How RAM Speed Affect the Performance of a Computer
Summary: Learn how RAM speed and memory capacity impact your computer's performance. Explore what more RAM does, how to check RAM MHz, and why RAM speed matters for efficiency.
Instructions
Your computer's system memory is made up of physical memory, called system memory or Random Access Memory (RAM), and virtual memory. System memory is not permanent storage, like a hard disk drive that saves its contents when you turn off your computer.
When you start a program, your processor gives a command to retrieve the program from the hard drive. Once the files are retrieved, the computer needs a workspace to manipulate the data and allow you to interact with it. This digital countertop is your RAM. Your computer places your programs in RAM or the digital countertop, temporarily while you are working with them so that the processor can access that information faster and more easily.
Understanding RAM
Generally, the more RAM your computer has, the larger the digital countertop you have to work on and the faster your programs runs. If your computer is running slowly due to a lack of RAM, you might be tempted to increase virtual memory because it is less expensive. However, adding RAM is a better solution because your processor can read data from RAM faster than from a hard drive.
RAM has two main attributes that affect your computer's performance: memory capacity and memory speed.
Operating System Limitations
Today, most computers are equipped with a 64-bit operating system. Some computers have older designs and use a 32-bit (X86) operating system. Before you upgrade your RAM, ensure that your operating system supports the new amount of memory. Microsoft has an excellent listing in the hyperlink below listing Windows versions and the amount of RAM supported: Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases 
Memory capacity: The more GB your memory module has, the more programs you can have open at once.
-
2-4 GB: This was the standard RAM capacity and shipped with computers running Windows Vista or XP. This amount of memory could handle single applications. If your computer has less than 4 GB of RAM, adding more RAM would greatly improve its performance.
-
4-6 GB: This standard RAM capacity handles an average user's tasks, such as web browsing, working in Word documents, and emailing, with ease.
- 6-8 GB: This larger RAM capacity works great for casual gamers and basic multimedia users. It can handle multiple programs open at one time and new technology so that users do not have to upgrade when their needs change.
- 8+ GB: This robust RAM capacity is perfect for hardcore gamers and high-end multimedia users and creators. These users want to try the newest technology on the market without upgrading their RAM.
Memory Speed: The amount of time that it takes RAM to receive a request from the processor and then read or write data. Generally, the faster the RAM, the faster the processing speed.
With faster RAM, you increase the speed at which memory transfers information to other components. Meaning, your fast processor now has an equally fast way of talking to the other components, making your computer more efficient.
RAM speed is measured in Megahertz (MHz), millions of cycles per second so that it can be compared to your processor's clock speed. For Dell desktops and laptops, memory speed can range from the standard 1333 MHz all the way up to speeds of 2133 MHz. The speed of your processor and the bus speed of the computer motherboard are the limiting factors on the speed of RAM installed in your computer. RAM upgrades limit the capability of the computer and the availability of expansion slots for adding RAM. Often, upgrading RAM may involve replacing existing RAM modules with larger modules that can be limited by the capability of the computer.
Many tablets and some entry-level laptops do not have upgradable RAM. Look up your computer at the Dell Support Website and check the specifications of the computer before purchasing expansion RAM memory.
Upgrading RAM
If you are considering upgrading your RAM to improve your computer's performance, first determine the amount of RAM your computer has and whether the processor uses a 32-bit (X86) or 64-bit register.
How to check the amount of system memory (RAM) installed in Windows 11 and Windows 10
- Right-click the Start Menu and select System.
- In the System section, next to Installed memory (RAM), you can view the amount of RAM your computer has.
- In the System section, under System type, you can view the register that your computer uses (Figure 1).
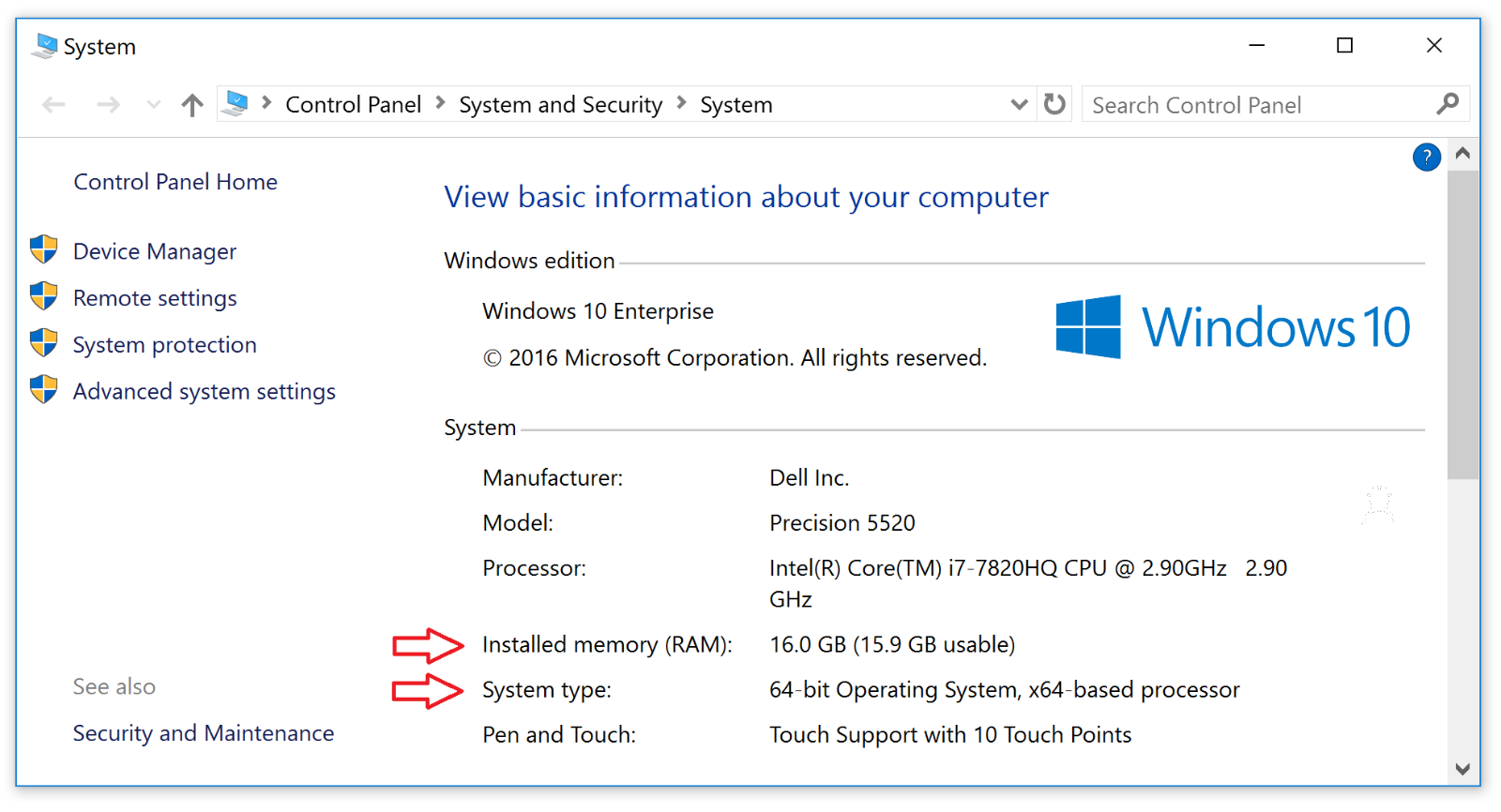
Figure 1: System Page
Remember, it is important to plan how you would like to use your Dell computer, both now and in the future. When you are ready to upgrade, go to Dell Support website for installation and to ensure that the memory module is compatible with your computer.
See these Dell Knowledge Base articles for related information:
- How to Optimize the System Memory (RAM) on a Dell Computer
- What Is System Memory (RAM)
- How to Upgrade or Install System Memory or RAM in a Dell Computer
- How to Diagnose and Resolve Common Memory Issues on a Dell Laptop
- How to Determine the Amount of Random Access Memory (RAM) Installed in your ChromeBook
Additional Information
 Out of warranty? No problem. Go to the Dell.com/support website and enter your Dell Service Tag and view our offers.
Out of warranty? No problem. Go to the Dell.com/support website and enter your Dell Service Tag and view our offers.