Data Domain: Verifying that Network Connectivity is Working As Expected
Summary: This article covers the basics of how to check the NIC physical connectivity and configuration in DDOS to ensure that the CIFS or NFS share is available on the network.
This article applies to
This article does not apply to
This article is not tied to any specific product.
Not all product versions are identified in this article.
Instructions
Verifying that Network Connectivity is Working Properly.
Symptoms:
- If network connectivity is not working as expected, then there is an issue with backup performance or it cannot access the CIFS or NFS share over the network at all.
- Restorer is not available.
- Backup application reports write error.
- Network path not found.
- Alert message:
Error: : RPC: Unable to send; errno = Broken pipe
Applies to:
- All Data Domain Systems
- All Software Releases
Resolution:
Physical Connection:
Connect a network cable to a valid NIC port on the DDR. NICs can be either on the motherboard, or an optional expansion card. Your Restorer may have the NICs in slightly different locations depending on the model, but their relative positions are equivalent.
NOTE: A Category 5e or 6 is recommended.
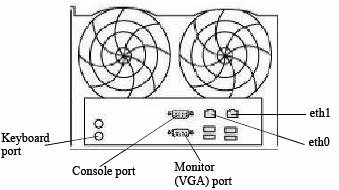
Let us say we have connected a network cable on eth0 on DDR box:
- eth0 connects to the left port on the back of the DDR when looking at it from the back)
- The other end connects to a switch.
Setting up and confirming the IP Address:
In our example, eth0 is configured with the following information:- IP address = 192.168.4.138
- Subnet = 255.255.255.0
- Gateway = 192.168.4.1
- DNS = 192.168.4.2, 192.168.4.3
NOTE: Prior to assigning an IP address, ensure that the address is not already allocated on the network.
From another computer, use the "ping" command to the IP address to be configured as eth0 (Use Ctrl+C to stop):
ping 192.168.4.138 PING 192.168.4.138 (192.168.4.138) 56(84) bytes of data. From 192.168.4.138 icmp_seq=1 Destination Host Unreachable From 192.168.4.138 icmp_seq=2 Destination Host Unreachable From 192.168.4.138 icmp_seq=3 Destination Host Unreachable ^C
If the IP address responds, then it is in use and another IP address must be allocated.
On the DDR box, we use the "net" command to verify the status of the NIC port eth0.
The below command gives us information about the physical cable (connected or not), whether the NIC is 10/100 / 10/100/1000, the MAC address of the NIC port, the speed, the duplex, and the type of NIC card.
net show hardware Port Speed Duplex Supp Speeds Hardware Address Physical Cable ----- -------- -------- ------------ ------------------ ------- ----- eth0 1000Mb/s full 10/100/1000 00:xx:xx:xx:xx:4c Copper yes eth1 unknown unknown 10/100/1000 00:xx:xx:xx:xx:e1 Copper no ----- -------- -------- ------------ ------------------ ------- -----
From the above example, we can see that eth0 can support 1000MB/s Full duplex, the physical type is Copper, and network cable is connected.
The "net config" command is used to configure eth0. Entering the command "net config set ?" provides the proper syntax for your DDOS version. Example:
net config set ?
Commands matching "net config":
net config <ifname> [type {floating | fixed}]
{[<ipaddr>] [netmask <mask>] | [<ipv6addr>] |
[dhcp {yes [ipversion {ipv4|ipv6}]|no}]}
{[autoneg] | [duplex {full | half} speed {10|100|1000|10000}]}
[up | down] [mtu {<size> | default}]
[txqueuelen <size>]
Configure an Ethernet interface. Create
an alias by giving an address to a new
alias number. Destroy an alias by
giving an address of zero. "Note:
Change of link parameters like speed,
duplex or autoneg on the DD VE is not
supported."
net config addresses [type {floating | fixed}]
Convert IP addresses to another type.
In our example:
1. The command below is used to set the IP address and subnet mask:
2. The command below is used to set the default gateway:
net config eth0 192.168.4.138 netmask 255.255.255.0</pre>
2. The command below is used to set the default gateway:
route set gateway 192.168.4.1 The Default Gateway is: 192.168.4.1
3. The command below is used to set up the DNS:
net set dns 192.168.4.2, 192.168.4.3 The Name (DNS) server list is: 192.168.4.2, 192.168.4.3
Verifying the IP Address
To verify interface eth0 is up and has a correct IP address and netmask, use the "net show config eth0" command:
net show config eth0 eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:xx:xx:xx:xx:4c inet addr:192.168.4.138 Bcast:192.168.4.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: beef::250:56ff:abcd:954c/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:6564330 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:3156402 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:1614169232 (1.5 GiB) TX bytes:3093309111 (2.8 GiB)
To verify it is on the network:
ping 192.168.4.1 PING 192.168.4.1 (192.168.4.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.4.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.512 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.4.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.296 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.4.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.284 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.4.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.275 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.4.1: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.295 ms ^C
2. Ping from another computer on the network to the eth0 IP (for example the one used earlier to verify the IP address was not in use)
ping 192.168.4.138 PING 192.168.4.138 (192.168.4.138 ) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.4.138 : icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.512 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.4.138 : icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.316 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.4.138 : icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.294 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.4.138 : icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.285 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.4.138 : icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.295 ms ^C
Affected Products
Data DomainProducts
Data DomainArticle Properties
Article Number: 000015001
Article Type: How To
Last Modified: 22 Feb 2024
Version: 6
Find answers to your questions from other Dell users
Support Services
Check if your device is covered by Support Services.