How to Analyze Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise and Threat Defense Endpoint Status
Summary: Learn about how to analyze endpoint statuses in Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise and Dell Threat Defense using these instructions.
Instructions
- As of May 2022, Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise has reached End of Maintenance. This product and its articles are no longer updated by Dell.
- As of May 2022, Dell Threat Defense has reached End of Maintenance. This product and its articles are no longer updated by Dell.
- For more information, reference Product Life Cycle (End of Support and End of Life) Policy for Dell Data Security. If you have any questions on alternative articles, either reach out to your sales team or contact endpointsecurity@dell.com.
- Reference Endpoint Security for additional information about current products.
Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise and Dell Threat Defense endpoint statuses can be pulled from a specific endpoint for in-depth review of threats, exploits, and scripts.
Affected Products:
- Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise
- Dell Threat Defense
Affected Platforms:
- Windows
- Mac
- Linux
Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise or Dell Threat Defense administrators may access an individual endpoint to review:
- Malware Contents
- Malware State
- Malware Type
An administrator should only perform these steps when troubleshooting why the advanced threat prevention (ATP) engine misclassified a file. Click Access or Review for more information.
Access
Access to malware information varies between Windows, macOS, and Linux. For more information, click the appropriate operating system.
Windows
By default, Windows does not record in-depth malware information.
- Right-click the Windows start menu and then click Run.

- In the Run UI, type
regeditand then press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER. This runs the Registry Editor as admin.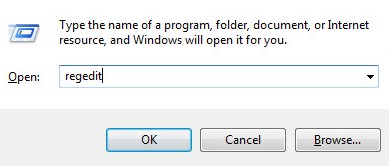
- In the Registry Editor, go to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Cylance\Desktop. - In the left pane, right-click Desktop and then select Permissions.
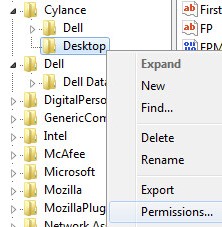
- Click Advanced.

- Click Owner.

- Click Other users or groups.
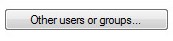
- Search for your account in the group and then click OK.

- Click OK.
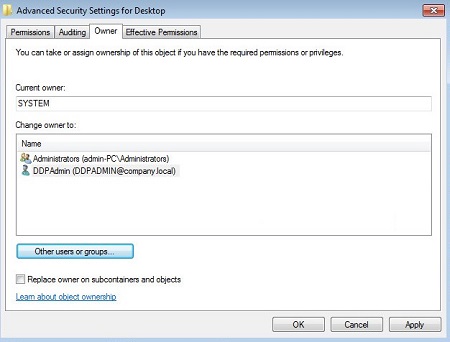
- Ensure that your group or username has Full Control checked and then click OK.
 Note: In the example, DDP_Admin (step 8) is a member of the Users group.
Note: In the example, DDP_Admin (step 8) is a member of the Users group. - At
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Cylance\Desktop, right-click the Desktop folder, select New, and then click DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Name the DWORD
StatusFileEnabled.
- Double-click
StatusFileEnabled.
- Populate Value data with
1and then press OK.
- At
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Cylance\Desktop, right-click the Desktop folder, select New, and then click DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Name the DWORD
StatusFileType.
- Double-click
StatusFileType.
- Populate Value data with either
0or1. Once Value data has been populated, press OK. Note: Value data choices:
Note: Value data choices:0= JSON file format1= XML format
- At
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Cylance\Desktop, right-click the Desktop folder, select New, and then click DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Name the DWORD
StatusPeriod.
- Double-click
StatusPeriod.
- Populate Value data with a number ranging from
15to60and then click OK. Note: The StatusPeriod is how often the file is written.
Note: The StatusPeriod is how often the file is written.
15 = 15 second interval
60 = 60 second interval - At
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Cylance\Desktop, right-click the Desktop folder, select New, and then clickString Value.
- Name the String
StatusFilePath.
- Double-click StatusFilePath.

- Populate Value data with the location to write the status file to and then click OK.
 Note:
Note:- Default path:
<CommonAppData>\Cylance\Status\Status.json - Example path:
C:\ProgramData\Cylance - A .json (JavaScript Object Notation) file can be opened in an ASCII text document editor.
- Default path:
macOS
In-depth malware information is in the Status.json file at:
/Library/Application Support/Cylance/Desktop/Status.json
Linux
In-depth malware information is in the Status.json file at:
/opt/cylance/desktop/Status.json
Review
The status file’s Contents include detailed information about multiple categories including Threats, Exploits, and Scripts. Click the appropriate information to learn more about it.
Contents
Status file contents:
snapshot_time |
The date and time the Status information was collected. The date and time are local to the device. |
ProductInfo |
|
Policy |
|
ScanState |
|
Threats |
|
Exploits |
|
Scripts |
|
Threats
Threats have multiple numerical-based categories to be deciphered in File_Status, FileState, and FileType. Reference the appropriate category for the values to be assigned.
File_Status
The File_Status field is a decimal value calculated based on the values that are enabled by FileState (see the table in the FileState section). For example, a decimal value of 9 for file_status is calculated from the file being identified as a threat (0x01) and the file has been quarantined (0x08).

FileState
Threats: FileState
| None | 0x00 |
| Threat | 0x01 |
| Suspicious | 0x02 |
| Allowed | 0x04 |
| Quarantined | 0x08 |
| Running | 0x10 |
| Corrupt | 0x20 |
FileType
Threats: FileType
| Unsupported | 0 |
| PE | 1 |
| Archive | 2 |
| 3 | |
| OLE | 4 |
Exploits
Exploits have two numerical-based categories to be deciphered in both ItemType and State.

Reference the appropriate category for the values to be assigned.
ItemType
Exploits: ItemType
StackPivot |
1 | Stack Pivot |
StackProtect |
2 | Stack Protect |
OverwriteCode |
3 | Overwrite Code |
OopAllocate |
4 | Remote Allocation of Memory |
OopMap |
5 | Remote Mapping of Memory |
OopWrite |
6 | Remote Write to Memory |
OopWritePe |
7 | Remote Write PE to Memory |
OopOverwriteCode |
8 | Remote Overwrite Code |
OopUnmap |
9 | Remote Unmap of Memory |
OopThreadCreate |
10 | Remote Thread Creation |
OopThreadApc |
11 | Remote APC Scheduled |
LsassRead |
12 | LSASS Read |
TrackDataRead |
13 | RAM Scraping |
CpAllocate |
14 | Remote Allocation of Memory |
CpMap |
15 | Remote Mapping of Memory |
CpWrite |
16 | Remote Write to Memory |
CpWritePe |
17 | Remote Write PE to Memory |
CpOverwriteCode |
18 | Remote Overwrite Code |
CpUnmap |
19 | Remote Unmap of Memory |
CpThreadCreate |
20 | Remote Thread Creation |
CpThreadApc |
21 | Remote APC Scheduled |
ZeroAllocate |
22 | Zero Allocate |
DyldInjection |
23 | DYLD Injection |
MaliciousPayload |
24 | Malicious Payload |
Oopreferences Out of ProcessCpreferences Child Process- For more information about violation types, refer to Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise Memory Protection Category Definitions.
State
Exploits: State
| None | 0 |
| Allowed | 1 |
| Blocked | 2 |
| Terminated | 3 |
Scripts
Exploits have a single numerical-based category to be deciphered in Action.

Scripts: Action
| None | 0 |
| Allowed | 1 |
| Blocked | 2 |
| Terminated | 3 |
To contact support, reference Dell Data Security International Support Phone Numbers.
Go to TechDirect to generate a technical support request online.
For additional insights and resources, join the Dell Security Community Forum.