Dell Networking SONiC: Bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD)
Summary: This article explains about Bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) in Dell Networking SONiC. This article uses a switch running Dell SONiC 4.1.
This article applies to
This article does not apply to
This article is not tied to any specific product.
Not all product versions are identified in this article.
Instructions
|
Prerequisites
Standard interface naming will be used to demonstrate the Concepts. See Dell article 202172 Dell Networking S-Series: Basic Interface Configuration - SONiC 4.0 for more information regarding interface naming
|
Index
IntroductionConfigure BFD
BFD with BGP
BFD with OSPF
BFD with PIM
BFD Profile
Apply a BFD Profile to a static peer
Apply a BFD Profile to a BGP Neighbor
Apply a BFD Profile to OSPF
Apply a BFD Profile to PIM
View BFD peer information
Introduction
Bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) rapidly detects communication failures between two adjacent routers. BFD replaces link-state detection mechanisms in existing routing protocols. It also provides a failure detection solution for links with no routing protocols.BFD provides forwarding-path failure detection in milliseconds instead of seconds. Because BFD is independent of routing protocols, it provides consistent network failure detection. BFD eliminates multiple protocol-dependent timers and methods. Networks converge is faster because BFD triggers link-state changes in the routing protocol sooner and more consistently.
BFD is a simple hello mechanism. Two neighboring routers running BFD establish a session using a three-way handshake. After the session is established, the routers exchange periodic control packets at subsecond intervals. If a router does not receive a hello packet within the specified time, routing protocols are notified that the forwarding path is down.
In addition, BFD sends a control packet when there is a state change or change in a session parameter. These control packets are sent without regard to transmit and receive intervals in a routing protocol.
BFD is an independent and generic protocol, which all media, topologies, and routing protocols can support using any encapsulation. Enterprise SONiC implements BFD at Layer 3 (L3) and with user datagram protocol (UDP) encapsulation. BFD is supported on static and dynamic routing protocols, such as BGP, OSPFv2, and PIM only. The system displays BFD state change notifications.
NOTE:BFD is not supported for VRRP and OSPFv3.
BFD session states
To establish a BFD session between two routers, enable BFD on both sides of the link. BFD routers can operate in active role. The active router starts the BFD session. Both routers can be active in the same session.A BFD session can occur in Asynchronous mode as Enterprise SONiC BFD supports only Asynchronous mode. In Asynchronous mode, both systems send periodic control messages at a specified interval to indicate that their session status is Up.
A BFD session can have four states: Administratively Down, Down, Init, and Up. The default BFD session state is Down.
● Administratively Down — The local BFD router does not participate in the session.
● Down — The remote BFD router is not sending control packets or does not send them within the detection time for the session.
● Init — The local BFD router is communicating to the remote router in the session.
● Up — Both BFD routers are sending control packets.
A BFD session's state changes to Down if:
● A control packet is not received within the detection time.
● Demand mode is active and a control packet is not received in response to a poll packet.
BFD session state changes example
The session state on a router change according to the status notification it receives from the peer router. For example, if the current session state is Down and the router receives a Down status notification from the remote router, the session state on the local router changes to Init.

Figure 1: BFD Session State Changes
Three-way handshake
A BFD session requires a three-way handshake between neighboring routers. In this example, the handshake assumes:
● One router is active, and the other router is passive.
● This is the first session established on this link.
● The default session state on both ports is Down.
1. The active system sends a steady stream of control packets to indicate that its session state is Down until the passive system responds. These packets are sent at the desired transmit interval of the Active system. The Your Discriminator field is set to one second.
2. When the passive system receives a control packet, it changes its session state to Init and sends a response to indicate its state change. The response includes its session ID in the My Discriminator field and the session ID of the remote system in the Your Discriminator field.
3. The active system receives the response from the passive system and changes its session state to Up. It then sends a control packet to indicate this state change. Discriminator values exchange, and transmit intervals negotiate.
4. The passive system receives the control packet and changes its state to Up. Both systems agree that a session is established. Because both members must send a control packet, which requires a response only when the session is Up, whenever there is a state change or change in a session parameter, the passive system sends a final response indicating the state change. After this, periodic control packets exchange.

Figure 2: BFD 3-way handshake
BFD Configuration Notes
Before you configure BFD for a routing protocol, first enable BFD on both routers in the link. BFD is disabled by default.
● Supports 128 BFD sessions with 300 ms intervals and a multiplier of three
● Does not support Demand mode or authentication.
● Does support BFD on multihop sessions.
● Supports protocol liveness only for routing protocols.
● BFD supports BGP, OSPF, and PIM; default and user VRFs are also supported.
Configure BFD
Before you configure BFD for static routing or a routing protocol, configure BFD on each router, including the BFD session settings. BFD is disabled by default.● Enable BFD Globally.
DELLSONiC (config)# bfd
dmin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure DELLSONiC(config)# bfd
● View BFD configuration
sonic# show running-configuration bfd ! bfd peer 192.168.2.1 interface Eth1/1 detect-multiplier 5 echo-interval 200 echo-mode receive-interval 200 transmit-interval 200 ! peer 192.168.2.1 multihop local-address 192.168.2.2 detect-multiplier 4 receive-interval 150 transmit-interval 150
○ detect-mutiplier (2-128) – Configures the detection multiplier to determine packet loss. The remote transmission interval will be multiplied by this value to determine the connection loss detection timer. The default value is 3.
Example: local system has detect-multiplier 5 and the remote system has transmission interval 300, the local system will detect failures only after 1500 milliseconds without receiving packets.
○ echo-interval (10-60000) - minimum transmission interval (less jitter) that this system wants to use to send BFD echo packets. The default value is 300.
○ echo-mode - Configure echo mode.
○ minimum-ttl (1-254) - minimum expected TTL for incoming multi-hop BFD peer packets. If the TTL of the received BFD packet is less than the configured TTL, the system discards the packet. The default value is 254.
○ passive-mode - a passive session will not attempt to initiate a connection and will wait for BFD control packets from peer before it becomes active. By default, passive-mode is disabled.
○ shutdown - disable BFD peer.
○ transmit-interval (10-60000) - minimum transmission interval that this system wants to use to send BFD control packets. The default value is 300.
○ receive-interval (10-60000) - minimum interval that this system can receive control packets. The default value is 300.
BFD with BGP
In a BGP core network, BFD enables faster network reconvergence. BFD rapidly detects communication failures in BGP fast-forwarding paths between internal BGP (iBGP) and external BGP (eBGP) peers.
BFD for BGP is supported on physical, port channel, and VLAN interfaces. BFD for BGP does support the BGP multihop feature. Before configuring BFD for BGP, first configure BGP on the interconnecting routers.
Example BFD with BGP
In this BFD for BGP configuration example Figure 3, Router 1 and Router 2 use eBGP in a transit network to interconnect AS1 and AS2. The eBGP routers exchange information with each other and with iBGP routers to maintain connectivity and accessibility within each autonomous system.
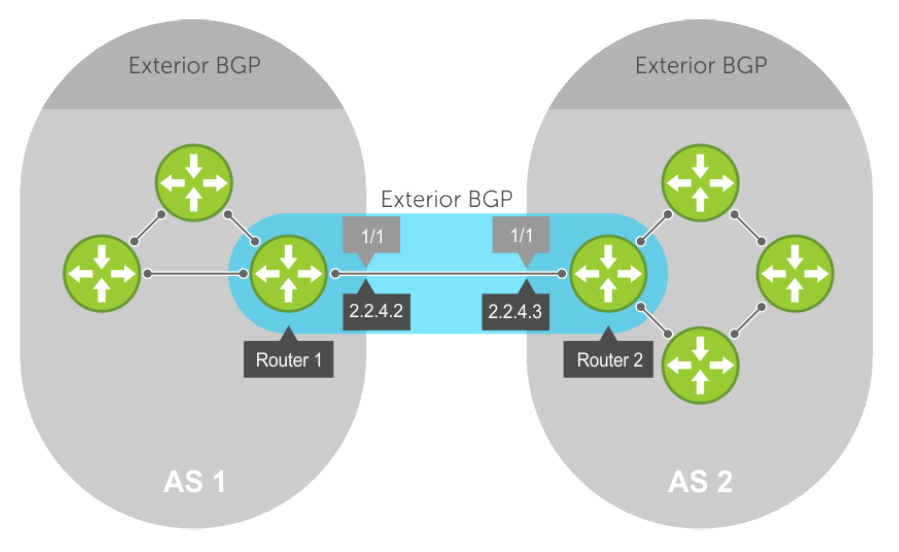
Figure 3: BFD with BGP
When you configure a BFD session with a BGP neighbor, you can establish a BFD session with a specified BGP neighbor using the neighbor ip-address and bfd commands.
Router 1
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(config)# bfd DELLSONiC(config)# router bgp 1 DELLSONiC(conf-router-bgp-1)# neighbor 2.2.4.3 DELLSONiC(conf-router-neighbor)# bfd DELLSONiC(conf-router-neighbor)#
Router 2
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(config)# bfd DELLSONiC(config)# router bgp 2 DELLSONiC(conf-router-bgp-2)# neighbor 2.2.4.2 DELLSONiC(conf-router-neighbor)# bfd
View BFD peer status
DELLSONiC# show bfd peers BFD Peers: peer 2.2.4.2 vrf default interface Vlan100 ID: 3939769244 Remote ID: 330903919 Passive mode: Disabled Status: up Uptime: 0 day(s), 0 hour(s), 0 min(s), 37 sec(s) Diagnostics: ok Remote diagnostics: ok Peer Type: dynamic Local timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 0ms Remote timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 300ms
BFD packets originating from a router are assigned to the highest priority egress queue to minimize transmission delays. Incoming BFD control packets that are received from the BGP neighbor are assigned to the highest priority queue within the control plane policing (CoPP) framework to avoid BFD packets drops due to queue congestion.
BFD notifies BGP of any failure conditions that it detects on the link. BGP initiates recovery actions. BFD for BGP is supported only on directly connected BGP neighbors and in both BGP IPv4 and IPv6 networks. A maximum of 100 simultaneous BFD sessions are supported.
If each BFD for BGP neighbor receives a BFD control packet within the configured BFD interval for failure detection, the BFD session remains up and BGP maintains its adjacencies. If a BFD for BGP neighbor does not receive a control packet within the detection interval, the router informs any clients of the BFD session, and other routing protocols, about the failure. It then depends on the routing protocol that uses the BGP link to determine the appropriate response to the failure condition. The normal response is to terminate the peering session for the routing protocol and reconverge by bypassing the failed neighboring router.
A log message generates whenever BFD detects a failure condition.
BFD with OSPF
You can configure BFD to monitor and notify reachability status between OSPF neighbors. When you use BFD with OSPF, BFD sessions are established between all neighboring interfaces participating with OSPF full state. If a neighboring interface fails, BFD notifies OSPF protocol that a link state change has occurred.Configure BFD for OSPF
1. Enable BFD globally.
2. Configure BFD on the OSPF interfaces within the related interconnecting routers.
Enable BFD
● Enable BFD globally.
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
● Enable BFD on the OSPF interfaces within the related interconnecting routers.
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(config)# interface Vlan 100 DELLSONiC(config-if-Vlan100)# ip ospf bfd
View BFD peer status
DELLSONiC# show bfd peers BFD Peers: peer 10.10.150.1 vrf default interface Vlan100 ID: 3939769244 Remote ID: 330903919 Passive mode: Disabled Status: up Uptime: 0 day(s), 0 hour(s), 2 min(s), 37 sec(s) Diagnostics: ok Remote diagnostics: ok Peer Type: dynamic Local timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 0ms Remote timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 300ms
BFD with PIM
You can enable BFD support for PIM on individual interfaces.
Configure BFD for PIM
1. Enable BFD globally.
2. Configure BFD on the PIM interfaces within the related interconnecting routers.
Enable BFD
● Enable BFD globally.
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
● Enable BFD on the PIM interfaces within the related interconnecting routers.
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(config)# interface Vlan 100 DELLSONiC(config-if-Vlan100)# ip pim bfd
View BFD peer status
DELLSONiC# show bfd peers BFD Peers: peer 10.10.150.1 vrf default interface Vlan100 ID: 3939769244 Remote ID: 330903919 Passive mode: Disabled Status: up Uptime: 0 day(s), 0 hour(s), 2 min(s), 37 sec(s) Diagnostics: ok Remote diagnostics: ok Peer Type: dynamic Local timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 0ms Remote timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 300ms
BFD profile
You can use a BFD profile to create a template of BFD configurations and apply to multiple BFD peers without configuring each BFD peer separately. BFD profile also enables changing BFD timers of dynamic sessions without configuring static BFD peers.
Within a BFD profile, you can configure all the necessary BFD parameters. When you apply the BFD profile to a static peer, BGP, OSPF, or PIM configuration, all parameters that you have configured under the profile are applied to those protocols.
Profile configuration scenarios
1. Scenario 1: You can apply a BFD profile without first creating it. However, the profile takes effect only after it is configured. The default BFD settings are used until you configure the profile.
2. Scenario 2: A BFD profile is associated with a static BFD peer and BFD parameters are configured in the static peer as well. Parameters that are configured in the static peer takes precedence over the BFD profile.
3. Scenario 3: BGP, OSPF, and PIM share a BFD session and the BFD profile that is associated with BGP, OSPF and PIM is different. The latest configured profile either in BGP, OSPF, or PIM takes effect.
4. Scenario 4: BFD profile configuration is changed dynamically. All the configuration parameters apply immediately and BFD timers is renegotiated using the polling method.
5. Scenario 5: BFD profile that is associated with BGP, OSPF, PIM, or BFD peer is deleted. The associated BFD session reverts to default values. The profile configuration should be deleted from BGP, OSPF, PIM, or BFD peer as well and reconfigured to take effect.
6. Scenario 6: A BFD profile is deleted. The BFD profile can be deleted from BFD without unconfiguring the profile from the protocols if any. Similarly, BFD profile can be unconfigured from protocols without deleting the profile in BFD. BFD profile configuration is allowed to be overwritten with new profile without unconfiguring the existing profile.
Configure BFD profile
● Enable BFD globally in CONFIGURATION mode.
DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
● Create a BFD profile in BFD CONFIGURATION mode.
DELLSONiC (conf-bfd)# profile profile-name
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC (conf-bfd)# profile profile-cx-1
● After configuring the peer, configure BFD parameters. Enter the no form of a command to remove the configured BFD setting and restore the default value.
DELLSONiC (conf-bfd-peer)# {detect-multiplier | echo-interval | echo-mode | minimum-ttl | passive-mode | receive-interval | transmit-interval}
○ detect-mutiplier (2-128) – Configures the detection multiplier to determine packet loss. The remote transmission interval will be multiplied by this value to determine the connection loss detection timer. The default value is 3.
Example: local system has detect-multiplier 5 and the remote system has transmission interval 300, the local system will detect failures only after 1500 milliseconds without receiving packets.
○ echo-interval (10-60000) - minimum transmission interval (less jitter) that this system wants to use to send BFD echo packets. The default value is 300.
○ echo-mode - Configure echo mode.
○ minimum-ttl (1-254) - minimum expected TTL for incoming multi-hop BFD peer packets. If the TTL of the received BFD packet is less than the configured TTL, the system discards the packet. The default value is 254.
○ passive-mode - a passive session will not attempt to initiate a connection and will wait for BFD control packets from peer before it becomes active. By default, passive-mode is disabled.
○ shutdown - disable BFD peer.
○ transmit-interval (10-60000) - minimum transmission interval that this system wants to use to send BFD control packets. The default value is 300.
View BFD profile
● Use the following command to view all BFD profiles that are configured on the system
DELLSONiC # show bfd profile
DELLSONiC# show bfd profile BFD Profile: Profile-name: profile-cx-1 Enabled: True Echo-mode: Enabled Passive-mode: Disabled Minimum-Ttl: 254 Detect-multiplier: 5 Receive interval: 200ms Transmission interval: 200ms Echo transmission interval: 200ms Profile-name: profile-cx-2 Enabled: True Echo-mode: Enabled Passive-mode: Disabled Minimum-Ttl: 254 Detect-multiplier: 10 Receive interval: 100ms Transmission interval: 100ms Echo transmission interval: 100ms
● Use the following command to view a specific BFD profile that is configured on the system
DELLSONiC # show bfd profile profile-cx-2
DELLSONiC# show bfd profile profile-cx-2 BFD Profile: Profile-name: profile-cx-2 Enabled: True Echo-mode: Enabled Passive-mode: Disabled Minimum-Ttl: 254 Detect-multiplier: 10 Receive interval: 100ms Transmission interval: 100ms Echo transmission interval: 100ms
Apply a BFD profile to a static peer
You can associate a BFD profile with a BFD peer. BFD parameters that are manually configured in the static BFD peer takes precedence over this BFD profile. You can enter a maximum of 63 characters as the profile name.
● Enable BFD globally in CONFIGURATION mode.
DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
● Create a BFD profile in BFD CONFIGURATION mode.
DELLSONiC (conf-bfd)# profile profile-name
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC (conf-bfd)# profile profile-cx-1 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# detect-multiplier 5 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# echo-interval 200 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# echo-mode DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# receive-interval 200 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# transmit-interval 200
● Apply the BFD profile that you configured previously to the static peer.
sonic(conf-bfd)# peer ip-address interface interface-type-number sonic(conf-bfd-peer)# profile profile-name
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd DELLSONiC(conf-bfd)# peer 192.168.2.1 interface Eth1/1 DELLSONiC(conf-bfd-peer)# profile profile-cx-1
View BFD peer status
DELLSONiC# show bfd peers BFD Peers: peer 192.168.2.1 vrf default interface Eth1/1 ID: 576939186 Remote ID: 2194348295 Passive mode: Disabled Profile: profile-cx-1 Status: up Uptime: 0 day(s), 0 hour(s), 25 min(s), 40 sec(s) Diagnostics: ok Remote diagnostics: ok Peer Type: dynamic Local timers: Detect-multiplier: 5 Receive interval: 200ms Transmission interval: 200ms Echo transmission interval: 200ms Remote timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 300ms
Apply a BFD profile to a BGP neighbor
Associate a BFD profile to a BGP neighbor. You can enter a maximum of 63 characters as the profile name.
● Enable BFD globally in CONFIGURATION mode.
DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
● Create a BFD profile in BFD CONFIGURATION mode.
DELLSONiC(conf-bfd)# profile profile-name
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(conf-bfd)# bfd DELLSONiC(conf-bfd)# profile profile-cx-1 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# detect-multiplier 5 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# echo-interval 200 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# echo-mode DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# receive-interval 200 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# transmit-interval 200
● Apply the BFD profile that you configured previously to the BGP neighbor or a peer group.
DELLSONiC (config-router-bgp-neighbor)# neighbor neighbor-ip-address DELLSONiC(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# bfd profile profile-name
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(config)# router bgp 500 DELLSONiC(config-router-bgp)# neighbor 10.10.150.2 DELLSONiC(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# bfd profile profile-cx-1
Or
DELLSONiC (config-router-bgp-neighbor-pg)# peer-group peer-group-name DELLSONiC(config-router-bgp-pg)# bfd profile profile-name
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(config)# router bgp 500 DELLSONiC(config-router-bgp)# neighbor 10.10.150.2 DELLSONiC(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# peer-group bgp-cx-1 DELLSONiC(config-router-bgp-pg)# bfd profile profile-cx-1
View BFD peer status
DELLSONiC# show bfd peers BFD Peers: peer 10.10.150.2 vrf default interface Vlan100 ID: 576939186 Remote ID: 2194348295 Passive mode: Disabled Profile: profile-cx-1 Status: up Uptime: 0 day(s), 0 hour(s), 25 min(s), 40 sec(s) Diagnostics: ok Remote diagnostics: ok Peer Type: dynamic Local timers: Detect-multiplier: 5 Receive interval: 200ms Transmission interval: 200ms Echo transmission interval: 200ms Remote timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms
Apply a BFD profile to an OSPF-enabled interface
Associate a BFD profile to an OSPF-enabled interface. You can enter a maximum of 63 characters as the profile name.
● Enable BFD globally in CONFIGURATION mode.
DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
● Create a BFD profile in BFD CONFIGURATION mode.
DELLSONiC (conf-bfd)# profile profile-name
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(conf-bfd)# bfd DELLSONiC(conf-bfd)# profile profile-cx-1 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# detect-multiplier 5 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# echo-interval 200 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# echo-mode DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# receive-interval 200 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# transmit-interval 200
● Apply the BFD peer profile on the OSPF interfaces within the related interconnecting routers.
DELLSONiC(config-if-Vlan100)# ip ospf bfd profile profile-name
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(config)# interface Vlan 100 DELLSONiC(config-if-Vlan100)# ip ospf bfd profile profile-cx-1
View BFD peer status
DELLSONiC# show bfd peers BFD Peers: peer 10.10.150.2 vrf default interface Vlan100 ID: 576939186 Remote ID: 2194348295 Passive mode: Disabled Profile: profile-cx-1 Status: up Uptime: 0 day(s), 0 hour(s), 25 min(s), 40 sec(s) Diagnostics: ok Remote diagnostics: ok Peer Type: dynamic Local timers: Detect-multiplier: 5 Receive interval: 200ms Transmission interval: 200ms Echo transmission interval: 200ms Remote timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms
Apply a BFD profile to PIM
Associate a BFD profile to an PIM-enabled interface. You can enter a maximum of 63 characters as the profile name.
● Enable BFD globally in CONFIGURATION mode.
DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd
● Create a BFD profile in BFD CONFIGURATION mode.
DELLSONiC (conf-bfd)# profile profile-name
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(conf)# bfd DELLSONiC(conf-bfd)# profile profile-cx-1 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# detect-multiplier 5 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# echo-interval 200 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# echo-mode DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# receive-interval 200 DELLSONiC(config-bfd-profile)# transmit-interval 200
● Apply the BFD peer profile on the PIM interfaces within the related interconnecting routers.
DELLSONiC(config-if-Vlan100)# ip pim bfd profile profile-name
admin@DELLSONiC:~$ sonic-cli DELLSONiC# configure terminal DELLSONiC(config)# interface Vlan 100 DELLSONiC(config-if-Vlan100)# ip pim profile profile-cx-1
View BFD peer status
DELLSONiC# show bfd peers BFD Peers: peer 10.10.150.2 vrf default interface Vlan100 ID: 576939186 Remote ID: 2194348295 Passive mode: Disabled Profile: profile-cx-1 Status: up Uptime: 0 day(s), 0 hour(s), 25 min(s), 40 sec(s) Diagnostics: ok Remote diagnostics: ok Peer Type: dynamic Local timers: Detect-multiplier: 5 Receive interval: 200ms Transmission interval: 200ms Echo transmission interval: 200ms Remote timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms
View BFD peer information
View BFD peer information.
sonic# show bfd peers BFD Peers: peer 172.11.0.1 vrf default interface Vlan101 ID: 2604839737 Remote ID: 2286829245 Passive mode: Disabled Profile: bfd_prof_0 Status: up Uptime: 0 day(s), 23 hour(s), 8 min(s), 14 sec(s) Diagnostics: ok Remote diagnostics: ok Peer Type: dynamic Local timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 0ms Remote timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 300ms
View multi-hop BFD peer information.
sonic# show bfd peer 10.1.1.2 multihop local-address 10.1.1.1 vrf default peer 10.1.1.2 multihop local-address 10.1.1.1 vrf default ID: 82748345 Remote ID: 0 Active mode Minimum TTL: 123 Status: down Downtime: 0 day(s), 0 hour(s), 0 min(s), 19 sec(s) Diagnostics: ok Remote diagnostics: ok Peer Type: configured Local timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 60ms Remote timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 1000ms Transmission interval: 1000ms Echo transmission interval: 0ms
View single hop BFD peer information
sonic# show bfd peer 10.1.1.2 vrf default interface Eth1/3 peer 10.1.1.2 vrf default interface Eth1/3 ID: 2286155092 Remote ID: 0 Passive mode Status: down Downtime: 0 day(s), 0 hour(s), 1 min(s), 6 sec(s) Diagnostics: ok Remote diagnostics: ok Peer Type: configured Local timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 0ms Remote timers: Switch protection 431 Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 1000ms Transmission interval: 1000ms Echo transmission interval: 0ms sonic# show bfd peer 172.11.0.1 vrf default interface Vlan 101 BFD Peers: peer 172.11.0.1 vrf default interface Vlan101 ID: 2604839737 Remote ID: 2286829245 Passive mode: Disabled Profile: bfd_prof_0 Status: up Uptime: 0 day(s), 23 hour(s), 17 min(s), 26 sec(s) Diagnostics: ok Remote diagnostics: ok Peer Type: dynamic Local timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 0ms Remote timers: Detect-multiplier: 3 Receive interval: 300ms Transmission interval: 300ms Echo transmission interval: 300ms
Affected Products
Enterprise SONiC Distribution, PowerSwitch S5048F-ON, PowerSwitch S5148F-ON, PowerSwitch S5212F-ON, PowerSwitch S5224F-ON, PowerSwitch S5232F-ON, PowerSwitch S5248F-ON, PowerSwitch S5296F-ON, PowerSwitch S5448F-ON, PowerSwitch Z9264F-ONArticle Properties
Article Number: 000218787
Article Type: How To
Last Modified: 20 Feb 2024
Version: 4
Find answers to your questions from other Dell users
Support Services
Check if your device is covered by Support Services.