Data Domain: Managing Host Certificates for HTTP and HTTPS
Summary: Host certificates allow browsers and applications to verify the identity of a Data Domain system when establishing secure management sessions. HTTPS is enabled by default. The system can use either a self-signed certificate or an imported certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). This article explains how to check, generate, request, import, and delete certificates for HTTP/HTTPS on Data Domain systems. ...
This article applies to
This article does not apply to
This article is not tied to any specific product.
Not all product versions are identified in this article.
Instructions
Certificates may expire or become invalid. If no certificate is imported, the system uses a self-signed certificate, which may not be trusted by browsers or integrated applications.
1. Check Existing Certificates.
On the Data Domain (DD-CLI), run the following command to view installed certificates:
adminaccess certificate show
If certificates are expired or nearing expiration:
-
- If self-signed, regenerate using DD-CLI.
- If imported, follow the CSR and import steps below.
2. Generate Self-Signed Certificates.
To regenerate the HTTPS certificate:
adminaccess certificate generate self-signed-cert
To regenerate HTTPS and trusted CA certificates:
adminaccess certificate generate self-signed-cert regenerate-ca3. Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
Use DD System Manager:
-
- Set a passphrase, if not done already:
system passphrase set - Navigate to Administration > Access > Administrator Access.
- Select HTTPS > Configure > Certificate tab > Add.
- Click Generate the CSR for this Data Domain system.
- Complete the CSR form and download the file from:
/ddvar/certificates/CertificateSigningRequest.csr
- Set a passphrase, if not done already:
CLI alternative: (Example)
adminaccess certificate cert-signing-request generate key-strength 2048bit country "CN" state "Shanghai" city "Shanghai" org-name "Dell EMC" org-unit "Dell EMC" common-name "ddve1.example.com" subject-alt-name "DNS:ddve1.example.com, DNS:ddve1"4. Import Signed Certificate
- Use DD System Manager:
- Select Administration > Access > Administrator Access
- In the Services area, select HTTPS and click Configure
- Select the Certificate tab
- Click Add
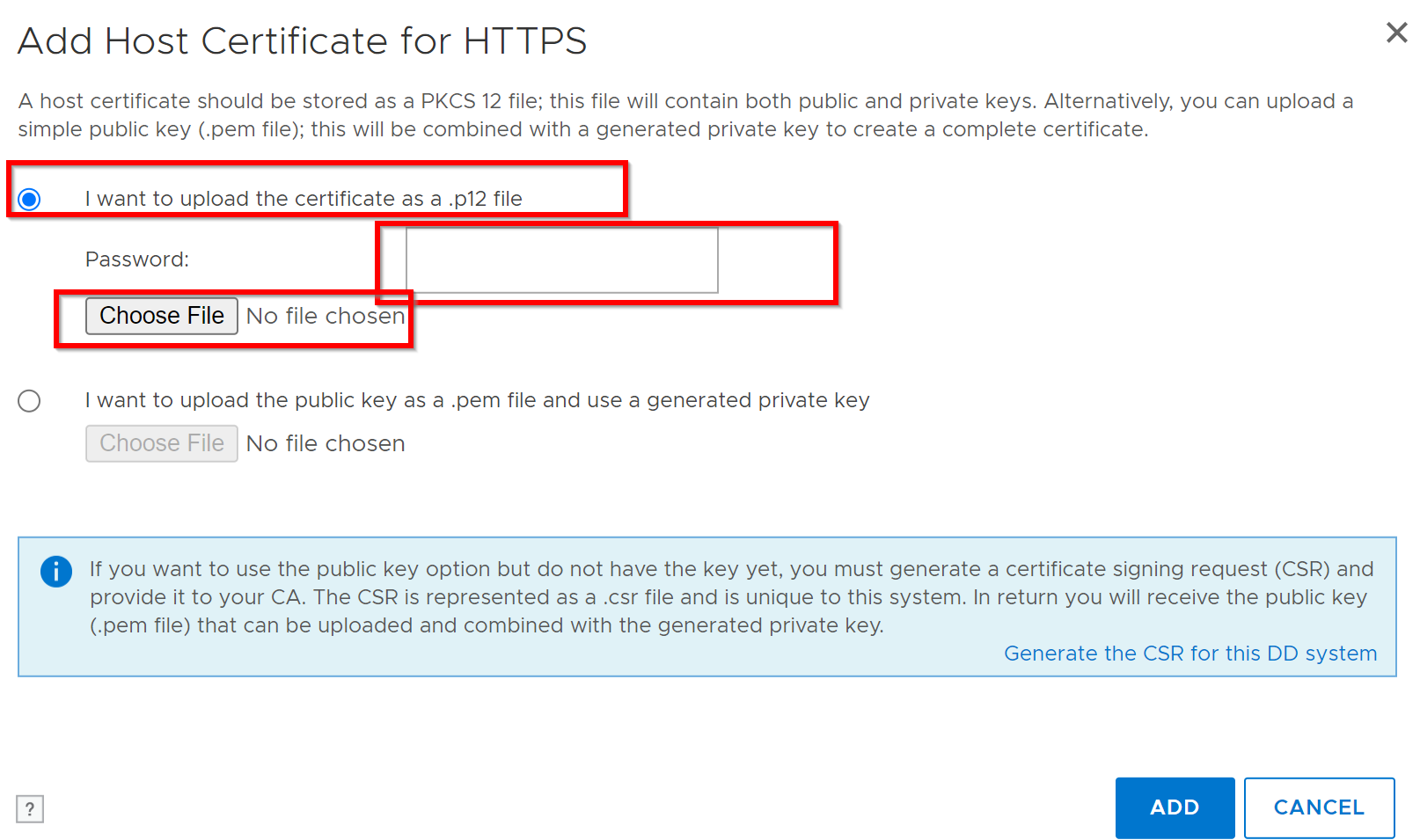
An Upload dialog appears:
- For
.p12file:- Select Upload certificate as .p12 file, enter password, browse, and upload.
- For
.pemfile:- Select Upload public key as .pem file and use generated private key, browse, and upload.
- DD-CLI alternative: Refer to KB: Data Domain: How to Generate a Certificate Signing Request and Use Externally Signed Certificates
- Select Upload public key as .pem file and use generated private key, browse, and upload.
- Example for .p12 selection:
5. Delete Existing Certificate.
Before adding a new certificate, delete the current one:
-
- Navigate to Administration > Access > Administrator Access > HTTPS > Configure > Certificate tab.
- Select certificate and click Delete.
6. CSR Validation
Validate CSR using Windows Command Prompt:
certutil -dump <CSR file path>Additional Information
- Private and public keys must be 2048 bits.
- DDOS supports one active CSR and one signed certificate for HTTPS at a time.
Reference: Deployment KB: Data Domain: How to use externally signed certificates
Affected Products
Data DomainArticle Properties
Article Number: 000205198
Article Type: How To
Last Modified: 27 Nov 2025
Version: 7
Find answers to your questions from other Dell users
Support Services
Check if your device is covered by Support Services.