Windows Server: Configuring Microsoft Cluster Sets on Dell PowerEdge
Summary: Guide on Configuring Cluster Sets on Windows Server 2019
Instructions
Cluster Sets, introduced in Windows Server 2019 (WS19) improves SDDC (Software Defined Data Center) flexibility and resilience. Cluster Set is a technology that allows administrators to combine multiple Windows 2019 Clusters into a single umbrella of Clusters.
Existing failover clusters can accommodate a maximum of 64 nodes. Cluster Sets technology combines multiple WS19 clusters in a single domain, with each of these clusters supporting up to 64 WS19 nodes. Compared to a Failover-Cluster, Cluster Set has more resiliency. For example, a 4-node failover cluster can survive 2-node failure. With the same 4-node cluster if we divide into two 2-node clusters and form a cluster sets out of it, it can survive one cluster failure plus one node failure from the remaining cluster. So, it can survive 3 node failures altogether.
For an overview of Cluster-Sets feature in Server 2019 refer "Introduction-to-cluster-sets-in-windows-server-2019


Lab Setup for Deploying Cluster Set on PowerEdge
Servers Used: Two PowerEdge R730XD’s and Two PowerEdge R740XD’s
- Created the first cluster using the two R730XD’s and named
S2D13G54(called Member Cluster 1). - Created the second cluster using the two R740XD’s and named
S2D14G54(called Member Cluster 2). - Created two CSV volumes on each of the above created Clusters.
- Created a VM ‘
vm1’ onMember Cluster 1and a VM ‘vm2’ onMember Cluster 2.Then, I combined these two VMs to create a Management Cluster (namedmgClus54) for the Cluster Set. No shared storage is required while creating the Management Cluster.
Installed the File-Services role in each of the nodes in the Member Cluster 1, Member Cluster 2 and Management Cluster:
Install-WindowsFeature File-Services -IncludeAllSubFeature –IncludeManagementTools –Restart
Created an Infrastructure SOFS File Server on Member Cluster 1, Member Cluster 2 and the Management Cluster:
Add-ClusterScaleOutFileServerRole -Name -Infrastructure
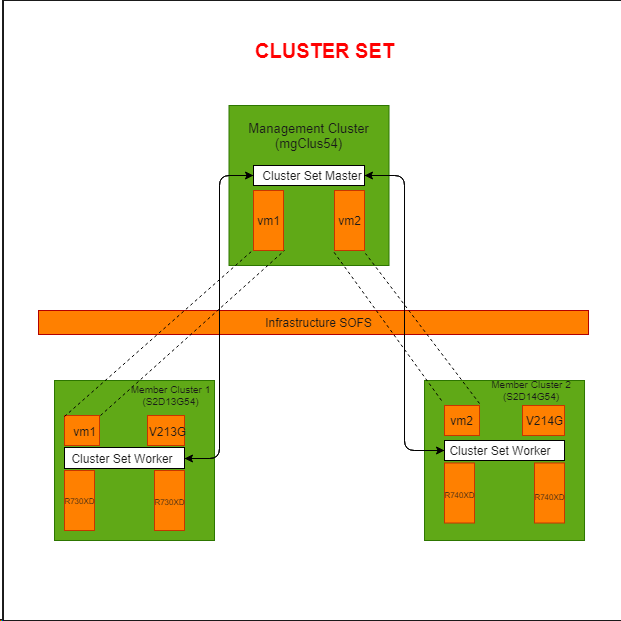
Created a Cluster Set named CLUSSET54:
New-ClusterSet -Name CLUSSET54 -NamespaceRoot -CimSession
And then add the created S2D14G54 and S2D13G54 Cluster to the cluster to the ClusterSet:
Add-ClusterSetMember -ClusterName S2D14G54 -CimSession -InfraSOFSName


Then I deploy
Get-ClusterSetMember -ClusterName | Register-ClusterSetVM -VMName
For Testing live migration across clusters, I tried to migrate VM "V213G" to Member Cluster 2. Before performing migration across clusters, we need to consider below points:
- VM settings, Processor Compatibility should be enabled.
- Configure Kerberos constrained delegation (KCD) between all pairs of cross-cluster nodes
- Constrained delegation guidance
from Microsoft Hyper-V product team will be useful in setting this up.
- Configure the cross-cluster virtual machine live migration authentication type to Kerberos on each node in the Cluster Set.
- Constrained delegation guidance
- foreach($h in $hosts){Set-VMHost -VirtualMachineMigrationAuthenticationType Kerberos -computerName $h }
-
-
- Add the management cluster to the local administrators group on each node in the cluster set.
-
- foreach($h in $hosts){ Invoke-Command -ComputerName $h -ScriptBlock {Net localgroup administrators /add $} }
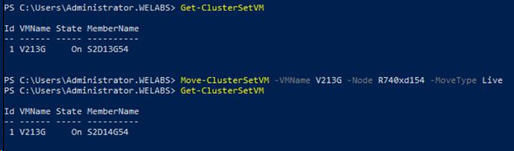
For performing any maintenance activity of a cluster in Cluster Set, migrate all the VMs that are part of the cluster to other clusters in the Cluster Set and then remove Cluster from the Cluster Set:
Remove-ClusterSetMember -ClusterName -CimSession
After performing the maintenance activity, add back the cluster to the Cluster Set.
In case of unexpected failure of a Member Cluster, Cluster Set is not intelligent enough to handle the fail-over. Only manual movement of resources from one cluster to another cluster is supported in Windows Server 2019; even though automatic VM failover continue to function within a single member cluster scope.
Existing failover clusters can accommodate a maximum of 64 nodes. Cluster Sets technology combines multiple WS19 clusters in a single domain, with each of these clusters supporting up to 64 WS19 nodes. Compared to a Failover-Cluster, Cluster Set has more resiliency. For example, a 4-node failover cluster can survive 2-node failure. With the same 4-node cluster if we divide into two 2-node clusters and form a cluster sets out of it, it can survive one cluster failure plus one node failure from the remaining cluster. So, it can survive 3 node failures altogether.
After performing the maintenance activity, add back the cluster to the Cluster Set.
In case of unexpected failure of a Member Cluster, Cluster Set is not intelligent enough to handle the fail-over. Only manual movement of resources from one cluster to another cluster is supported in Windows Server 2019; even though automatic VM failover continue to function within a single member cluster scope.
This blog has been written by DELL Engineer AS Nithya Priya