NVP vProxy: How to Enable Remote System Logging (rsyslog)
Summary: This KB details how to configure rsyslog capabilities with the NetWorker VMware Protection (NVP) vProxy appliance.
This article applies to
This article does not apply to
This article is not tied to any specific product.
Not all product versions are identified in this article.
Instructions
The NetWorker 19.8 vProxy deployment offers remote system logging (rsyslog) capabilities:
- vProxy does not stop logging to the local server even if it loss connection with Remote Server.
- vProxy provides option to send log using Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
- vProxy provides remote logging functionality with minimal overhead.
- vProxy redirects every log message to the remote server.
- Necessary code changes are implemented in the vProxy source code.
- vProxy can send logs to the local server or a remote server.
Limitations:
- The vProxy appliance can only send logs to one remote server.
Requirements:
- vProxy 4.3.0-38 or later is installed.
- Linux server with rsyslog package is installed.
NOTE:
rsyslog is a third-party utility not provided with NetWorker software. See operating system vendor instructions for installing the rsyslog package.
Process:
Configure the monitoring server:
- Log in to the
syslogmonitoring server and confirm thatrsyslogis installed:
# rsyslogd -vExample:
root@linux1:~# rsyslogd -v rsyslogd 8.24.0-57.el7_9.3, compiled with: PLATFORM: x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu PLATFORM (lsb_release -d): FEATURE_REGEXP: Yes GSSAPI Kerberos 5 support: Yes FEATURE_DEBUG (debug build, slow code): No 32bit Atomic operations supported: Yes 64bit Atomic operations supported: Yes memory allocator: system default Runtime Instrumentation (slow code): No uuid support: Yes Number of Bits in RainerScript integers: 64
See the
http://www.rsyslog.com
rsyslog site for more information:
http://www.rsyslog.com

- Modify the
rsyslogconfiguration file to allow TCP or UDP and set the location of the log output:
# vi /etc/rsyslog.confFor TCP, uncomment the following lines:
# Provides TCP syslog reception #$ModLoad imtcp #$InputTCPServerRun 514For UDP, uncomment the following lines:
# Provides UDP syslog reception #$ModLoad imudp #$UDPServerRun 514
NOTE: The settings shown use the default port (514). If you chose to change the port, the change must also be reflected in the vProxy configuration.
Set the log output location (this path is user-defined and can be changed as per your discretion):
$template FILENAME,"/var/log/syslog/%HOSTNAME%/syslog.log" *.* ?FILENAME
Example of completed changes for UDP monitoring:
# Provides UDP syslog reception $ModLoad imudp $UDPServerRun 514 # Provides TCP syslog reception #$ModLoad imtcp #$InputTCPServerRun 514 $template FILENAME,"/var/log/syslog/%HOSTNAME%/syslog.log" *.* ?FILENAME
Save the file.
- Restart
syslogd:
# systemctl restart rsyslog.service
NOTE: If firewalls are present, configure a rule to allow this port to communicate through the firewall using TCP or UDP as per the above configurations. See operating system vendor instructions for configuring operating system firewall rules.
- Confirm that the port is listed with
netstat:
# netstat -apn | grep rsyslog root@linux1:~# netstat -apn | grep rsyslog udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:514 0.0.0.0:* 5795/rsyslogd udp6 0 0 :::514 :::* 5795/rsyslogd
Configure the vProxy:
The configuration on the vProxy appliance uses the following syntax:
[IP_or_FQDN_of_syslog_server]:[syslog_port]/{tcp|udp} Example:
linux1.amer.lan:514/udp
NOTE: If TCP or UDP protocols are not specified, UDP is used as the default protocol.
- This setting can be applied using either of the following methods:
- During deploying the OVF template:
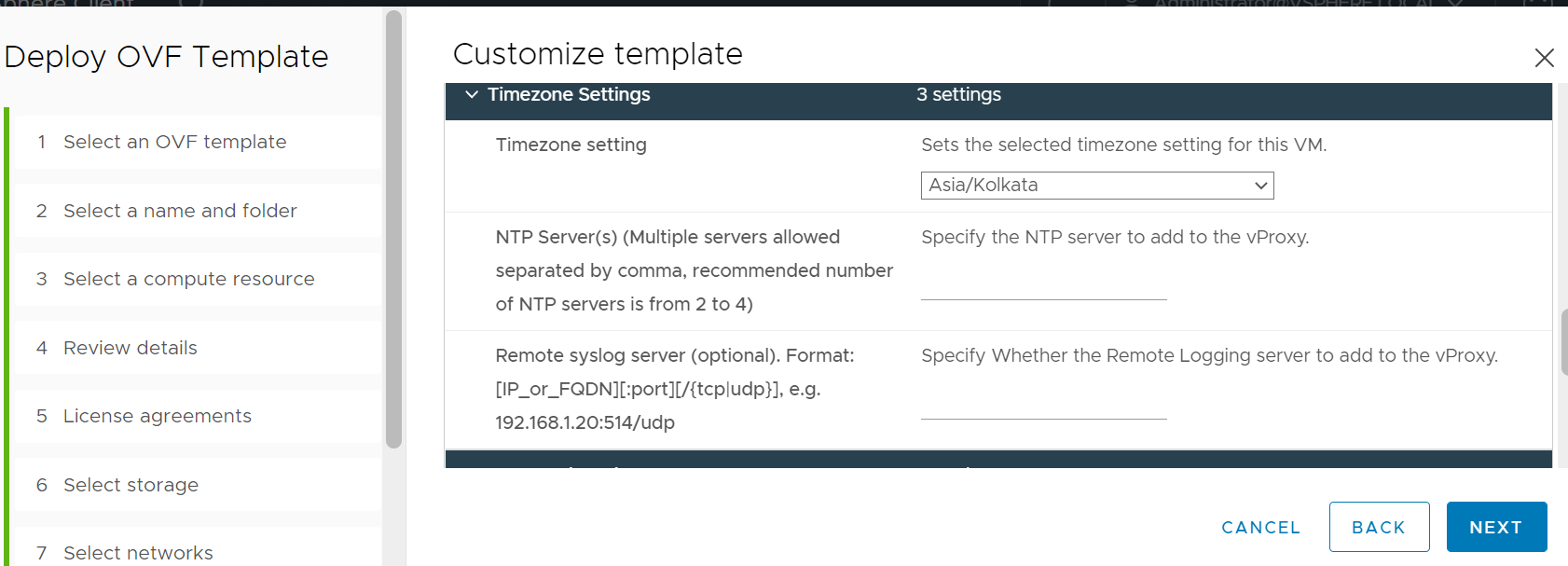
Figure 1: Deploying the OVF Template
- In the vProxy's
/opt/emc/vproxy/conf/rsyslog.conffile. This can be done at any time after deployment.
NOTE: If this file does not exist, it can be created with a text editor.
- Log in to the vProxy appliance as admin, and then switch to root:
$ sudo su -
- Confirm the settings in the
/opt/emc/vproxy/conf/rsyslog.conffile:
vproxy01:~ # cat /opt/emc/vproxy/conf/rsyslog.conf linux1.amer.lan:514/udp
- If no Virtual Machine (VM) backup operations are running on the vProxy, you can force some messages to the
syslogserver by restarting thevbackupdservice:
# systemctl restart vbackup
Conclusion:
Once the above settings are applied, syslog files should be generated on thesyslog server for the vProxy appliance. This depends on the path set in your syslog configuration.
Example:
root@linux1:~# tail -n 10 /var/log/syslog/vproxy01.amer.lan/syslog.log 2023-03-01T09:47:00-08:00 vproxy01.amer.lan vProxy[8014]: 2023-03-01T17:47:00Z TRACE: Configured with 1 resource types. 2023-03-01T09:47:00-08:00 vproxy01.amer.lan vProxy[8014]: 2023-03-01T17:47:00Z NOTICE: Logging to '/opt/emc/vproxy/runtime/logs/vbackupd/vbackupd-snapmgr.log' on host 'vproxy01.amer.lan'. 2023-03-01T09:47:00-08:00 vproxy01.amer.lan vProxy[8014]: 2023-03-01T17:47:00Z NOTICE: Release: '4.3.0-38_1', Build number: '1', Build date: '2022-11-04T08:24:00Z' 2023-03-01T09:47:00-08:00 vproxy01.amer.lan vProxy[8014]: 2023-03-01T17:47:00Z NOTICE: Setting log level to INFO. 2023-03-01T09:47:00-08:00 vproxy01.amer.lan vProxy[8014]: 2023-03-01T17:47:00Z NOTICE: Opened Snapshot Manager log file '/opt/emc/vproxy/runtime/logs/vbackupd/vbackupd-snapmgr.log' using level info. 2023-03-01T09:47:00-08:00 vproxy01.amer.lan vProxy[8014]: 2023-03-01T17:47:00Z INFO: Loaded snapshot map from '/opt/emc/vproxy/runtime/state/vbackupd/SnapshotMaps.gob'. 2023-03-01T09:47:00-08:00 vproxy01.amer.lan vProxy[8014]: 2023-03-01T17:47:00Z NOTICE: vCenter 'vcsa.amer.lan' has no Remove Snapshot requests. 2023-03-01T09:47:00-08:00 vproxy01.amer.lan vProxy[8014]: 2023-03-01T17:47:00Z NOTICE: No remove snapshot requests associated with vCenter 'vcsa.amer.lan'. 2023-03-01T09:47:00-08:00 vproxy01.amer.lan vProxy[8014]: 2023-03-01T17:47:00Z INFO: Saved snapshot map to '/opt/emc/vproxy/runtime/state/vbackupd/SnapshotMaps.gob'. 2023-03-01T09:47:00-08:00 vproxy01.amer.lan vProxy[8014]: 2023-03-01T17:47:00Z NOTICE: Started Snapshot Manager.
Additional Information
Log Rotation:
Optionally, log rotation can be configured on the remote logging server. For example, if the rsyslog configuration looks similar to:
$template FILENAME,"/var/log/syslog/%HOSTNAME%/syslog.log" *.* ?FILENAME
The /etc/logrotate.conf could contain:
/var/log/syslog/*/syslog.log {
rotate 5
weekly
delaycompress
compress
}
weekly- This is the log rotation period; the logs are rotated every week. Other possible values are daily and monthly.Rotate 5- This indicates that only five rotated logs should be kept. The oldest file is removed on the subsequent run.compressanddelaycompress- These are used to tell that all rotated logs, except for the most recent log, should be compressed.- Other options are found in the
logrotateman page on the Linux site.
This results in the log rotating once per week:
root@linux1:~# ls -l /var/log/syslog/vproxy01.amer.lan/ total 32760 -rw------- 1 root root 6698746 Mar 6 07:15 syslog.log -rw------- 1 root root 24760221 Mar 5 03:17 syslog.log-20230305
NOTE: The backup or system administrator must perform any required system changes.
Affected Products
NetWorkerProducts
NetWorker Family, NetWorker SeriesArticle Properties
Article Number: 000210555
Article Type: How To
Last Modified: 25 Mar 2025
Version: 6
Find answers to your questions from other Dell users
Support Services
Check if your device is covered by Support Services.