How to Add Exclusions in Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise
Summary: Exclusions may be added to Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise for memory protection, execution control, application control, and script control by following these instructions.
Instructions
- As of May 2022, Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise has reached End of Maintenance. This article is no longer updated by Dell. For more information, reference Product Life Cycle (End of Support and End of Life) Policy for Dell Data Security. If you have any questions on alternative articles, either reach out to your sales team or contact endpointsecurity@dell.com.
- Reference Endpoint Security for additional information about current products.
This article covers how to add exclusions to Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise.
Affected Products:
- Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise
Affected Operating Systems
- Windows
- Mac
- Linux
Exclusions may be added to Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise for compatibility with third-party software or scripts.
- From a web browser, go to the Dell Data Security administration console at https://servername.company.com:8443/webui.
Note:
- The example, servername.company.com, may differ from the server DNS in your environment.
- The port, 8443, may differ from the Remote Management Console port in your environment.
- Sign in to the Dell Data Security administration console.

- From the left menu pane, expand the Populations tab and then click Enterprise.
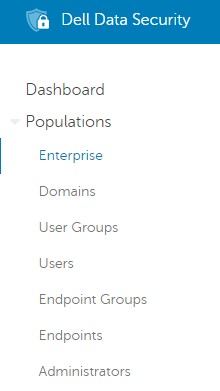
- From the Threat Prevention subheading, click Advanced Threat Prevention.
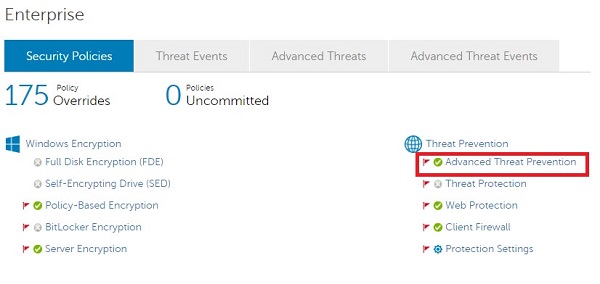
- Click Show advanced settings.
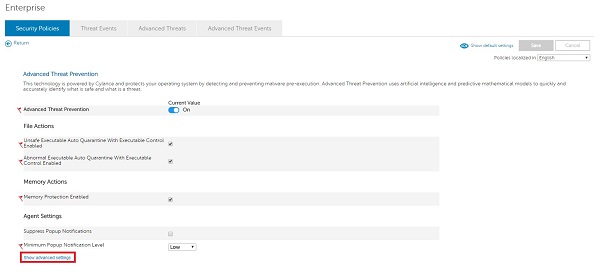
- Exclusions may be added for:
- Memory Protection
- Memory exploit protection
- Execution Control
- Execution launch protection
- Application Control
- Restricts application modifications
- Script Control
- Malicious script protection
- Memory Protection
For more information about exclusions, click the appropriate control.
Memory Protection
How to Add Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise Memory Protection Exclusions
Duration: 02:55
Closed captions: Available in multiple languages
- Check Enable Exclude executable files.
- Exclude executable files by populating the relative path and file name.
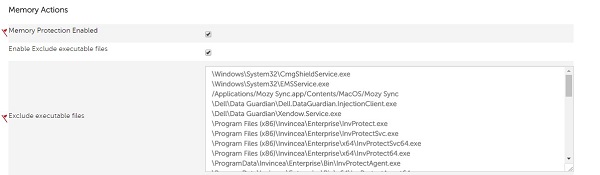 Note:
Note:
Example Exclusions:- Windows
- Correct:
\Application\SubFolder\[EXECUTABLE].exe - Incorrect:
C:\Application\SubFolder\ - The example Windows relative path would apply to both:
C:\Program\Application\SubFolder\[EXECUTABLE].exeD:\Test\Application\SubFolder\[EXECUTABLE].exe
- Use caution when adding generic relative paths as it could potentially weaken your environment’s security posture.
- Correct:
- Mac
- Correct:
/Users/application.app/[EXECUTABLE] - Incorrect:
/Users/application.app
- Correct:
[EXECUTABLE]= The application name- Folder exclusions do not support network paths, wildcards, or special characters.
- Enclose an exclusion in quotation marks ("…") if any of the following characters are used:
- Comma (,)
- Brackets ([…])
- Tilde (~)
- Windows
- In the upper right, click Save.
- Commit the policy.
Note:
- For detailed steps on committing policy, reference How to Commit Policies for Dell Data Security Servers.
- Endpoint will get the policy change after a reboot or policy poll (whatever option occurs first). For more information, reference How to Check for Policy Updates for Dell Data Security.
Execution Control
How to Add Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise Execution Control Exclusions
Duration: 01:52
Closed captions: Available in multiple languages
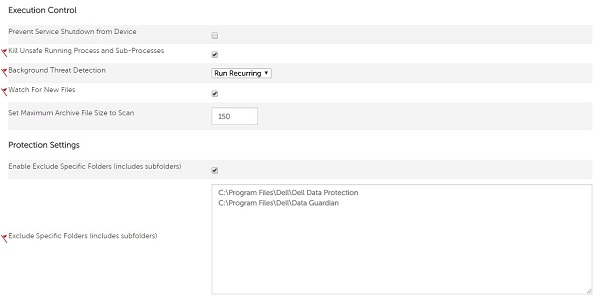
- Under Protection Settings, check Enable Exclude Specific Folders (includes subfolders).
- Exclude Specific Folders (includes subfolders) by populating the absolute path.
 Note:
Note:
Example Exclusions:- Windows
- Correct:
C:\Program Files\Dell - Incorrect:
\Program Files\Dell\[EXECUTABLE].exe
- Correct:
- Mac
- Correct:
/Mac\ HD/Users/Application\ Support/Dell - Incorrect:
/Mac HD/Users/Application Support/Dell/[EXECUTABLE]
- Correct:
[EXECUTABLE]= The application name
- Windows
- In the upper right, click Save.
- Commit the policy.
Note:
- For detailed steps on committing policy, reference How to Commit Policies for Dell Data Security Servers.
- Endpoint will get the policy change after a reboot or policy poll (whatever option occurs first). For more information, reference How to Check for Policy Updates for Dell Data Security.
Application Control
How to Add Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise Application Control Exclusions
Duration: 02:15
Closed captions: Available in multiple languages
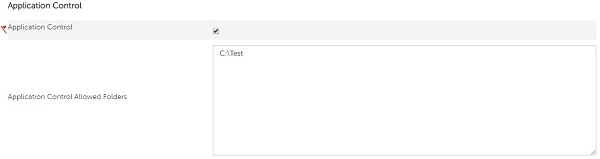
- Exclude Application Control Allowed Folders by populating the absolute path.
 Note: Example Exclusions:
Note: Example Exclusions:- Windows
- Correct:
C:\Program Files\Dell - Incorrect:
\Program Files\Dell\[EXECUTABLE].exe
- Correct:
[EXECUTABLE]= The application name- Folder exclusions do not support network paths, wildcards, or special characters.
- Enclose an exclusion in quotation marks ("…") if any of the following characters are used:
- Comma (,)
- Brackets ([…])
- Tilde (~)
- Windows
- In the upper right, click Save.
- Commit the policy.
Note:
- For detailed steps on committing policy, reference How to Commit Policies for Dell Data Security Servers.
- Endpoint will get the policy change after a reboot or policy poll (whatever option occurs first). For more information, reference How to Check for Policy Updates for Dell Data Security.
Script Control
How to Add Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise Script Control Exclusions
Duration: 02:30
Closed captions: Available in multiple languages
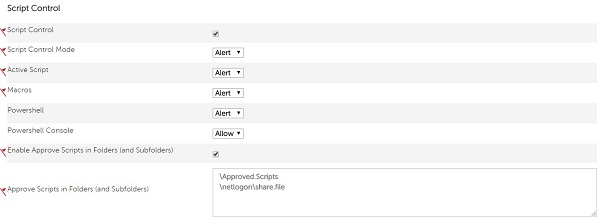
- Check Enable Approve Scripts in Folders (and Subfolders).
- Enable Approve Scripts in Folders (and Subfolders) by populating the relative path of the script directory.
 Note: Example Exclusions:
Note: Example Exclusions:- Windows
- Correct:
/Users/*/temp/script*.vbs - Incorrect:
C:\Users\*\temp\script*.vbs\ - The example Windows relative path applies to both:
C:\Program\Application\ApprovedScripts\D:\Test\Application\ApprovedScripts\
- Use caution when adding generic relative paths as it could potentially weaken your environment’s security posture.
- Correct:
- Mac
- Correct:
/Mac\ HD/Users/Cases/ScriptsAllowed - Incorrect:
/Mac HD/Users/*
- Correct:
- Folder paths can be to a local drive, a mapped network drive, or a universal naming convention (UNC) path.
- Any specified folder path also includes any subfolders.
- Wildcards (*) may be used in Script Control exclusions.
- Dell Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise Agent version 1491 or higher is required.
- The Dell Data Security (formerly Dell Data Protection) server must have strict validation set to disabled.
- Wildcard exclusions must use forward slashes in the UNIX style for Windows computers. For example:
/windows/system*/ - The only character that is supported for wildcards is *.
- Folder exclusions with a wildcard must have a slash at the end of the path to differentiate between a folder and a file.
- Folder:
/Windows/system32/*/ - File:
/Windows/system32/*
- Folder:
- A wildcard must be added for each level of folder depth. For example,
/folder/*/script.vbsmatches\folder\test\script.vbsor\folder\exclude\script.vbs, but does not work for\folder\test\001\script.vbs. This would require either/folder/*/001/script.vbsor/folder/*/*/script.vbs. - Wildcards support full and partial exclusions.
- Full wildcard:
/folder/*/script.vbs - Partial wildcard:
/folder/test*/script.vbs
- Full wildcard:
- Wildcards support network paths.
- Wildcards may lower one’s security stance if used too broadly. For example, excluding the entire
\Windows\Tempfolder is not recommended.
- Windows
- In the upper right, click Save.
- Commit the policy.
Note:
- For detailed steps on committing policy, reference How to Commit Policies for Dell Data Security Servers.
- Endpoint will get the policy change after a reboot or policy poll (whatever option occurs first). For more information, reference How to Check for Policy Updates for Dell Data Security.
To contact support, reference Dell Data Security International Support Phone Numbers.
Go to TechDirect to generate a technical support request online.
For additional insights and resources, join the Dell Security Community Forum.