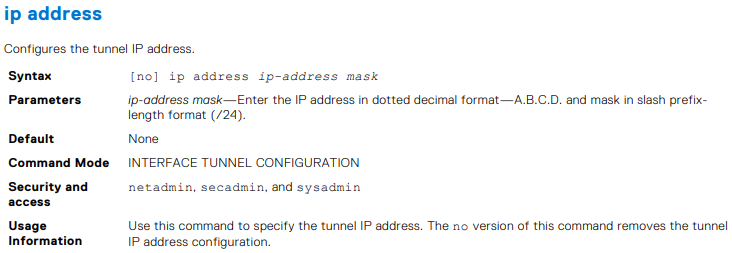
Dell Networking OS10 – Einführung in die GRE-Konfiguration
Summary: Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) ist ein IP-Kapselungsprotokoll, mit dem eine virtuelle Punkt-zu-Punkt-Verbindung zwischen zwei Routern in einem Netzwerk hergestellt wird. Es wird häufig verwendet, um Routingprotokolle wie RIP und OSPF zwischen verschiedenen Standorten zu tunneln. GRE wird in Request for Comments (RFC 2784) beschrieben. ...
This article applies to
This article does not apply to
This article is not tied to any specific product.
Not all product versions are identified in this article.
Instructions
Wichtige Themen
Konfiguration von GRE-Tunneln:
- GRE-Tunnel werden zwischen zwei Routern konfiguriert, um GRE-Pakete direkt zu senden und zu empfangen.
- Die Konfiguration umfasst das Einrichten von Tunnelschnittstellen, das Festlegen von Tunnelmodus, Quelle und Ziel.
Einschränkungen und Begrenzungen:
- Unterstützung von maximal 100 Tunneln
- IPv6 wird auf Underlay- und Overlay-Pfaden nicht unterstützt.
- Bestimmte Schnittstellen und IP-Adressen haben Einschränkungen, wenn sie mit GRE-Tunneln verwendet werden.
Einstellungen für Tunnel-Keepalive:
- Konfigurieren von Keepalive-Einstellungen zur Überwachung der Erreichbarkeit von Tunnelendpunkten mithilfe von ICMP-Echo- und Antwortpaketen (Internet Control Message Protocol).
Equal-Cost MultiPath (ECMP)-Overlay und -Underlay:
- ECMP-Lastverteilung zum Verteilen des Datenverkehrs auf verfügbare Routen
- Unterstützte Kombinationen für Überlagerungs- und Underlay-ECMP-Routen.
Befehle und Beispiele:
- Detaillierte Befehlssyntax und Beispiele für die Konfiguration von GRE-Tunneln, Keepalive-Einstellungen und ECMP-Routen
Mögliche Probleme mit einer Fehlkonfiguration
Tunnel-Flattern:
- Falsche Keepalive-Einstellungen können dazu führen, dass der Tunnel häufig auf und ab geht, was zu Instabilität führt.
MTU-Nichtübereinstimmung:
- GRE-Tunnel über Pfade mit unterschiedlichen MTU-Einstellungen können zu Paketfragmentierung oder -verlust führen.
Routing-Schleifen:
- Falsch konfiguriertes Routing kann zu Schleifen führen, die übermäßigen Datenverkehr und potenzielle Netzwerkausfälle verursachen.
Best Practices
Konsistente MTU-Einstellungen:
- Stellen Sie sicher, dass die MTU-Einstellungen im gesamten GRE-Tunnel konsistent sind, um eine Fragmentierung zu vermeiden.
Richtige Keepalive-Konfiguration:
- Konfigurieren Sie Keepalive-Einstellungen, um die Tunnelintegrität zu überwachen und unnötiges Flapping zu vermeiden.
Übersichtliche Dokumentation:
- Pflegen Sie eine klare Dokumentation der Tunnelkonfigurationen und der zugehörigen Routen, um Fehlkonfigurationen zu vermeiden.
Anwendungsfälle für GRE-Tunnel.
Verbinden von Remotestandorten:
- GRE-Tunnel können Remotestandorte über das Internet verbinden und ermöglichen so eine sichere und effiziente Kommunikation.
Tunneln von Nicht-IP-Datenverkehr:
- GRE kann Nicht-IP-Datenverkehr kapseln, wodurch es für verschiedene Netzwerkprotokolle vielseitig einsetzbar ist.
Lastenausgleich:
- Durch die Verwendung von ECMP mit GRE-Tunneln kann die Datenverkehrslast auf mehrere Pfade verteilt werden, wodurch die Netzwerkleistung verbessert wird.
Beispiel für eine Netzwerktopologie
Stellen Sie sich ein Netzwerk mit zwei Remotestandorten vor, Standort A und Standort B, die über das Internet verbunden sind. Jeder Standort verfügt über einen Router, zwischen dem ein GRE-Tunnel konfiguriert ist.
Die Topologie würde wie folgt aussehen:
Standort A (10.10.10.0/24) ---- OS10-1 ---- Internet ---- OS10-2 ---- Standort B (10.20.10.0/24)

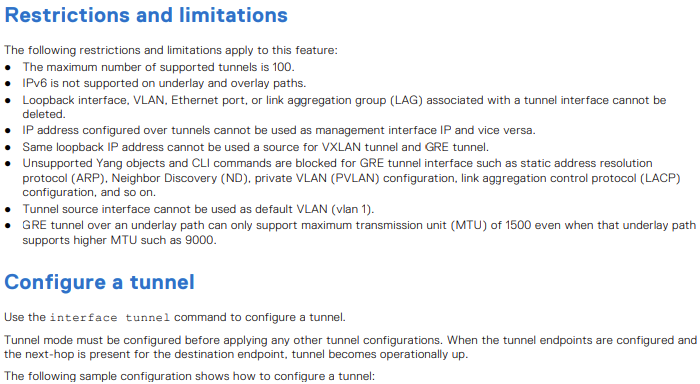
OS10(config)# interface tunnel 10 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# <165>1 2022-11-11T17:55:16.614662+00:00 OS10 dn_alm 731 - - Node.1-Unit.1:PRI [event], Dell (OS10) %IFM_ASTATE_UP: Interface admin state up :tunnel10 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# ip vrf forwarding red % Error: Interface tunnel10, Tunnel mode is mandatory config and must exist for other tunnel configs. OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# mode gre-ipv4 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# ip vrf forwarding red OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# ip address 120.1.1.1/24 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# <165>1 2022-11-11T17:55:31.454972+00:00 OS10 dn_alm 731 - - Node.1-Unit.1:PRI [event], Dell (OS10) %IP_ADDRESS_ADD: IP Address add is successful. IP 120.1.1.1/24 in VRF:red added successfully OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# tunnel destination 16.16.16.16 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# tunnel source loopback10 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# <165>1 2022-11-11T17:56:17.197783+00:00 OS10 dn_alm 731 - - Node.1-Unit.1:PRI [event], Dell (OS10) %IFM_OSTATE_UP: Interface operational state is up :tunnel10

OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# show configuration ! interface tunnel10 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip vrf forwarding red ip address 120.1.1.1/24 tunnel destination 10.10.10.10 tunnel source loopback10 keepalive down-timer 10 keepalive enable keepalive probe-interval 6 keepalive up-timer 12

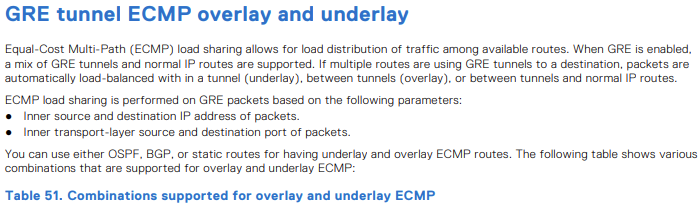
| Unterlegen von ECMP-Routen | Overlay von ECMP-Routen | Unterstützt |
|---|---|---|
| Störgeräusch | Störgeräusch | Ja |
| Störgeräusch | OSPF | Ja |
| Störgeräusch | BGP | Ja |
| OSPF | Störgeräusch | Ja |
| OSPF | OSPF | Nein |
| OSPF | BGP | Ja |
| BGP | Störgeräusch | Ja |
| BGP | OSPF | Ja |
| BGP | BGP | Nein |

OS10(config)# hardware overlay-ecmp-profile mode balanced-overlay-ecmp OS10(config)# <165>1 2022-10-11T10:25:26.474891+00:00 AG1-9978 dn_alm 717 - - Node.1- Unit.1:PRI [event], Dell (OS10) %VXLAN_OVERLAY_ECMP_PROFILE_MODIFIED: VxLAN Overlay ECMP: Configuration is modified, Save and Reload the device for the profile to be effect

OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 21 ! interface tunnel21 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 10.10.10.2/24 tunnel destination 5.5.5.5 tunnel source loopback3 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 22 ! interface tunnel22 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 10.10.10.3/24 tunnel destination 6.6.6.6 tunnel source loopback4 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 23 ! interface tunnel23 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 10.10.10.4/24 tunnel destination 7.7.7.7 tunnel source loopback5 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 24 ! interface tunnel24 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 10.10.10.5/24 tunnel destination 8.8.8.8 tunnel source loopback6 OS10# show running-configuration route ! ip route 77.1.1.0/24 100.1.1.2 ip route 77.1.1.0/24 10.10.10.2 ip route 77.1.1.0/24 10.10.10.3 ip route 77.1.1.0/24 10.10.10.4 ip route 77.1.1.0/24 10.10.10.5 OS10# show ip route 10.1.1.0/24 Routing entry for 77.1.1.0/24 Known via static Distance 1, Metric 0 Last update 08:57:53 Routing descriptors Blocks: via 100.1.1.2 tunnel10 via 10.10.10.2 tunnel21 via 10.10.10.3 tunnel22 via 10.10.10.4 tunnel23 via 10.10.10.5 tunnel24

OS10# show ip route 67.67.67.0/24 Routing entry for 67.67.67.0/24 Known via ospf, type Distance 110, Metric 21 Last update 09:35:46 Routing descriptors Blocks: via 10.1.1.2 ethernet1/1/25:1 via 12.1.1.2 ethernet1/1/25:2 via 23.2.2.2 vlan2 via 23.2.3.2 vlan3 via 23.2.4.2 vlan4 via 23.2.5.2 vlan5 via 23.2.6.2 vlan6 via 23.2.7.2 vlan7 via 23.2.8.2 vlan8 via 23.2.9.2 vlan9 OS10# show ip route 68.68.68.0/24 Routing entry for 68.68.68.0/24 Known via ospf, type Distance 110, Metric 21 Last update 09:36:35 Routing descriptors Blocks: via 10.1.1.2 ethernet1/1/25:1 via 12.1.1.2 ethernet1/1/25:2 via 23.2.2.2 vlan2 via 23.2.3.2 vlan3 via 23.2.4.2 vlan4 via 23.2.5.2 vlan5 via 23.2.6.2 vlan6 OS10# show running-configuration interface vlan 2 ! interface vlan2 no shutdown ip address 23.2.2.1/24 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 OS10# show running-configuration interface vlan 3 ! interface vlan3 no shutdown ip address 23.2.3.1/24 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 OS10# show running-configuration interface vlan 4 ! interface vlan4 no shutdown ip address 23.2.4.1/24 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 21 ! interface tunnel21 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 131.131.131.1/24 tunnel destination 67.67.67.67 tunnel source loopback3 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 22 ! interface tunnel22 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 132.132.132.1/24 tunnel destination 68.68.68.68 tunnel source loopback4

-
Beispiel
OS10# clear counters interface tunnel 10


-
Beispiel
OS10(config)# interface tunnel 10

-
Beispiel
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-40)# ip address 10.1.1.1/24


-
Beispiel
OS10(conf)# ip route 1.1.1.0/24 interface tunnel 10 OS10(conf)# ip route 2.2.2.0/24 3.3.3.3 interface tunnel 10


-
Beispiel
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-4)# ip vrf forwarding Vrf_red


-
Beispiel
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# keepalive down-timer 10


-
Beispiel
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# keepalive enable


-
Beispiel
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# keepalive probe-interval 10


-
Beispiel
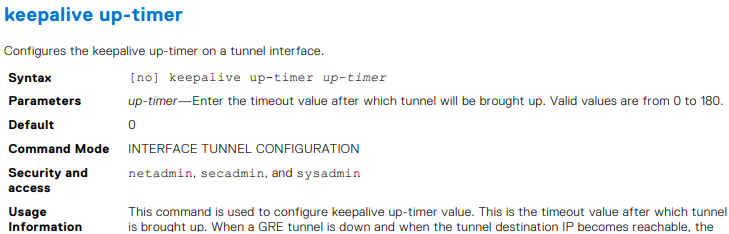
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# keepalive up-timer 10

-
Beispiel
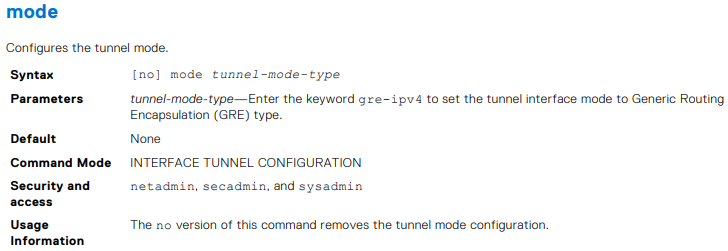
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# mode gre-ipv4

-
Beispiel
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-40)# tunnel destination 10.10.10.10


-
Beispiel
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-4)# tunnel source vlan 10


-
Beispiel
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# tunnel ttl 220


-
Beispiel
OS10# show interface tunnel 10 Tunnel 10 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Tunnel Tunnel mode GREv4 Tunnel source IP 2.2.2.2, Tunnel source Intf loopback1 Tunnel destination 7.7.7.7 Tunnel TTL 255 Tunnel keepalive enabled Keepalive probe interval 10, Up timer 5, Down timer 5 Interface index is 45 Internet address is 10.1.1.1/24 Mode of IPv4 Address Assignment: MANUAL Interface IPv6 oper status: Enabled ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout: 60 Last clearing of "show interface" counters: 00:11:22 Queuing strategy: fifo Input statistics: 0 packets, octets Output statistics: 0 packets, octets Time since last interface status change: 00:27:11


-
Beispiel
OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel ! interface tunnel10 no shutdown mode gre-ipv4 ip address 100.1.1.1/24 tunnel destination 3.3.3.3 tunnel source 1.1.1.1 ! interface tunnel20 no shutdown mode gre-ipv4 ip address 101.1.1.1/24 tunnel destination 5.5.5.5 tunnel source 6.6.6.6 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 10 ! interface tunnel10 no shutdown mode gre-ipv4 ip address 100.1.1.1/24 tunnel destination 3.3.3.3 tunnel source 1.1.1.1


Beispiel
OS10# show tunnel Name Mode Source-IP Destination-IP SrcIntf TTL VRF Status Protocol ================================================================================================= Tunnel 1 GREv4 1.1.1.1 6.6.6.6 Loopback 2 255 default up up Tunnel 2 GREv4 2.2.2.2 7.7.7.7 Loopback 123 255 default up up Tunnel 3 GREv4 3.3.3.3 8.8.8.8 Loopback 100 255 default up up OS10# show tunnel 10 Name Mode Source-IP Destination-IP SrcIntf TTL VRF Status Protocol ================================================================================================= Tunnel 10 GREv4 1.1.1.1 7.6.6.6 Loopback 2 255 default up up


-
Beispiel
OS10# show ip int gig 1/3 GigabitEthernet 1/3 is up, line protocol is down Internet address is 10.11.0.1/24 Broadcast address is 10.11.0.255 Address determined by user input IP MTU is 1500 bytes Helper address is 192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2 Directed broadcast forwarding is disabled



-
Beispiel
OS10# show ip route Codes: C - connected S - static B - BGP, IN - internal BGP, EX - external BGP, EV - EVPN BGP O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area, N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2, E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, * - candidate default, + - summary route, > - non-active route Gateway of last resort is not set Destination Gateway Dist/Metric Last Change -------------------------------------------------------------------- C 1.1.1.0/24 via 1.1.1.1 ethernet1/1/1:1 0/0 01:32:53 C 10.1.1.0/24 via 100.1.1.1 loopback1 0/0 00:00:06 C 2.2.2.0/24 via 2.1.1.1.1 Tunnel 1 0/0 00:00:15 OS10# show ip route static Codes: C - connected S - static B - BGP, IN - internal BGP, EX - external BGP, EV - EVPN BGP O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area, N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2, E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, * - candidate default, + - summary route, > - non-active route Gateway of last resort is not set Destination Gateway Dist/Metric Last Change ---------------------------------------------------------------------- C 1.1.1.0/24 via 1.1.1.1 ethernet1/1/1:1 0/0 01:32:53 C 10.1.1.0/24 via 100.1.1.1 loopback1 0/0 00:00:06 S 80.1.10.0/24 via 100.1.1.1 tunnel10 1/0 00:02:33


OS10# show ip ospf interface tunnel 10 tunnel10 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 100.1.1.1/24, Area 0.0.0.0 Process ID 1, Router ID 1.1.1.1, Network Type broadcast, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 1.1.1.1 (local), Interface address 100.1.1.1 Backup Designated router (ID) , Interface address 0.0.0.0 Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0 OS10# show ip ospf 1 interface tunnel 10 tunnel10 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 100.1.1.1/24, Area 0.0.0.0 Process ID 1, Router ID 1.1.1.1, Network Type broadcast, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 1.1.1.1 (local), Interface address 100.1.1.1 Backup Designated router (ID) , Interface address 0.0.0.0 Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0


-
Beispiel
OS10# show ip ospf 1 statistics interface tunnel 10 Interface tunnel10 Receive Statistics rx-invalid 0 rx-invalid-bytes 0 rx-hello 0 rx-hello-bytes 0 rx-db-des 0 rx-db-des-bytes 0 rx-ls-req 0 rx-ls-req-bytes 0 rx-ls-upd 0 rx-ls-upd-bytes 0 rx-ls-ack 0 rx-ls-ack-bytes 0 Transmit Statistics tx-failed 0 tx-failed-bytes 0 tx-hello 52 tx-hello-bytes 3328 tx-db-des 0 tx-db-des-bytes 0 tx-ls-req 0 tx-ls-req-bytes 0 tx-ls-upd 0 tx-ls-upd-bytes 0 tx-ls-ack 0 tx-ls-ack-bytes 0 Error packets (Receive statistics) bad-src 0 dupe-id 0 hello-err 0 mtu-mismatch 0 nbr-ignored 0 wrong-proto 0 resource-err 0 bad-lsa-len 0 lsa-bad-type 0 lsa-bad-len 0 lsa-bad-cksum 0 auth-fail 0 netmask-mismatch 0 hello-tmr-mismatch 0 dead-ivlmismatch 0 options-mismatch 0 nbr-admin-down 0 own-hellodrop 0 self-orig 0 wrong-length 0 checksumerror 0 version-mismatch 0 area-mismatch 0

Additional Information
Affected Products
SmartFabric OS10 SoftwareArticle Properties
Article Number: 000228691
Article Type: How To
Last Modified: 03 Oct 2025
Version: 2
Find answers to your questions from other Dell users
Support Services
Check if your device is covered by Support Services.