NetWorker: Windows Client System BugCheck Event Causes System Reboot During Backup
Summary: Windows client machine gets rebooted whenever file system backup is initiated. Custer environment. Both the nodes having same problem.
Symptoms
A NetWorker file system backup of a Windows host fails.
There are no obvious errors indicating cause in the NetWorker logs:
181407:save: Step (1 of 5) for PID-10948: Save has been started on the client '<client-name>'. 174412:save: Step (2 of 5) for PID-10948: Running the backup on the client '<client-name>' for the save set 'pseudo_saveset'. 174424:save: Step (3 of 5) for PID-10948: Creating the snapshot for the selected save sets. --- Job Indications --- <client-name>:pseudo_saveset: retried 1 times.
184008 08/16/2023 02:30:58 AM 1 5 0 999192384 50244 0 <NetWorker-Server> savegrp NSR notice Client '<client-name>' is being skipped because no savesets of this client have been backed up as part of the backup action. 148758 08/16/2023 02:31:03 AM 1 5 0 999192384 50244 0 <NetWorker-Server> savegrp NSR notice Action backup traditional 'Backup' with job id 33079478 is exiting with status 'failed', exit code 1
On the Windows client, the System Event Logs show a BugCheck event occurred simultaneously when a backup is scheduled. That event caused the client machine to reboot.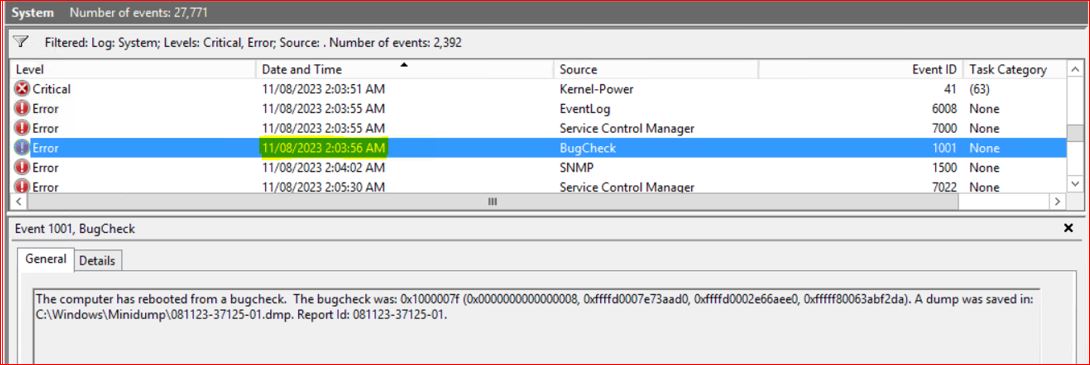
This only appears during Volume Shadow copy Service (VSS) enabled backups (default). If the Windows client is configured in NetWorker with save operations VSS:*=off, the backup succeeds.
Cause
During VSS snapshot creation, kernel-mode file system filter drivers from multiple security products can stack together (for example, Antivirus (AV), HIPS, DLP, disk encryption, EDR). Concurrent real-time filters from two AV products increase kernel stack usage during complex I/O paths. This can exhaust the stack and trigger a BugCheck.
Resolution
Diagnostic Checklist (Collect before choosing a resolution path)
- Capture BugCheck details:
Event Viewer → System → Event ID 1001 (BugCheck). Record the STOP code and faulting the driver (for example, xxx.sys) if available.
Collect minidumps (%SystemRoot%\Minidump).
- VSS health:
vssadmin list writers (look for Stable with No error)vssadmin list providers
Check Event Viewer → Application for VSS (IDs 8193, 12293), VolSnap (for example, 25), and defender/mcafee operational logs at the incident time.
For more details, see: NetWorker: Troubleshooting Backup Failures Due to VSS Issues
- Filter driver stack inventory:
fltmc (list file system filter drivers and order)
- Repro control: Confirm that backup completes consistently with
VSS:*=Off(establishes that the crash is VSS-path-specific).
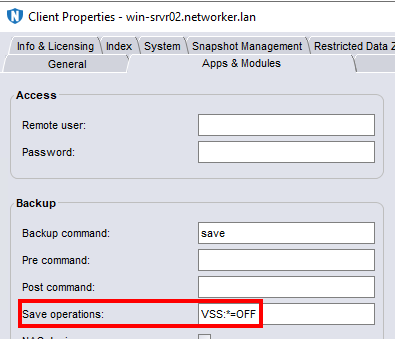
DISASTER_RECOVERY:\ save set is not backed up. A backup without VSS would not be BMR consistent.
Resolution (Tiered—prefer minimal disruption)
A. Make VSS and NetWorker "AV-friendly" (recommended first)
- Real-time scanning exclusions (both AV products):
- Processes:
nsrexecd.exe,save.exe,savefs.exe,nsrsvc.exe(if present), and any NetWorker helper binaries underC:\Program Files\EMC NetWorker\nsr\bin\(or your install path). - Folders:
C:\Program Files\EMC NetWorker\(entirensrtree), NetWorker temporary, and cache paths if customized. - VSS artifacts:
Exclude access to\\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy*and VSS staging locations to avoid deep inspection of snapshot volumes during creation.
- Processes:
- Defender: Prefer Passive mode when a third‑party AV manages real‑time protection (using policy or Defender configuration). This keeps EDR visibility while avoiding dual real-time filter contention.
- McAfee: Apply NetWorker/VSS recommended exclusions; ensure that HIPS or DLP policies do not inspect shadow copies or block
volsnap/vssvc.
Result: Reduces filter activity during VSS operations and lowers kernel stack pressure without removing AV.
B. Reduce driver and filter depth during VSS.
- Temporarily disable nonessential endpoint modules (HIPS, DLP, device control) during backup windows by policy if your security team approves.
- Update AV drivers or definitions and Windows VSS/VolSnap cumulative updates—outdated drivers contribute to stack usage inefficiencies.
- If a third‑party VSS provider is present, force Microsoft Software Shadow Copy provider (test impact):
- Service checks: Ensure
Volume Shadow Copyservice is healthy. - Disable or untangle non-Microsoft providers if they are known to conflict (in coordination with the platform or security team).
- Service checks: Ensure
C. Scheduling and load mitigation
- Run backups outside peak activity (heavy I/O, scans, or endpoint tasks).
- Stagger jobs so fewer clients trigger VSS snapshot simultaneously if central policies cause synchronized scans.
D. Last resort (avoid unless mandated)
- Choose one real-time AV product. If the policy permits, set Defender to passive/EDR-only mode or fully disable real-time when McAfee is the primary AV.
Uninstalling an AV should be a final step, not the default recommendation.
E. Operational workaround (if business needs override)
- Continue backups with
VSS:*=Offtemporarily if consistency risk is acceptable for the affected workload. Document that VSS-level application consistency (writers) may be reduced (for example, open files). Use for noncritical datasets only while remediation proceeds.
Verification
- After applying exclusions and driver optimizations, run:
vssadmin list writers→ confirmStable- Test a manual snapshot:
wmic shadowcopy call create Volume='C:\'(monitor events for bugchecks) - Run a NetWorker file system backup on a single volume; then scale up.
- Confirm no BugCheck and the job completes with VSS enabled.