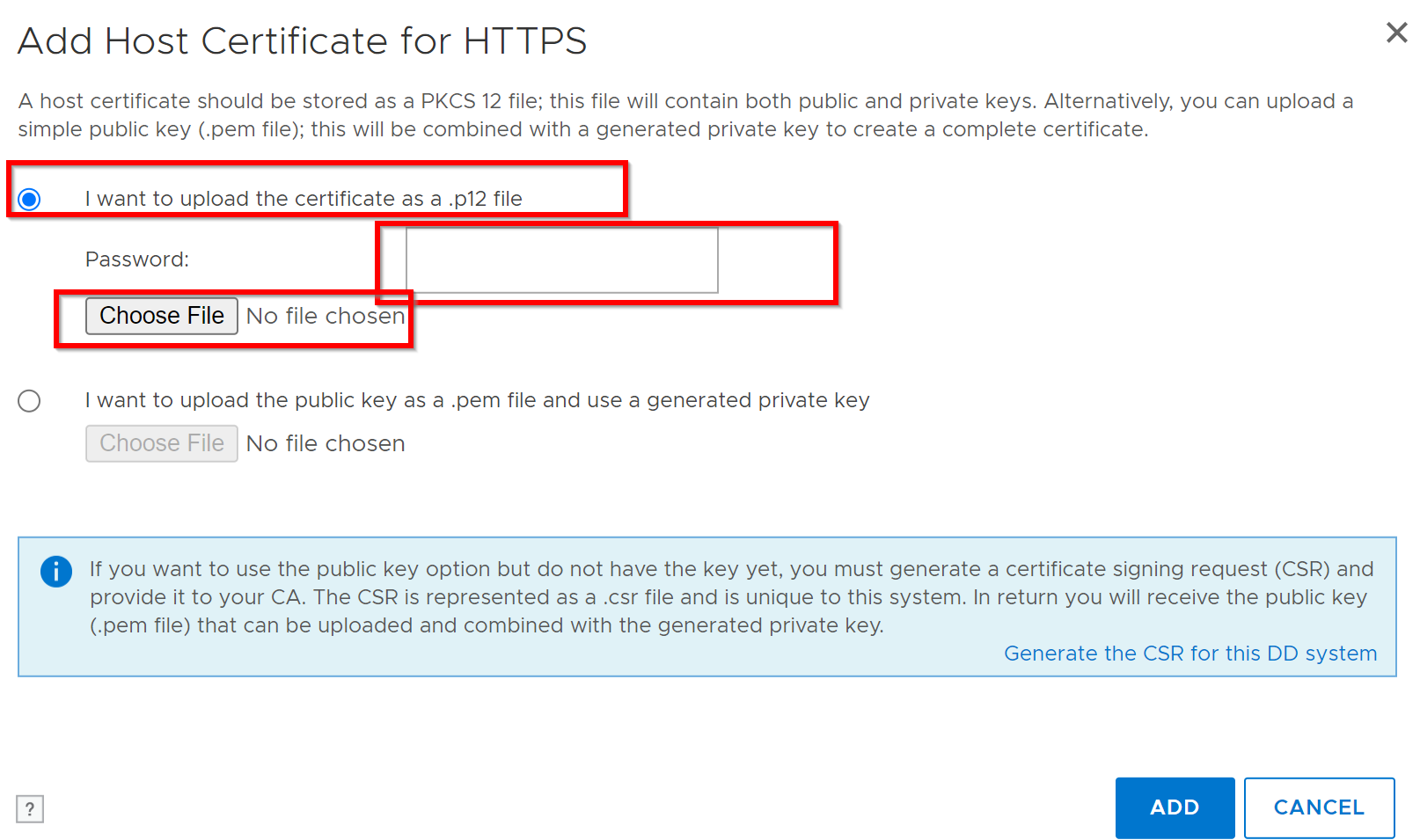
An Upload dialog appears:
- For
.p12file:- Select Upload certificate as .p12 file, enter password, browse, and upload.
- For
.pemfile:- Select Upload public key as .pem file and use generated private key, browse, and upload.
- DD-CLI alternative: Refer to KB: Data Domain: How to Generate a Certificate Signing Request and Use Externally Signed Certificates
- Select Upload public key as .pem file and use generated private key, browse, and upload.
- Example for .p12 selection:
5. Delete Existing Certificate.
Before adding a new certificate, delete the current one:
-
- Navigate to Administration > Access > Administrator Access > HTTPS > Configure > Certificate tab.
- Select certificate and click Delete.
6. CSR Validation
Validate CSR using Windows Command Prompt:
certutil -dump <CSR file path>Mais informações
- Private and public keys must be 2048 bits.
- DDOS supports one active CSR and one signed certificate for HTTPS at a time.
Reference: Deployment KB: Data Domain: How to use externally signed certificates
Produtos afetados
Data DomainPropriedades do artigo
Número do artigo: 000205198
Tipo de artigo: How To
Último modificado: 27 nov. 2025
Versão: 7
Encontre as respostas de outros usuários da Dell para suas perguntas.
Serviços de suporte
Verifique se o dispositivo está coberto pelos serviços de suporte.