Data Domain: Configuring interface groups for Managed File Replication (MFR)
Summary: Interface groups can be used to control the interfaces used for DD Boost MFR, to direct the replication connection over a specific network, and to use multiple network interfaces with high bandwidth and reliability for failover conditions. All protection system IP types are supported—IPv4 or IPv6, Alias IP/VLAN IP, and LACP/failover aggregation. ...
Instructions
Steps for UI (UI)
Adding a replication path to an interface group
Use the IP Network tab to add replication paths to interface groups.
Steps
-
Select Protocols > DD Boost > IP Network.
-
In the Configured Replication Paths section, click Add (+).
-
Enter values for MTree or Remote Host, or both.
-
Select a previously configured interface group, and click OK.
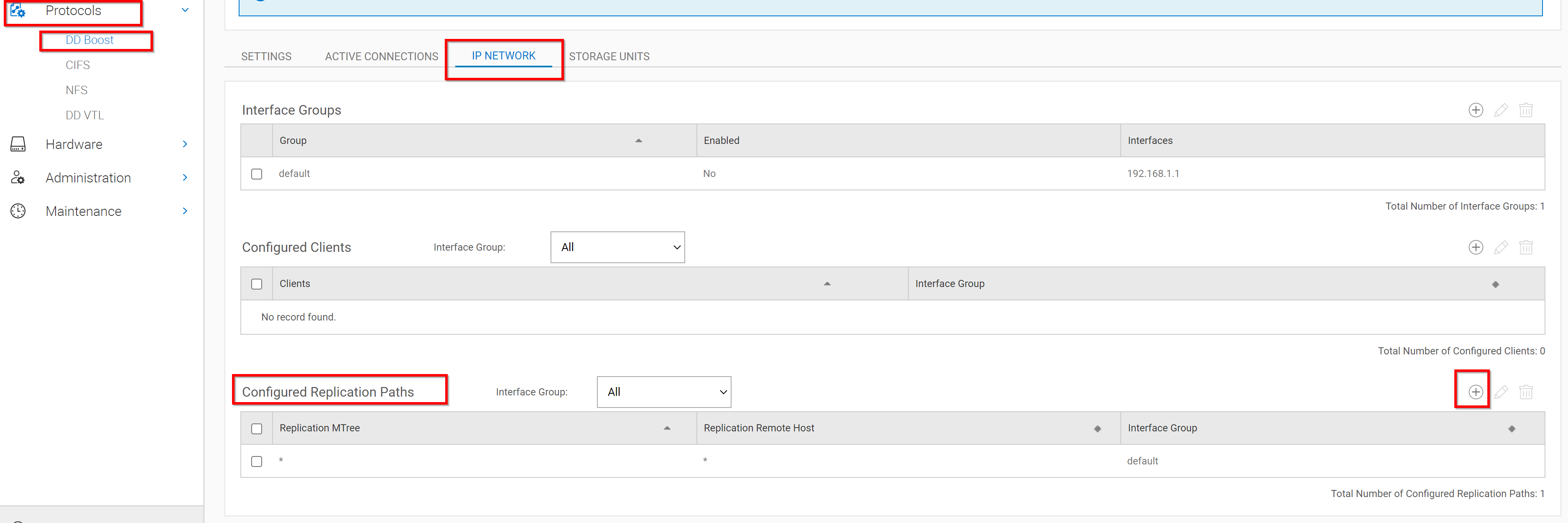
In the screenshot above you can see a * was entered for replication paths and remote hosts. This is the simplest configuration and allows MFR to use any interface in the interface groups.
Modifying a replication path for an interface group
Use the IP Network tab to modify replication paths for interface groups.
Steps
-
Select Protocols > DD Boost > IP Network.
-
In the Configured Replication Paths section, select the replication path.
-
Click Edit (pencil).
-
Modify any or all values for MTree, Remote Host, or Interface Group.
-
Click OK.
Deleting a replication path for an interface group
Use the IP Network tab to delete replication paths for interface groups.
Steps
-
Select Protocols > DD Boost > IP Network.
-
In the Configured Replication Paths section, select the replication path.
-
Click Delete (X).
-
In the Delete Replication Paths dialog, click OK.
Steps to setup interface groups for MFR in the Command-line interface
DDboost Ifgroups for Replication
DDOS version 6.0 higher
# ifgroup create <group-name>
Example: # ifgroup create Repl
# ifgroup replication assign <group-name> {mtree mtree-path | remote hostname | mtree mtree-path remote hostname}
Example: # ifgroup replication assign Repl mtree /data/col1/REPLX remote ddp-880-1.datadomain.com
Assigned replication mtree "/data/col1/REPLX" with remote "ddp-880-1.datadomain.com" to ifgroup "Repl".
The hostname configuration is case-sensitive; however, this command automatically converts input entered as uppercase to lowercase. At upgrade, all previously configured hostnames are automatically converted to lowercase.
Removing DDboost Ifgroups for Replication
DDOS version 6.0 higher
# ifgroup replication unassign <group-name> {mtree mtree-path | remote hostname | mtree mtree-path remote hostname}
Unassign a replication MTree and remote host from group-name. Role required: admin, limited-admin.
Example: # ifgroup replication unassign Repl mtree /data/col1/REPLX remote ddp-880-1.datadomain.com 10GLab
Unassigned replication mtree "/data/col1/REPLX" with remote "ddp-880-1.datadomain.com" from ifgroup "Repl".
Additional Information In order for ifgroups to replicate all ddboost data; please use the following command: 6.0+: # ifgroup replication assign <group name> mtree * remote * This is recommended and should be performed on both source and destination systems
MFR ifgroup only applies to ddboost replication and does not apply to native DD replication.
Additional Information
Using interface groups for Managed File Replication (MFR) Interface groups can be used to control the interfaces used for DD Boost MFR, to direct the replication connection over a specific network, and to use multiple network interfaces with high bandwidth and reliability for failover conditions. All protection system IP types are supported—IPv4 or IPv6, Alias IP/VLAN IP, and LACP/failover aggregation.
Without the use of interface groups, configuration for replication requires several steps:
-
Adding an entry in the
/etc/hostsfile on the source system for the target system and hard coding one of the private LAN network interfaces as the destination IP address. -
Adding a route on the source system to the target system specifying a physical or virtual port on the source system to the remote destination IP address.
-
Configuring LACP through the network on all switches between the systems for load balancing and failover.
-
Requiring different applications to use different names for the target system to avoid naming conflicts in the
/etc/hostsfile.
Using interface groups for replication simplifies this configuration by using the DDOS System Manager orDDOS CLIcommands.
Using interface groups to configure the replication path lets you:- Redirect a hostname-resolved IP address away from the public network, using another private system IP address.
- Identify an interface group based on configured selection criteria, providing a single interface group where all the interfaces are reachable from the target system.
- Select a private network interface from a list of interfaces belonging to a group, ensuring that the interface is healthy.
- Provide load balancing across multiple system interfaces within the same private network.
- Provide a failover interface for recovery for the interfaces of the interface group.
- Provide a host failover if configured on the source system.
- Use Network Address Translation (NAT) The selection order for determining an interface group match for file replication is:
- Local MTree (storage-unit) path and a specific remote system hostname
- Local MTree (storage-unit) path with any remote system hostname
- Any MTree (storage-unit) path with a specific system hostname The same MTree can appear in multiple interface groups only if it has a different system hostname.
The same system hostname can appear in multiple interface groups only if it has a different MTree path.
The remote hostname is expected to be an FQDN, such as dd9900-1.example.com.
The interface group selection is performed locally on both the source system and the target system, independent of each other.
For a WAN replication network, only the remote interface group must be configured since the source IP address corresponds to the gateway for the remote IP address.
Data Domain - Creating interface groups for backups
Data Domain: What is the maximum number of ifgroups supported?(Dell Support account is required to view this article)
(Unable to add more than 64 DDBoost clients to an IFGroup - 000041140)
Deciding when to use DDBoost ifgroup or LACP bonding and the use of both at the same time.(Dell Support account is required to view this article)
How do DDboost Ifgroups work on Data Domain - high level view(Dell Support account is required to view this article)
Data Domain : How to Configure DDboost Ifgroups for Backups and Replication(Dell Support account is required to view this article)
NET: DDBoost Ifgroup troubleshooting guide(Dell Support account is required to view this article)