Data Domain — NFSv4 简介
摘要: 由于 NFS 客户端越来越多地使用 NFSv4.x 作为默认 NFS 协议级别,因此保护系统现在可以使用 NFSv4,而不要求客户端在向后兼容模式下工作。 客户端可以在 NFSv4 和 NFSv3 必须能够访问相同 NFS 导出的混合环境中工作。 DDOS NFS 服务器可以配置为支持 NFSv4 和 NFSv3,具体取决于现场要求。您可以让每个 NFS 导出仅适用于 NFSv4 客户端和/或 NFSv3 客户端。 ...
说明
有几个因素可能会影响您选择 NFSv4 还是 NFSv3:
● NFS 客户端支持
某些 NFS 客户端可能仅支持 NFSv3 或 NFSv4,或者可能使用某个版本可以更好地运行。
●作要求
企业可以严格标准化以使用 NFSv4 或 NFSv3。
● 安全性
如果您需要更高的安全性,NFSv4 提供比 NFSv3 更高的安全级别,包括 ACL 和扩展的所有者和组配置。
● 功能要求
如果您需要字节范围锁定或 UTF-8 文件,则应选择 NFSv4。
● NFSv3 子装载
如果您的现有配置使用 NFSv3 子装载,NFSv3 可能是合适的选择。
NFSv4 与 NFSv3
的比较与 NFSv3 相比,NFSv4 提供了增强的功能和特性。
下表比较了 NFSv3 与 NFSv4 的功能。
表 NFSv4 与 NFSv3 的比较
| 功能 | NFSv3 | NFSv4 |
| 基于标准的网络文件系统 | 是的 | 是的 |
| Kerberos 支持 | 是的 | 是的 |
| 带 LDAP 的 Kerberos | 是的 | 是的 |
| 配额报告 | 是的 | 是的 |
| 具有基于客户端的访问列表的多个导出 | 是的 | 是的 |
| ID 映射 | 是的 | 是的 |
| UTF-8 字符支持 | 否 | 是的 |
| 基于文件/目录的访问控制列表 (ACL) | 否 | 是的 |
| 扩展所有者/组 (OWNER@) | 否 | 是的 |
| 文件共享锁定 | 否 | 是的 |
| 字节范围锁定 | 否 | 是的 |
| DD-CIFS 集成(锁定、ACL、AD) | 否 | 是的 |
| 有状态文件打开并恢复。 | 否 | 是的 |
| 全局命名空间和伪 FS | 否 | 是的 |
| 使用引用的多系统命名空间 | 否 | 是的 |
NFSv4 端口
您可以单独启用或禁用 NFSv4 和 NFSv3。此外,您可以将 NFS 版本移到不同的端口;两个版本不需要占用相同的端口。
使用 NFSv4 时,如果更改端口,则不需要重新启动文件系统。在此类情况下,只需要重新启动 NFS。
与 NFSv3 一样,如果启用了 NFSv4,则默认在端口 2049 上运行。
NFSv4 不使用 portmapper(端口 111)或 mountd(端口 2052)。
ID 映射概览
NFSv4 通过通用外部格式(如 joe@example.com)标识所有者和组。这些常见格式称为标识符或 ID。
标识符存储在 NFS 服务器中,并使用内部表示形式,例如 ID 12345 或 ID S-123-33-667-2。内部和外部标识符之间的转换称为 ID 映射。
标识符与以下内容相关联:
● 文件和目录
的所有者● 文件和目录
的所有者组● 访问控制列表 (ACL)
中的条目保护系统对 NFS 和 CIFS/SMB 协议使用通用内部格式,允许在 NFS 和 CIFS/SMB 之间共享文件和目录。
每个协议使用自己的 ID 映射将内部格式转换为外部格式。
外部格式
NFSv4 标识符的外部格式遵循 NFSv4 标准(例如,NFSv4.0 的 RFC-7530)。此外,
还支持补充格式以实现互作性。
标准标识符格式
Standard external identifiers for NFSv4 have the format identifier@domain. This identifier is used for NFSv4 owners,
owner-groups, and access control entries (ACEs). The domain must match the configured NFSv4 domain that was set using the
nfs option command.
The following CLI example sets the NFSv4 domain to mycorp.com for the NFS server:
nfs option set nfs4-domain mycorp.com
See client-specific documentation you have for setting the client NFS domain. Depending on the operating system, you might
need to update a configuration file (for example, /etc/idmapd.conf) or use a client administrative tool.
ACE extended identifiers
For ACL ACE entries, protection system NFS servers also support the following standard NFSv4 ACE extended identifiers
defined by the NFSv4 RFC:
● OWNER@, The current owner of the file or directory
● GROUP@, the current owner group of the file or directory.
● The special identifiers INTERACTIVE@, NETWORK@, DIALUP@, BATCH@, ANONYMOUS@, AUTHENTICATED@,
SERVICE@.
替代格式
为了实现互作性,保护系统中的 NFSv4 服务器支持一些用于输入和输出的替代标识符格式。
● 数字标识符;例如,“12345”。
● Windows 兼容安全标识符 (SID),表示为“S-NNN-NNN-...”
有关这些格式限制的详细信息,请参阅有关输入映射和输出映射的部分。
内部标识符格式
DD 文件系统将标识符与文件系统中的每个对象(文件或目录)一起存储。所有对象都具有数字用户 ID (UID) 和组 ID (GID)。
这些与模式位一起允许传统的 UNIX/Linux 标识和访问控制。
通过 CIFS/SMB 协议或在启用 NFSv4 ACL 时由 NFSv4 协议创建的对象也具有扩展的安全描述符 (SD)。每个 SD 包含以下内容:
● 所有者安全标识符 (SID)
● 所有者组 SID
● 自主ACL(DACL)
●(可选)系统ACL(SACL)
每个 SID 都包含一个相对 ID (RID) 和一个不同的域,其方式与 Windows SID 类似。请参阅有关 NFSv4 和
CIFS 互作性,了解有关 SID 和 SID 映射的更多信息。
发生
ID 映射时保护系统 NFSv4 服务器在以下情况下执行映射:
● 输入映射
NFS 服务器从 NFSv4 客户端接收标识符。
● 输出映射:
标识符从 NFS 服务器发送到 NFSv4 客户端。
● 凭证映射
RPC 客户端凭据映射到内部身份,以进行访问控制和其他作。
输入映射
当 NFSv4 客户端向保护系统 NFSv4 服务器发送标识符时,就会发生输入映射 — 例如,设置文件的所有者或所有者组。输入映射不同于凭据映射。
标准格式标识符(如 joe@mycorp.com)将根据配置的转换规则转换为内部 UID/GID。如果启用了 NFSv4 ACL,还将根据配置的转换规则生成 SID。
如果客户端未使用 Kerberos 身份验证,则数字标识符(例如,“12345”)将直接转换为相应的 UID/GID。如果在使用 Kerberos,则会根据 NFSv4 标准的建议生成错误。如果 NFSv4 ACL 是
enabled,将根据转换规则生成 SID。
Windows SID(例如,“S-NNN-NNN-...”)经过验证并直接转换为相应的 SID。将
根据转换规则生成UID/GID。
输出映射
Output mapping occurs when the NFSv4 server sends an identifier to the NFSv4 client; for example, if the server returns the
owner or owner-group of a file.
1. If configured, the output might be the numeric ID.
This can be useful for NFSv4 clients that are not configured for ID mapping (for example, some Linux clients).
2. Mapping is attempted using the configured mapping services, (for example, NIS or Active Directory).
3. The output is a numeric ID or SID string if mapping fails and the configuration is allowed.
4. Otherwise, nobody is returned.
The nfs option nfs4-idmap-out-numeric configures the mapping on output:
● If nfs option nfs4-idmap-out-numeric is set to map-first, mapping will be attempted. On error, a numeric string
is output if allowed. This is the default.
● If nfs option nfs4-idmap-out-numeric is set to always, output will always be a numeric string if allowed.
● If nfs option nfs4-idmap-out-numeric is set to never, mapping will be attempted. On error, nobody@nfs4-
domain is the output.
If the RPC connection uses GSS/Kerberos, a numeric string is never allowed and nobody@nfs4-domain is the output.
The following example configures the protection system NFS server to always attempt to output a numeric string on output. For
Kerberos the name nobody is returned:
nfs option set nfs4-idmap-out-numeric always
凭据映射
NFSv4 服务器为 NFSv4 客户端提供凭据。
这些凭据执行以下功能:
● 确定作的访问策略;例如,读取文件的能力。
● 确定新文件和目录的默认所有者和所有者组。
从客户端发送的凭据可能是 john_doe@mycorp.com 或系统凭据,例如 UID=1000、GID=2000。
系统凭据指定 UID/GID 以及辅助组 ID。
如果禁用了 NFSv4 ACL,则 UID/GID 和辅助组 ID 会用于凭据。
如果启用了 NFSv4 ACL,则配置的映射服务将用于为
构建扩展安全描述符凭据:
● 所有者、所有者组和辅助组的 SID 已映射并添加到安全描述符 (SD)。
● 凭据权限(如果有)将添加到 SD。
NFSv4 和 CIFS/SMB 互作性
NFSv4 和 CIFS 使用的安全描述符从 ID 映射的角度来看是相似的,但存在差异。
为确保获得最佳互作性,您应注意以下事项:
● 应为 CIFS 和 NFSv4 配置 Active Directory,并且应将 NFS ID 映射器配置为使用 Active
ID 映射的目录。
● 如果您广泛使用 CIFS ACL,通常可以通过启用 NFSv4 ACL 来提高兼容性。
○ 启用 NFSv4 ACL 允许在评估 DACL 访问时将 NFSv4 凭据映射到相应的 SID。
● CIFS 服务器从 CIFS 客户端接收凭据,包括默认 ACL 和用户权限。
○ 相比之下,NFSv4 服务器接收一组更有限的凭据,并在运行时使用其
ID 映射器。因此,文件系统可能会看到不同的凭据。
CIFS/SMB Active Directory 集成
The protection system NFSv4 server can be configured to use the Windows Active Directory configuration that is set with the
protection system CIFS server.
The system is mapped to use Active Directory if possible. This functionality is disabled by default, but you can enable it using the
following command:
nfs option set nfs4-idmap-active-directory enabled
NFSv4
的默认 DACLNFSv4 设置的默认 DACL(自由访问控制列表)与 CIFS 提供的默认 DACL 不同。
默认 NFSv4 DACL 中仅定义 OWNER@、GROUP@ 和 EVERYONE@。您可以使用 ACL 继承
如果适用,默认情况下自动添加具有 CIFS 意义的 ACE。
系统默认 SID
NFSv3 和不带 ACL 的 NFSv4 创建的文件和目录使用默认系统域,有时也称为
默认 UNIX 域:
● 系统域中的用户 SID 的格式为 S-1-22-1-N,其中 N 是 UID。
● 系统域中的组 SID 的格式为 S-1-22-2-N,其中 N 是 GID。
例如,UID 为 1234 的用户的所有者 SID 为 S-1-22-1-1234。
NFSv4 ACL 和 SID
中的常见标识符NFSv4 ACL 中的 EVERYONE@标识符和其他特殊标识符(例如 BATCH@)使用等效
的兼容 CIFS 和 SIDS。
OWNER@ 和 GROUP@ 标识符在 CIFS 中没有直接对应关系;它们显示为文件或目录的当前所有者和当前所有者组。
NFS 推荐
引用功能允许 NFSv4 客户端访问一个或多个位置的导出(或文件系统)。位置可以位于
同一 NFS 服务器或位于不同 NFS 服务器上,并使用相同或不同的路径访问导出。
由于推荐是 NFSv4 功能,因此仅适用于 NFSv4 装载。
可以推荐任何使用 NFSv4 或更高版本的服务器,包括:
● 启用了 NFSv4 且运行
NFS 的保护系统● 其他支持 NFSv4 的服务器,包括 Linux 服务器、NAS 设备和 VNX 系统。
推荐可以使用 NFS 导出点,无论该导出点是否在 DD 文件系统中具有当前底层路径。
具有引用的 NFS 导出可以通过 NFSv3 装载,但不会重定向 NFSv3 客户端,因为引用是 NFSv4 功能。
此特性在横向扩展系统中非常有用,允许在文件管理级别重定向导出。
推荐位置
NFSv4 参照始终具有一个或多个位置。
这些位置包括以下内容:
● 远程 NFS 服务器上指向引用的文件系统的路径。
● 一个或多个服务器网络地址,允许客户端访问远程 NFS 服务器。
通常,当多个服务器地址与同一位置关联时,这些地址位于同一 NFS
上服务器。
推荐位置名称
您可以在 NFS 导出中命名每个引用位置。您可以使用该名称访问引荐,以及修改或
删除它。
引荐名称最多可包含以下字符集中的 80 个字符:
● A-Z
● A-Z
● 0-9
● ”。
●“,”
●“_”
●“-”
以“.”开头的名称保留供保护系统自动创建。您可以删除这些名称,但不能使用命令行界面 (CLI) 或系统管理服务 (SMS) 创建或修改它们。
推荐和横向扩展系统
如果您要横向扩展保护系统,NFSv4 引用和位置可以更好地实现访问。
由于您的系统可能包含也可能尚未包含全局命名空间,因此以下两种方案描述了如何使用 NFSv4 引用:
● 您的系统不包含全局命名空间。
○ 您可以使用 NFSv4 引用来构建该全局命名空间。系统管理员可以构建这些全局命名空间,或
是您可以根据需要使用智能系统管理器 (SM) 元素构建推荐。
● 您的系统已经有一个全局命名空间。
○ 如果您的系统具有在特定节点中放置 MTree 的全局命名空间,则可以创建 NFS 引用,以将对这些 MTree 的访问重定向到添加到横向扩展系统的节点。
如果有必要的 SM 或文件管理器 (FM) 信息可用,您可以创建这些引用或让它们在 NFS 中自动执行。
NFSv4 和高可用性
使用 NFSv4 时,协议导出(例如 /data/col1/<mtree> 在高可用性 (HA) 设置中进行镜像。但是,配置导出,例如 /ddvar 不镜像。
这 /ddvar 文件系统对于 HA 对的每个节点都是唯一的。因此, /ddvar 导出及其关联的客户端访问
列表不会镜像到 HA 环境中的备用节点。
中的信息 /ddva当活动节点故障切换到备用节点时,R 会变得过时。授予给 /ddvar 在发生故障切换之后,必须在新的活动节点上重新创建原始活动节点上。
您还必须添加任何其他 /ddvar 导出及其客户端(例如, /ddvar/core) 到发生故障切换后,从原始活动节点上创建的数据更新到新的活动节点。
最后,任何需要的 /ddvar 必须从客户端卸载导出,然后在发生故障切换后重新装载导出。
NFSv4 全局命名空间
NFSv4 服务器提供称为 PseudoFS 的虚拟目录树,以将 NFS 导出连接到一组可搜索的路径。
使用 PseudoFS 可将 NFSv4 与使用 MOUNTD 辅助协议的 NFSv3 区分开来。
在大多数配置中,从 NFSv3 MOUNTD 到 NFSv4 全局命名空间的更改是透明的,并由 NFSv4 客户端和服务器自动处理。
NFSv4 全局命名空间和 NFSv3 子装载
如果您使用 NFSv3 导出子装载,NFSv4 的全局命名空间特征可能会阻止在NFSv4 装载上看到
子装载。
NFSv3 主导出和子装载导出
如果 NFSv3 具有主导出和子装载导出,则这些导出可能使用相同的 NFSv3 客户端,但具有不同的访问级别:
表 NFSv3 主导出和子装载导出
| 导出 | 路径 | 客户端 | 选项 |
| MT1 | /data/col1/mt1 | client1.example.com | Ro |
| MT1-sub | /data/col1/mt1/subdir | client1.example.com | 乌尔曼 |
在上表中,以下内容适用于 NFSv3:
● 如果 client1.example.com 安装 /data/col1/mt1,则客户端将获得只读访问权限。
● 如果 client1.example.com 安装 /data/col1/mt1/subdir时,客户端将获得读/写访问权限。
NFSv4 对最高级别的导出路径以相同的方式运行。对于 NFSv4,client1.example.com 导航 NFSv4 PseudoFS,直到它到达最高级别的导出路径, /data/col1/mt1,在其中获得只读访问权限。
但是,由于已选择导出,因此子装载导出 (Mt1-sub) 不是客户端的 PseudoFS 的一部分,并且不会提供读/写访问权限。
最佳实践如果您的系统使用 NFSv3 导出子装载,以便根据装载路径为客户端提供读/写访问权限,则必须在将 NFSv4 与这些子装载导出配合使用之前考虑这一点。
使用 NFSv4 时,每个客户端都有一个单独的 PseudoFS。
表 NFSv3 子装载导出
| 导出 | 路径 | 客户端 | 选项 |
| MT1 | /data/col1/mt1 | client1.example.com | Ro |
| MT1-sub | /data/col1/mt1/subdir | client2.example.com | 乌尔曼 |
NFSv4 配置
The default protection system configuration only enables NFSv3. To use NFSv4, you must first enable the NFSv4 server.
Enabling the NFSv4 Server
Steps
1. Enter nfs enable version 4 to enable NFSv4:
# nfs enable version 4
NFS server version(s) 3:4 enabled.
2. (Optional) If you want to disable NFSv3, enter nfs disable version 3.
# nfs disable version 3
NFS server version(s) 3 disabled.
NFS server version(s) 4 enabled.
Next steps
After the NFSv4 server is enabled, you might need to perform additional NFS configuration tasks specifically for your site. These
tasks can include:
● Setting the NFSv4 domain
● Configuring NFSv4 ID mapping
● Configuring ACL (Access Control Lists)
Setting the default server to include NFSv4
About this task
The NFS command option default-server-version controls which NFS version is enabled when you enter the nfs
enable command without specifying a version.
Steps
Enter the nfs option set default-server-version 3:4 command:
# nfs option set default-server-version 3:4
NFS option 'default-server-version' set to '3:4'.
更新现有导出
You can update existing exports to change the NFS version used by your protection system.
Steps
Enter the nfs export modify all command:
# nfs export modify all clients all options version=version number
To ensure all existing clients have either version 3, 4, or both, you can modify the NFS version to the appropriate string. The
following example shows NFS modified to include versions 3 and 4:
#nfs export modify all clients all options version=3:4
For more information about the nfs export command, see the DDOS Command Reference Guide for more information.
其他信息
Kerberos 和 NFSv4
NFSv4 和 NFSv3 均使用 Kerberos 身份验证机制来保护用户凭据。
Kerberos 可防止用户凭据在 NFS 数据包中被假冒,并保护它们在传输到保护系统的过程中不被篡改。
基于 NFS 的 Kerberos 有多种类型:
● Kerberos 5 (sec=krb5)
使用 Kerberos 获取用户凭据。
● 带完整性的 Kerberos 5 (sec=krb5i)
使用 Kerberos 并使用加密校验和检查 NFS 负载的完整性。
● 具有安全性的 Kerberos 5 (sec=krb5p)
使用带完整性的 Kerberos 5 并加密整个 NFS 有效负载。
使用基于 Linux 的 KDC 配置 Kerberos
Prerequisites
You should ensure that all your systems can access the Key Distribution Center (KDC).
If the systems cannot reach the KDC, check the domain name system (DNS) settings.
About this task
The following steps allow you to create keytab files for the client and the protection system:
● In Steps 1-3, you create the keytab file for the protection system.
● In Steps 4-5, you create the keytab file for the client.
Steps
1. Create the nfs/<ddr_dns_name>@<realm> service principal.
kadmin.local: addprinc -randkey nfs/ddr12345.<domain-name>@<domain-name>
2. Export nfs/<ddr_dns_name>@<realm> to a keytab file.
kadmin.local: ktadd –k /tmp/ddr.keytab nfs/ddr12345.corp.com@CORP.COM
3. Copy the keytab file to the protection system at the following location:
/ddr/var/krb5.keytab
4. Create one of the following principals for the client and export that principal to the keytab file:
nfs/<client_dns_name>@<REALM>
root/<client_dns_name>@<REALM>
5. Copy the keytab file to the client at the following location:
/etc/krb5.keytab
NOTE: It is recommended that you use an NTP server to keep the time synchronized on all entities.
使用基于 Linux 的 KDC 配置 Kerberos
Configuring the protection System to Use Kerberos Authentication
Steps
1. Configure the KDC and Kerberos realm on the protection system by using the authentication command:
# authentication kerberos set realm <realm> kdc-type unix kdcs <kdc-server>
2. Import the keytab file:
# authentication kerberos keytab import
3. (Optional) Configure the NIS server by entering the following commands:
# authentication nis servers add <server>
# authentication nis domain set <domain-name>
# authentication nis enable
# filesys restart
4. (Optional) Make the nfs4-domain the same as the Kerberos realm using the nfs option command:
nfs option set nfs4-domain <kerberos-realm>
5. Add a client to an existing export by adding sec=krb5 to the nfs export add command:
nfs export add <export-name> clients * options version=4,sec=krb5
使用基于 Linux 的 KDC 配置 Kerberos
Configuring Clients
Steps
1. Configure the DNS server and verify that forward and reverse lookups are working.
2. Configure the KDC and Kerberos realm by editing the /etc/krb5.conf configuration file.
You might need to perform this step based on the client operating system you are using.
3. Configure NIS or another external name mapping service.
4. (Optional) Edit the /etc/idmapd.conf file to ensure it is the same as the Kerberos realm.
You might need to perform this step based on the client operating system you are using.
5. Verify the keytab file /etc/krb5.keytab contains an entry for the nfs/ service principal or the root/ principal.
[root@fc22 ~]# klist -k
Keytab name: FILE:/etc/krb5.keytab
KVNO Principal
---- --------------------------------------------------------------------------
3 nfs/fc22.domain-name@domain-name
6. Mount the export using the sec=krb5 option.
[root@fc22 ~]# mount ddr12345.<domain-name>:/data/col1/mtree1 /mnt/nfs4 –o
sec=krb5,vers=4
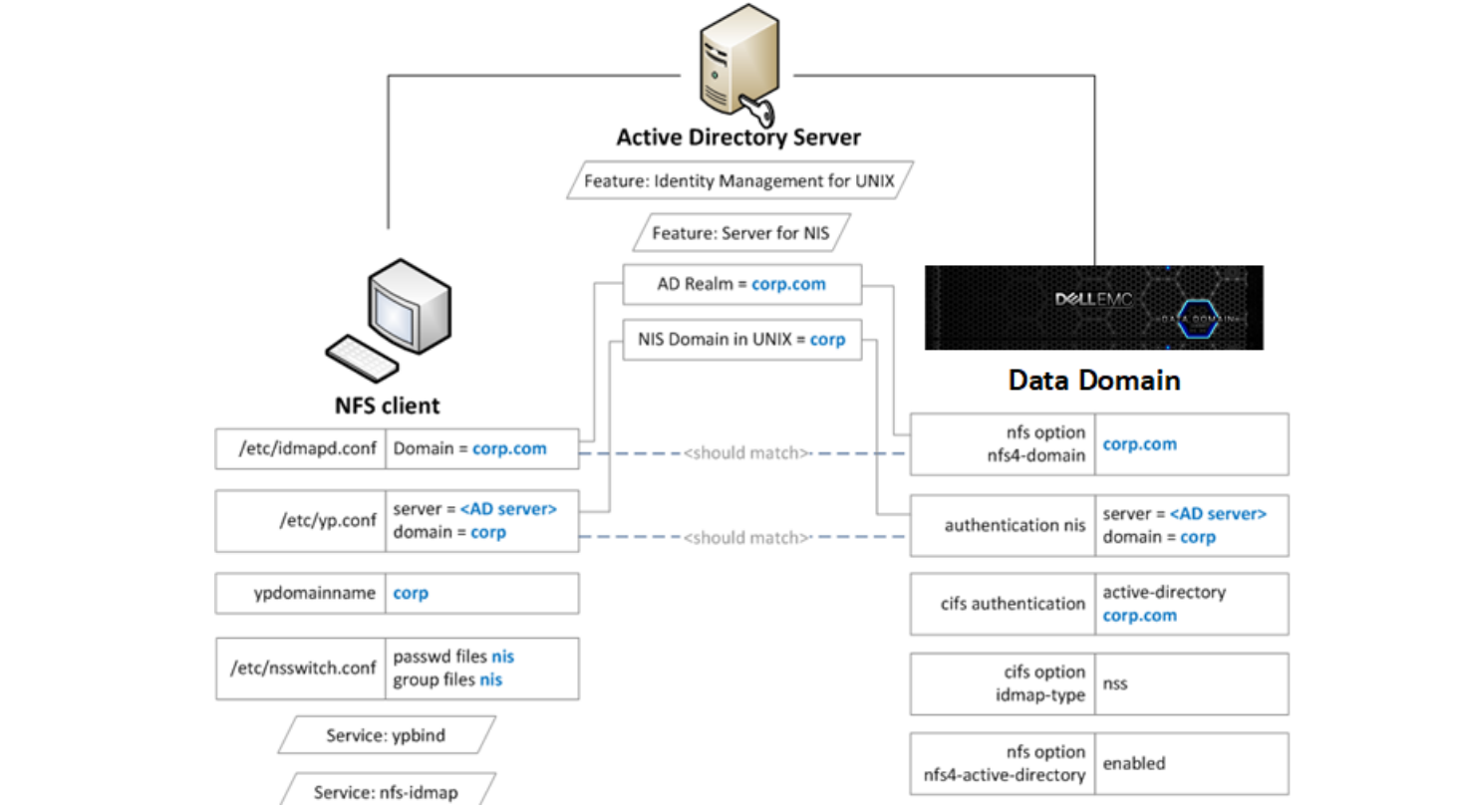
启用 Active Directory
About this task
Configuring Active Directory authentication makes the protection system part of a Windows Active Directory realm. CIFS clients
and NFS clients use Kerberos authentication.
Steps
1. Join an active directory realm using the cifs set command:
# cifs set authentication active-directory <realm>
Kerberos is automatically set up on the system, and the required NFS/ service principal is automatically created on the KDC.
2. Configure NIS using the authentication nis command:
# authentication nis servers add <windows-ad-server>
# authentication nis domain set <ad-realm>
# authentication nis enable
3. Configure CIFS to use NSS for ID mapping by using cifs commands:
# cifs disable
# cifs option set idmap-type nss
# cifs enable
# filesys restart
4. Set the nfs4-domain to be the same as the Active Directory realm:
# nfs option set nfs4-domain 5. Enable Active Directory for NFSv4 id mapping by using the nfs command: # nfs option set nfs4-idmap-active-directory enabled
配置 Active Directory
Steps
1. Install the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) role on the Windows server.
2. Install the Identity Management for UNIX components.
C:\Windows\system32>Dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:adminui /all
C:\Windows\system32>Dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:nis /all
3. Verify the NIS domain is configured on the server.
C:\Windows\system32>nisadmin
The following are the settings on localhost
Push Interval : 1 days
Logging Mode : Normal
NIS Domains
NIS Domain in AD Master server NIS Domain in UNIX
---------------- ------------- ----------------
corp win-ad-server corp
4. Assign AD users and groups UNIX UID/GIDs for the NFSv4 server.
a. Go to Server Manager > Tools > Active Directory.
b. Open the Properties for an AD user or group.
c. Under the UNIX Attributes tab, fill in the NIS domain, UID, and Primary GID fields.