Microsoft Windows: How to Configure Guest RDMA on Windows Server
摘要: This article explains how to configure Guest Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) on a Windows Server.
说明
Table of Contents
- Introduction of Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA)
- Lab Environment
- Hardware Configuration
- Configuring Guest RDMA
- Powershell Cmdlets
- Download Links
Introduction of Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA)
Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) is a great technology that enables computers to transfer data across the network without involving the CPU or OS resources of the hosts involved (Compute and Storage). This improves throughput and performance and reduces latency and CPU overhead.
There are two popular RDMA implementations today:
- RoCE
- Transport: UDP/IP (RoCE v2)
- Rely on Data Center Bridging (DCB)
- iWarp
- Underlying Network: TCP/IP
- TCP provides flow control and congestion management.
RoCE relies heavily on DCB configuration such as Enhanced Transmission Service (ETS) and Priority Flow Control (PFC), which can become a problem if network switches are not configured properly. iWARP does not require any switch configuration.
Microsoft started supporting RDMA on Windows Server 2012 and added new features in the later Windows Server OS. One feature available on Microsoft’s Windows Server 2019 is the ability to present RDMA to the Guest OS (VM). This allows the Guest to have the same low-latency access to a network storage as the native host, reducing CPU overhead and improving throughput and performance directly in the VM.
Dell offers great options for 25 Gbps RDMA such as the Cavius QLogic FastLinQ 41262 Dual Port 25 GbE SFP28 (iWarp/RoCE) and the Mellanox ConnectX-4 Lx 25 Gbps RDMA (RoCE). This example uses the Mellanox ConnectX-4 Lx RDMA (RoCEv2 mode) to demo the Guest RDMA feature.
Lab Environment
Servers:
- 2 x Dell R7425 (AMD EPYC 7551 32-Core Processor)
- 256 GB Memory
- Mellanox ConnectX-4 Lx fully updated (Firmware (incl. BIOS), drivers, and OS)
Roles and Features Installed:
- Hyper-V
- DCB
- Failover Clustering
- S2D
Switch:
- Dell S5048F-ON - MGMT VLAN 2
- SMB VLAN 15
Hardware Configuration
- Reboot the servers and go to the System Setup (press F2 during POST).
- Select Device Settings.
Figure 1 - BIOS Device Settings
- Select the NIC in Slot 1 Port 1 - Mellanox.
Figure 2 - Mellanox Slot 1 Port 1 Device Settings
- Go to Device Level Configuration.
Figure 3 - Device Level Configuration
- Select SR-IOV in Virtualization Mode.
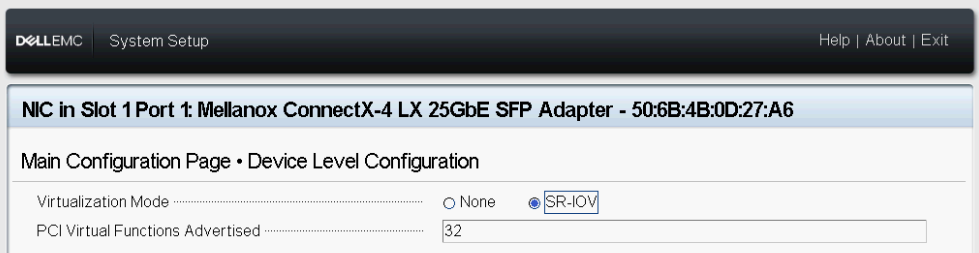
Figure 4 - SR-IOV Setting
- Repeat the steps above on the NIC in Slot 1 Port 2 - Mellanox.
Figure 5 - Mellanox Slot 1 Port 2 Device Settings
- Go back to System Setup Main Menu then select System BIOS.
Figure 6 - System BIOS
- Select Integrated Devices.
Figure 7 - BIOS-Integrated Devices
- Enable SR-IOV Global option.

Figure 8 - SR-IOV Global
- Save your configuration and reboot the server.
Configuring Guest RDMA
- Install Windows Server 2019+.
- Install the Hyper-V Role and the Data Center Bridging (DCB) feature.
- Configure Quality-of-Service (QoS), DCB, PFC, ETS. Ensure that the server NIC and QoS configuration match the switch configuration.
- Configure Hyper-V Switch Embedded Team (SET).

Figure 9 - vSwitch Configuration
- Test RDMA communication between the physical servers prior to configuring the VMs. Download Microsoft
Diskspdand the Microsoft Test-RDMA PowerShell script. Follow the steps below only if communication is working properly. Otherwise, check the switch configuration and or DCB settings on the host.
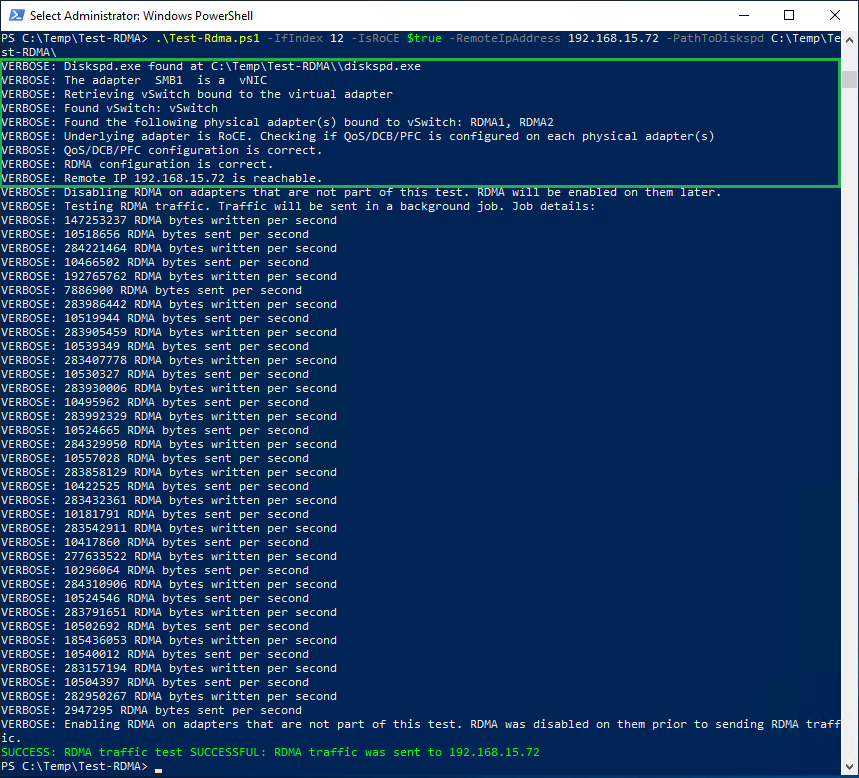
Figure 10 - Test-RDMA Physical Hosts
- Verify if SR-IOV is enabled on the RDMA adapters on both servers.
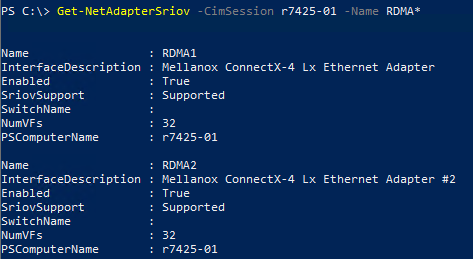
Figure 11 - SR-IOV Enabled
- Create two Gen 2 VMs (Guest OS), one on each server then install Windows Server 2019. In this scenario, a Guest OS is created with two vNICs, one for MGMT traffic (VLAN 2) and one for SMB traffic (VLAN 15).
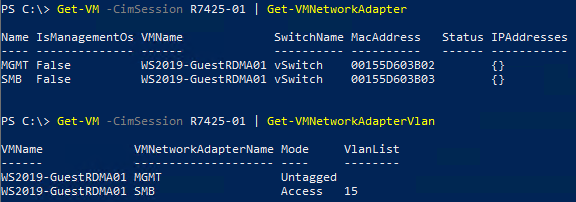
Figure 12 - Guest OS Network Configuration Host R7425-01
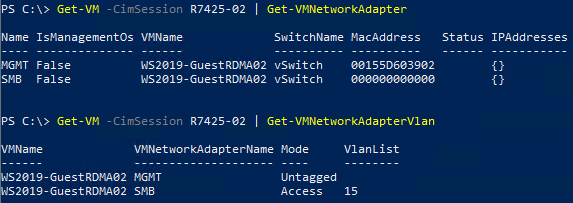
Figure 13 - Virtual Machine Network Configuration Host R7425-02
- Shut down the VMs.
- Enable SR-IOV and RDMA on the Guest OS.
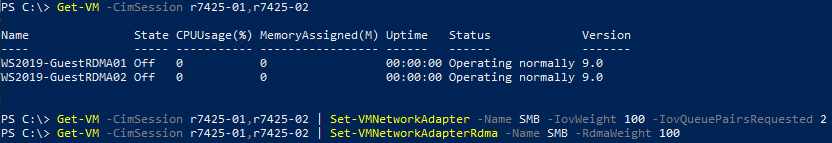
Figure 14 - Enable SR-IOV/RDMA on Guest OSs.
- Start the VMs then open Device Manager. The Mellanox Virtual Function (VF) should be listed under Network Adapters. The VF is not presented as a regular network adapter in Network Connections as seen on Figure 15.
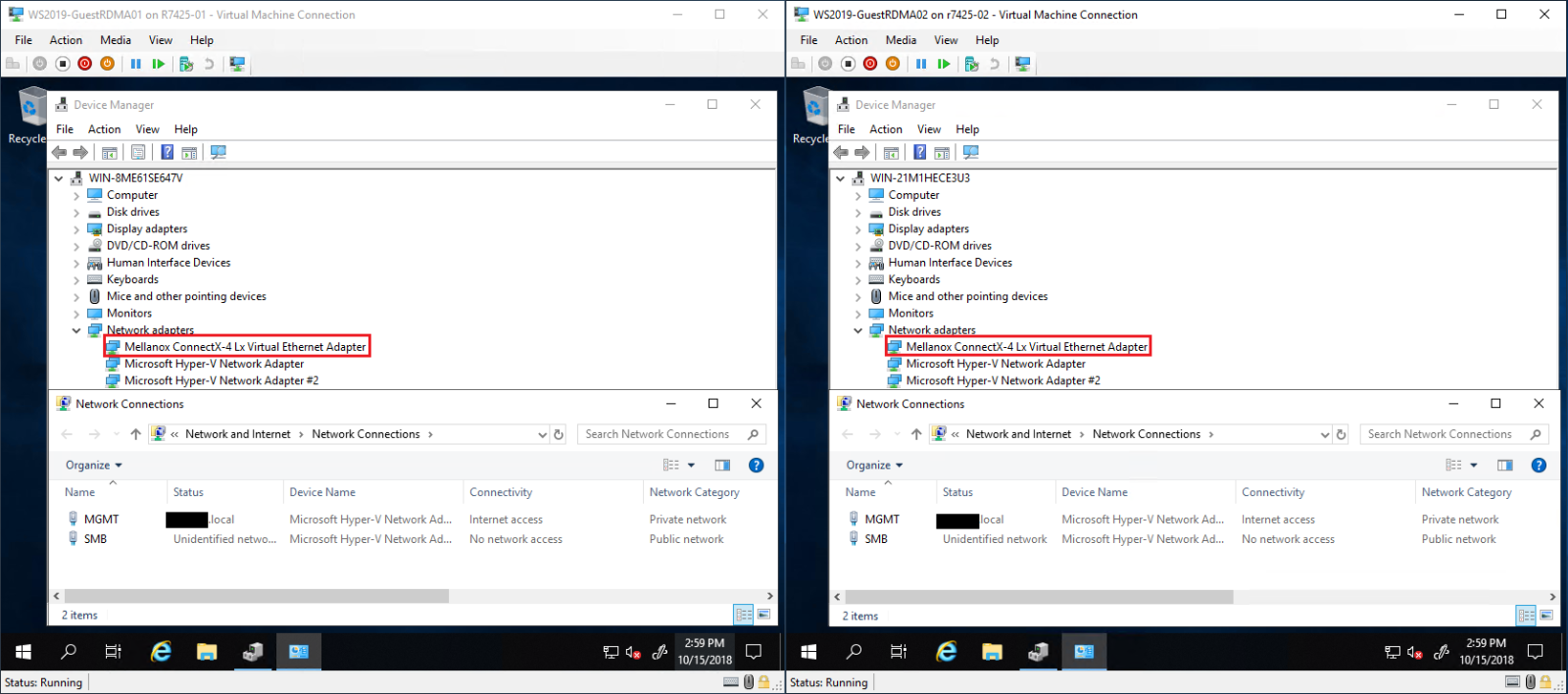
Figure 15 - Guest OS Device Manager and Network Connections
- Enable RDMA on SMB vNIC. RDMA functionality is already enabled on the Mellanox VF (Ethernet4 - Figure 16).
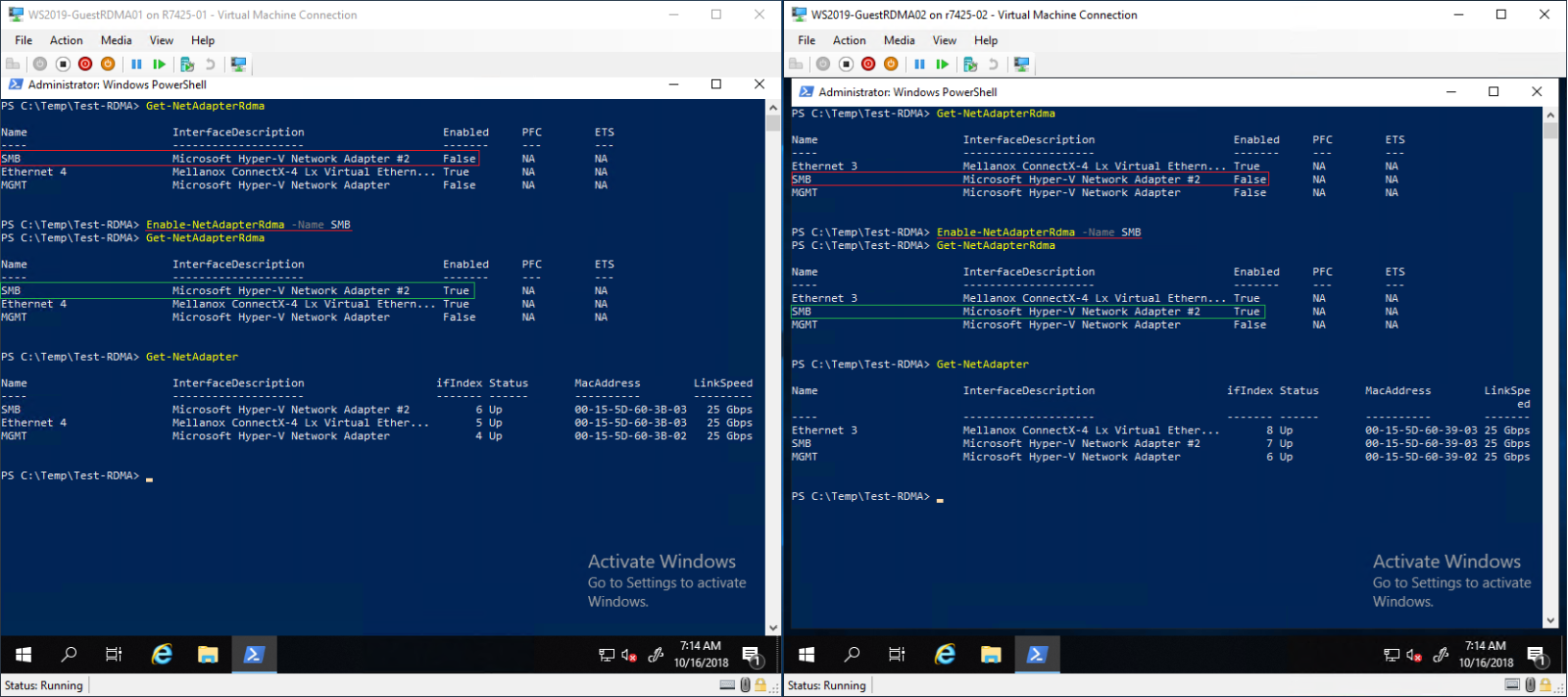
Figure 16 - Enable RDMA on SMB vNIC.
- Test Guest RDMA.
IfIndex (vNIC Interface Index) and the VfIndex (Mellanox VF Interface Index).
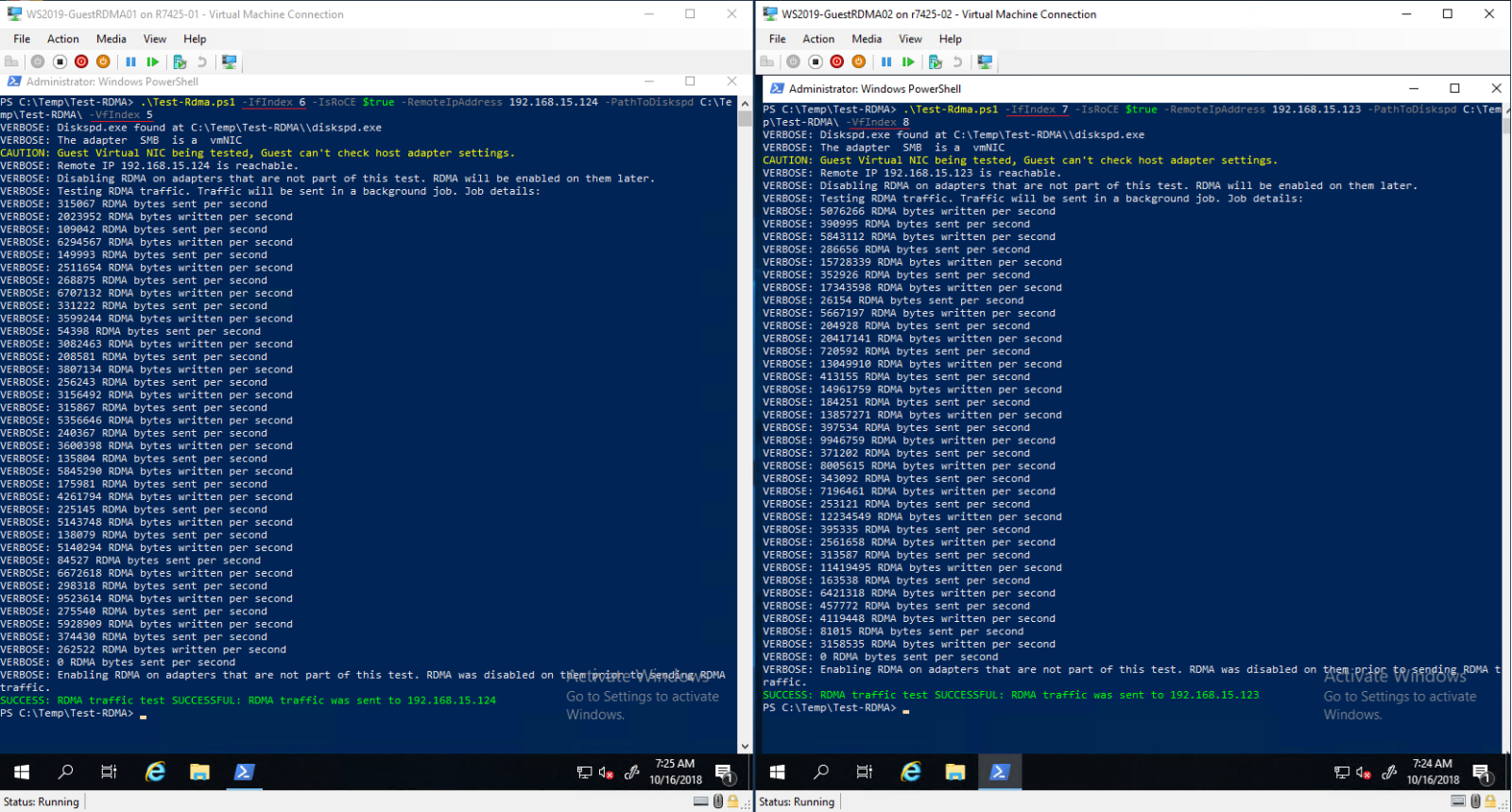
Figure 17 - Test-RDMA Guest OS
Powershell Cmdlets
#Create new virtual switch with SRIOV option enabled New-VMSwitch -Name xxxx -NetadapterName xxxx,xxxx -AllowManagementOS $true -EnableEmbeddedTeaming $true -EnableIov $true #Verify if SRIOV is enabled on physical adapter Get-NetAdapterSriov -Name xxxx #Get VM network configuration Get-VM -Name xxxx| Get-VMNetworkAdapter #Get VM network VLAN configuration Get-VM -Name | Get-VMNetworkAdapterVlan #Set VM SRIO and RDMA on Virtual Machine(Guest OS) vNIC Get-VM -Name xxxx | Set-VMNetworkAdapter -Name xxx -IovWeight 100 -IoVQueuePairsRequested 2 Get-VM -Name xxxx | Set-VMNetworkAdapterRdma -Name xxx -RdmaWeight 100 #Enable RDMA on NetAdapter Enable-NetAdapterRdma -Name xxxx #Test-Rdma Physical Host .\Test-Rdma.ps1 -IfIndex xx -IsRoCE $true -RemoteIpAddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx -PathToDiskspd xxxxx #Test-Rdma Virtual Machine (Guest OS) .\Test-Rdma.ps1 -IfIndex xx -IsRoCE $true -RemoteIpAddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx -PathToDiskspd xxxxx -VfIndex xx
Download Links
Have any comments, questions, or suggestions? Contact us on WinServerBlogs@dell.com
