Windows Server: Troubleshooting Active Directory and DNS Replication
Summary: This article provides information about troubleshooting Active Directory and DNS replication.
Instructions
Table of Contents:
1. Find the Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) role holders
2. Narrow down the problem
3. Visually inspect DNS
4. Visually inspect sites and services
5. Use event IDs to narrow troubleshooting
6. Other tools
Issue 1. Find the Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) role holders:
Begin by finding the domain controllers (DCs) in the organization. Focus on the health of your forest root and work your way out.
Find the FSMO role holders by opening an elevated command prompt and typing:
netdom query fsmo
This returns a list of the DCs holding each role:
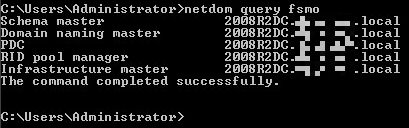
Issue 2. Narrow down the problem:
To narrow down the problem, you must be systematic. Use the following tools to test various DCs, their connection to the root domain or role holder, their ability to resolve names to IP addresses, open ports, and replication results.
Try to pinpoint a specific server that does not communicate and determine if the source or destination server is the cause. Event logs and replication results are ways to gain additional information.
dcdiag /v /c /d /e /s: > c:\dcdiag.txtipconfig /all(from all DCs and DNS servers)repadmin /showrepl(from each DC)repadmin /replsumdcdiag /test:dns /s: /dnsbasicrepadmin /syncall /aped- Ping each DC by name and verify that the name resolves to the correct IP address.
- Use
nslookupto test DNS across different DCs. - Use
tracertto test the routes between servers. repadmin /bind servername- Can the DCs bind to each other?
Issue 3. Visually inspect DNS:
Open the DNS console by going to Start -> Administrative Tools -> DNS. Click the DNS server in the left pane.
Review the forward lookup zones and all other zones related to the forest and domain partitions.
Guidance is available from Microsoft TechNet using this link: Troubleshooting DNS
Some things to look for in the DNS console include:
- Start of authority (properties) - multiple names for servers that do not exist.
- Records that have incorrect IP addresses.
- Stale records that have not been deleted.
- "(Same as parent folder)" host records that do not reference the DCs.
- Find the start of authority (SOA) and name server (NS) records in the domain forward lookup zone (see image below).
- Right-click each and select Properties.
- Verify the name servers and other information are correct.
- Look in the
_msdcsfolder. - Are there missing entries?

You can find more information about the DNS infrastructure from the Microsoft TechNet DNS Server
Issue 4. Visually inspect sites and services:
The Active Directory Sites and Services console contains several items that may help troubleshoot replication failures. Inspect and open every folder and look for the following:
- Verify that subnets have been created and assigned to the correct sites.
- Ensure that each site object contains the correct servers.
- Inspect the NTDS settings to verify the replication connections.
- Verify that the server names exist.
Issue 5. Use event IDs to narrow troubleshooting:
AD-related errors can be found in the Event Viewer console.
The fastest way to get there is to go to Start -> Run and type eventvwr.msc.
Relevant event logs include the System, DNS, Directory Service, and File Replication Service log.
Use the following articles to help determine the next steps, based on errors found in the logs:
- Troubleshooting Replication
- How AD Replication Topology Works
- Troubleshooting Active Directory Replication Problems
Issue 6. Other tools:
Nltest is a useful command-line tool that can return many kinds of information about an AD domain.
The metadata cleanup process is used to remove AD references to DCs that were taken offline without being properly demoted.
Lingering objects are AD objects that have been deleted from one DC but remain on another due to a replication failure.
Removing these objects is a necessary step in restoring proper replication.
- How to remove data in Active Directory after an unsuccessful domain controller demotion
- Clean Up Server Metadata
- Nltest
- Clean that Active Directory forest of lingering objects