Présentation de la configuration GRE par Dell Networking OS10
Summary: Le protocole GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) est un protocole d’encapsulation IP utilisé pour établir une connexion virtuelle point à point entre deux routeurs sur un réseau. Il est couramment utilisé pour tunneliser les protocoles de routage tels que RIP et OSPF entre différents sites. GRE est décrit dans la demande de commentaires (RFC 2784. ...
This article applies to
This article does not apply to
This article is not tied to any specific product.
Not all product versions are identified in this article.
Instructions
Principaux sujets abordés
Configuration des tunnels GRE :
- Les tunnels GRE sont configurés entre deux routeurs pour envoyer et recevoir directement des paquets GRE.
- La configuration implique la configuration des interfaces de tunnel, en spécifiant le mode tunnel, la source et la destination.
Restrictions et limites :
- Un maximum de 100 tunnels pris en charge
- IPv6 n’est pas pris en charge sur les chemins de sous-couche et de superposition.
- Certaines interfaces et adresses IP ont des restrictions lorsqu’elles sont utilisées avec des tunnels GRE.
Paramètres de connexion persistante dans le tunnel :
- Configuration des paramètres keepalive pour surveiller l’accessibilité des points de terminaison du tunnel à l’aide des paquets d’écho et de réponse ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol).
Superposition et sous-couche ECMP (Equal-Cost MultiPath) :
- Partage de charge ECMP pour la répartition du trafic entre les routes disponibles
- Combinaisons prises en charge pour les routes ECMP superposées et sous-jacentes.
Commandes et exemples :
- Syntaxe de commande détaillée et exemples pour la configuration des tunnels GRE, des paramètres keepalive et des routes ECMP
Problèmes possibles liés à une mauvaise configuration
Battement du tunnel :
- Des paramètres keepalive incorrects peuvent entraîner des montées et descentes fréquentes du tunnel, entraînant une instabilité.
MTU Mismatch :
- Les tunnels GRE sur des chemins avec des paramètres MTU différents peuvent entraîner une fragmentation ou une perte de paquets.
Boucles de routage :
- Un routage mal configuré peut entraîner des boucles, un trafic excessif et des pannes de réseau potentielles.
Pratiques d’excellence
Paramètres MTU cohérents :
- Assurez-vous que les paramètres MTU sont cohérents dans l’ensemble du tunnel GRE afin d’éviter la fragmentation.
Configuration keepalive appropriée :
- Configurez les paramètres keepalive pour surveiller l’état du tunnel et éviter les battements inutiles.
Documentation claire :
- Conservez une documentation claire sur les configurations de tunnel et les itinéraires associés afin d’éviter les erreurs de configuration.
Cas d’utilisation des tunnels GRE.
Connexion de sites distants :
- Les tunnels GRE peuvent connecter des sites distants sur Internet, ce qui permet une communication sécurisée et efficace.
Tunnelisation du trafic non-IP :
- GRE peut encapsuler le trafic non IP, ce qui le rend polyvalent pour divers protocoles réseau.
Équilibrage:
- L’utilisation d’ECMP avec des tunnels GRE peut répartir la charge du trafic sur plusieurs chemins, améliorant ainsi les performances du réseau.
Exemple de topologie réseau
Imaginez un réseau avec deux sites distants, le site A et le site B, connectés via Internet. Chaque site dispose d’un routeur avec un tunnel GRE configuré entre eux.
La topologie se présente comme suit :
Site A (10.10.10.0/24) ---- OS10-1 ---- Internet ---- OS10-2 ---- Site B (10.20.10.0/24)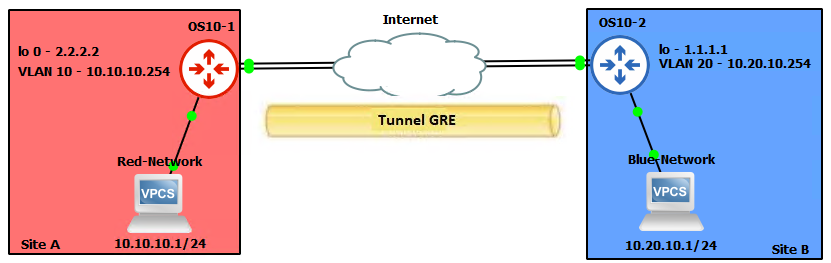


OS10(config)# interface tunnel 10 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# <165>1 2022-11-11T17:55:16.614662+00:00 OS10 dn_alm 731 - - Node.1-Unit.1:PRI [event], Dell (OS10) %IFM_ASTATE_UP: Interface admin state up :tunnel10 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# ip vrf forwarding red % Error: Interface tunnel10, Tunnel mode is mandatory config and must exist for other tunnel configs. OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# mode gre-ipv4 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# ip vrf forwarding red OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# ip address 120.1.1.1/24 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# <165>1 2022-11-11T17:55:31.454972+00:00 OS10 dn_alm 731 - - Node.1-Unit.1:PRI [event], Dell (OS10) %IP_ADDRESS_ADD: IP Address add is successful. IP 120.1.1.1/24 in VRF:red added successfully OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# tunnel destination 16.16.16.16 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# tunnel source loopback10 OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# <165>1 2022-11-11T17:56:17.197783+00:00 OS10 dn_alm 731 - - Node.1-Unit.1:PRI [event], Dell (OS10) %IFM_OSTATE_UP: Interface operational state is up :tunnel10

OS10(conf-if-tunnel-10)# show configuration ! interface tunnel10 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip vrf forwarding red ip address 120.1.1.1/24 tunnel destination 10.10.10.10 tunnel source loopback10 keepalive down-timer 10 keepalive enable keepalive probe-interval 6 keepalive up-timer 12


| Routes ECMP sous-jacentes | Superposition des routes ECMP | Prise en charge |
|---|---|---|
| Parasite | Parasite | Oui |
| Parasite | OSPF | Oui |
| Parasite | BGP | Oui |
| OSPF | Parasite | Oui |
| OSPF | OSPF | Aucune |
| OSPF | BGP | Oui |
| BGP | Parasite | Oui |
| BGP | OSPF | Oui |
| BGP | BGP | Aucune |

OS10(config)# hardware overlay-ecmp-profile mode balanced-overlay-ecmp OS10(config)# <165>1 2022-10-11T10:25:26.474891+00:00 AG1-9978 dn_alm 717 - - Node.1- Unit.1:PRI [event], Dell (OS10) %VXLAN_OVERLAY_ECMP_PROFILE_MODIFIED: VxLAN Overlay ECMP: Configuration is modified, Save and Reload the device for the profile to be effect

OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 21 ! interface tunnel21 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 10.10.10.2/24 tunnel destination 5.5.5.5 tunnel source loopback3 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 22 ! interface tunnel22 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 10.10.10.3/24 tunnel destination 6.6.6.6 tunnel source loopback4 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 23 ! interface tunnel23 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 10.10.10.4/24 tunnel destination 7.7.7.7 tunnel source loopback5 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 24 ! interface tunnel24 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 10.10.10.5/24 tunnel destination 8.8.8.8 tunnel source loopback6 OS10# show running-configuration route ! ip route 77.1.1.0/24 100.1.1.2 ip route 77.1.1.0/24 10.10.10.2 ip route 77.1.1.0/24 10.10.10.3 ip route 77.1.1.0/24 10.10.10.4 ip route 77.1.1.0/24 10.10.10.5 OS10# show ip route 10.1.1.0/24 Routing entry for 77.1.1.0/24 Known via static Distance 1, Metric 0 Last update 08:57:53 Routing descriptors Blocks: via 100.1.1.2 tunnel10 via 10.10.10.2 tunnel21 via 10.10.10.3 tunnel22 via 10.10.10.4 tunnel23 via 10.10.10.5 tunnel24

OS10# show ip route 67.67.67.0/24 Routing entry for 67.67.67.0/24 Known via ospf, type Distance 110, Metric 21 Last update 09:35:46 Routing descriptors Blocks: via 10.1.1.2 ethernet1/1/25:1 via 12.1.1.2 ethernet1/1/25:2 via 23.2.2.2 vlan2 via 23.2.3.2 vlan3 via 23.2.4.2 vlan4 via 23.2.5.2 vlan5 via 23.2.6.2 vlan6 via 23.2.7.2 vlan7 via 23.2.8.2 vlan8 via 23.2.9.2 vlan9 OS10# show ip route 68.68.68.0/24 Routing entry for 68.68.68.0/24 Known via ospf, type Distance 110, Metric 21 Last update 09:36:35 Routing descriptors Blocks: via 10.1.1.2 ethernet1/1/25:1 via 12.1.1.2 ethernet1/1/25:2 via 23.2.2.2 vlan2 via 23.2.3.2 vlan3 via 23.2.4.2 vlan4 via 23.2.5.2 vlan5 via 23.2.6.2 vlan6 OS10# show running-configuration interface vlan 2 ! interface vlan2 no shutdown ip address 23.2.2.1/24 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 OS10# show running-configuration interface vlan 3 ! interface vlan3 no shutdown ip address 23.2.3.1/24 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 OS10# show running-configuration interface vlan 4 ! interface vlan4 no shutdown ip address 23.2.4.1/24 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 21 ! interface tunnel21 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 131.131.131.1/24 tunnel destination 67.67.67.67 tunnel source loopback3 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 22 ! interface tunnel22 mode gre-ipv4 no shutdown ip address 132.132.132.1/24 tunnel destination 68.68.68.68 tunnel source loopback4

-
Exemple
OS10# clear counters interface tunnel 10


-
Exemple
OS10(config)# interface tunnel 10

-
Exemple
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-40)# ip address 10.1.1.1/24



-
Exemple
OS10(conf)# ip route 1.1.1.0/24 interface tunnel 10 OS10(conf)# ip route 2.2.2.0/24 3.3.3.3 interface tunnel 10


-
Exemple
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-4)# ip vrf forwarding Vrf_red


-
Exemple
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# keepalive down-timer 10


-
Exemple
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# keepalive enable


-
Exemple
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# keepalive probe-interval 10



-
Exemple
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# keepalive up-timer 10


-
Exemple
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# mode gre-ipv4

-
Exemple
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-40)# tunnel destination 10.10.10.10


-
Exemple
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-4)# tunnel source vlan 10


-
Exemple
OS10(conf-if-tunnel-1)# tunnel ttl 220


-
Exemple
OS10# show interface tunnel 10 Tunnel 10 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Tunnel Tunnel mode GREv4 Tunnel source IP 2.2.2.2, Tunnel source Intf loopback1 Tunnel destination 7.7.7.7 Tunnel TTL 255 Tunnel keepalive enabled Keepalive probe interval 10, Up timer 5, Down timer 5 Interface index is 45 Internet address is 10.1.1.1/24 Mode of IPv4 Address Assignment: MANUAL Interface IPv6 oper status: Enabled ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout: 60 Last clearing of "show interface" counters: 00:11:22 Queuing strategy: fifo Input statistics: 0 packets, octets Output statistics: 0 packets, octets Time since last interface status change: 00:27:11

-
Exemple
OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel ! interface tunnel10 no shutdown mode gre-ipv4 ip address 100.1.1.1/24 tunnel destination 3.3.3.3 tunnel source 1.1.1.1 ! interface tunnel20 no shutdown mode gre-ipv4 ip address 101.1.1.1/24 tunnel destination 5.5.5.5 tunnel source 6.6.6.6 OS10# show running-configuration interface tunnel 10 ! interface tunnel10 no shutdown mode gre-ipv4 ip address 100.1.1.1/24 tunnel destination 3.3.3.3 tunnel source 1.1.1.1


Exemple
OS10# show tunnel Name Mode Source-IP Destination-IP SrcIntf TTL VRF Status Protocol ================================================================================================= Tunnel 1 GREv4 1.1.1.1 6.6.6.6 Loopback 2 255 default up up Tunnel 2 GREv4 2.2.2.2 7.7.7.7 Loopback 123 255 default up up Tunnel 3 GREv4 3.3.3.3 8.8.8.8 Loopback 100 255 default up up OS10# show tunnel 10 Name Mode Source-IP Destination-IP SrcIntf TTL VRF Status Protocol ================================================================================================= Tunnel 10 GREv4 1.1.1.1 7.6.6.6 Loopback 2 255 default up up


-
Exemple
OS10# show ip int gig 1/3 GigabitEthernet 1/3 is up, line protocol is down Internet address is 10.11.0.1/24 Broadcast address is 10.11.0.255 Address determined by user input IP MTU is 1500 bytes Helper address is 192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2 Directed broadcast forwarding is disabled



-
Exemple
OS10# show ip route Codes: C - connected S - static B - BGP, IN - internal BGP, EX - external BGP, EV - EVPN BGP O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area, N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2, E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, * - candidate default, + - summary route, > - non-active route Gateway of last resort is not set Destination Gateway Dist/Metric Last Change -------------------------------------------------------------------- C 1.1.1.0/24 via 1.1.1.1 ethernet1/1/1:1 0/0 01:32:53 C 10.1.1.0/24 via 100.1.1.1 loopback1 0/0 00:00:06 C 2.2.2.0/24 via 2.1.1.1.1 Tunnel 1 0/0 00:00:15 OS10# show ip route static Codes: C - connected S - static B - BGP, IN - internal BGP, EX - external BGP, EV - EVPN BGP O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area, N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2, E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, * - candidate default, + - summary route, > - non-active route Gateway of last resort is not set Destination Gateway Dist/Metric Last Change ---------------------------------------------------------------------- C 1.1.1.0/24 via 1.1.1.1 ethernet1/1/1:1 0/0 01:32:53 C 10.1.1.0/24 via 100.1.1.1 loopback1 0/0 00:00:06 S 80.1.10.0/24 via 100.1.1.1 tunnel10 1/0 00:02:33


OS10# show ip ospf interface tunnel 10 tunnel10 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 100.1.1.1/24, Area 0.0.0.0 Process ID 1, Router ID 1.1.1.1, Network Type broadcast, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 1.1.1.1 (local), Interface address 100.1.1.1 Backup Designated router (ID) , Interface address 0.0.0.0 Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0 OS10# show ip ospf 1 interface tunnel 10 tunnel10 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 100.1.1.1/24, Area 0.0.0.0 Process ID 1, Router ID 1.1.1.1, Network Type broadcast, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 1.1.1.1 (local), Interface address 100.1.1.1 Backup Designated router (ID) , Interface address 0.0.0.0 Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0


-
Exemple
OS10# show ip ospf 1 statistics interface tunnel 10 Interface tunnel10 Receive Statistics rx-invalid 0 rx-invalid-bytes 0 rx-hello 0 rx-hello-bytes 0 rx-db-des 0 rx-db-des-bytes 0 rx-ls-req 0 rx-ls-req-bytes 0 rx-ls-upd 0 rx-ls-upd-bytes 0 rx-ls-ack 0 rx-ls-ack-bytes 0 Transmit Statistics tx-failed 0 tx-failed-bytes 0 tx-hello 52 tx-hello-bytes 3328 tx-db-des 0 tx-db-des-bytes 0 tx-ls-req 0 tx-ls-req-bytes 0 tx-ls-upd 0 tx-ls-upd-bytes 0 tx-ls-ack 0 tx-ls-ack-bytes 0 Error packets (Receive statistics) bad-src 0 dupe-id 0 hello-err 0 mtu-mismatch 0 nbr-ignored 0 wrong-proto 0 resource-err 0 bad-lsa-len 0 lsa-bad-type 0 lsa-bad-len 0 lsa-bad-cksum 0 auth-fail 0 netmask-mismatch 0 hello-tmr-mismatch 0 dead-ivlmismatch 0 options-mismatch 0 nbr-admin-down 0 own-hellodrop 0 self-orig 0 wrong-length 0 checksumerror 0 version-mismatch 0 area-mismatch 0

Additional Information
Affected Products
SmartFabric OS10 SoftwareArticle Properties
Article Number: 000228691
Article Type: How To
Last Modified: 03 Oct 2025
Version: 2
Find answers to your questions from other Dell users
Support Services
Check if your device is covered by Support Services.