PowerVault ME5, ME52: Degradation of Sequential Write Performance Warning Message When Creating a Disk Group
Zhrnutie: Applications like video streaming applications (for example, recording) that generate sequential write I/O benefit from using aligned disk groups to improve I/O performance. Other use cases the disk group configuration meets users storage requirements and provides adequate performance to serve their application and expected end-user I/O responses. ...
Pokyny
When provisioning a RAID 5 or RAID 6 disk group on PowerVault ME5 series SANs, you may receive the following warning dialog.
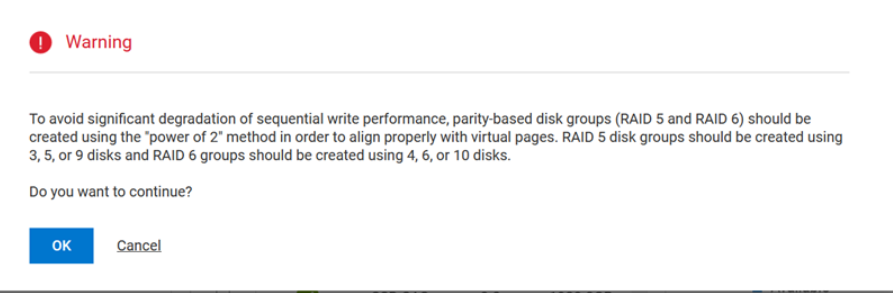
What action must the SAN administrator take?
How to proceed depends on the profile of the host applications generating write I/O to the SAN. Based on field experience most application writes are random I/O, for most users this configuration meets their storage needs, choose OK to proceed.
In use cases such as an application that generates streaming I/O, for example, storing recording output from security cameras, administrators must take the number of disks into consideration. Video datafiles are typically larger than other use case files. Once written, these files are unlikely to be changed at random position, therefore sequential write speed matters most.
Disk count per RAID level
The controllers allocate virtual volume storage in 4-MiB pages, which are referenced paged tables in memory. There is a sequential write performance penalty when RAID 5 or RAID 6 disk groups are used in a virtual pool and the stripe size of the disk group does not align well with the 4-MiB page.
- Example 1: Consider a RAID 5 disk group with five disks. The equivalent of four disks provides usable capacity, and the equivalent of one disk is used for parity (parity is distributed among disks). The four disks providing usable capacity are the data disks, and the disk providing parity is the parity disk. In reality, the parity is distributed among all the disks, but conceiving of it in this way helps with the example.
- Example 2: Consider a RAID 5 disk group with six disks. The equivalent of five disks now provides usable capacity. Assume that the controller again uses a stripe unit of 512 KiB. When a 4-MiB page is pushed to the disk group, one stripe contains a full page, but the controller must read old data and old parity from two of the disks with the new data in order to calculate new parity. This is known as a read-modify-write, and it is a performance killer with sequential workloads. In essence, every page push to a disk group would result in a read-modify-write.
The controllers use a stripe unit of 64 KiB when a RAID 5 or RAID 6 disk group is not created with a power-of-two data disk to mitigate this issue. This results in many more full-stripe writes, but at the cost of many more I/O transactions per disk to push the same 4-MiB page.
The following table shows recommended disk counts for RAID 6 and RAID 5 disk groups. Each entry specifies the total number of disks and the equivalent numbers of data and parity disks in the disk group. Parity is distributed among all the disks.
To ensure best performance with sequential workloads and RAID 5 and RAID 6 disk groups, use a power-of-two data disk.
Disk group expansion
Only ADAPT disk groups can be expanded in virtual pool mode. RAID 5 and RAID 6 disk groups cannot be expanded in virtual pool mode. To expand the capacity of a virtual pool that contains existing RAID 5 or RAID 6 disk groups, the administrator must add sufficient disks to create a new disk group. See the Disk Groups chapter in the Dell PowerVault ME5 Series Administrator's Guide .
More Information
PowerVault ME series SANs have many configuration options available to suite different I/O workloads. If you would like to learn more, see the Dell PowerVault ME5 Storage System Best Practices whitepaper.
The Dell PowerVault ME5 Series Administrator's Guide has a Best Practices chapter that discuses the following optimizations.
- Pool setup
- RAID selection
- Disk count per RAID level
- Disk groups in a pool
- Tier setup
- Multipath configuration
Dell Technologies InfoHub contains number of best practice documents that may help you design and implement PowerVault ME series as part of your solution.
