SSL Certificate shows the warning "Your connection is not private" when browsing a web server UI
Summary: SSL Certificate shows the warning "Your connection is not private" when browsing a web server UI.
Symptoms
Symptom: SSL Certificate shows the warning "Your connection is not private" when browsing a web server UI (Chrome browser).
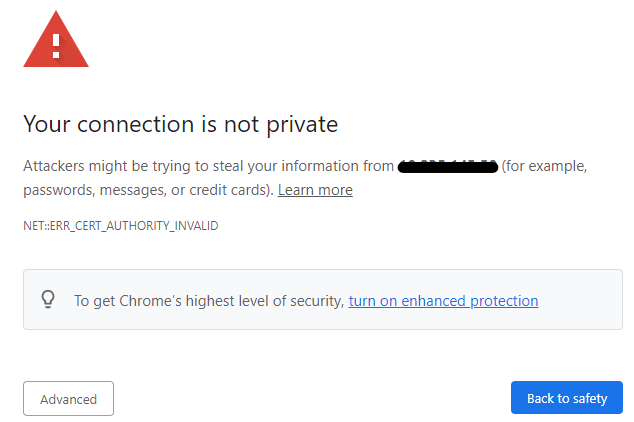
And if clicking "Not secure" on the left side of the browser address field, it shows the following warning information (Chrome browser).
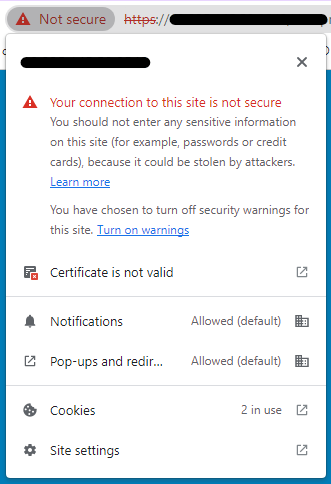
Cause
- The certificate is self-signed
- The client browser does not trust the CA certificate
- The FQDN, Hostname, or IP typed in the browser address field does not match any of the entries in certificate subject alternative names
Resolution
- When a browser shows an invalid certificate error for a self-signed certificate, it means that the certificate presented by the server is not signed by a trusted certificate authority. Self-signed certificates are not signed by a trusted certificate authority, but instead, they are signed by the entity that generated them.
Scenario #2: Internal CA signed certificate.
- If the web browser is displaying an "invalid certificate" error for an internal CA signed certificate, it may be because the certificate is not trusted by the browser.
The specific steps to do this depend on your browser and operating system. Here are some general steps:
-
Export the CA certificate from your internal CA server. Access the CA server's web interface, go to the CA certificate, and then export it in a format that can be imported into your browser.
-
Import the CA certificate into your browser. Open your Windows Control Panel, then select Internet Options, Content tab, click Certificate at bottom, then Trusted Root Certificate Authorities. Click Import to import the CA certificate into the trusted store
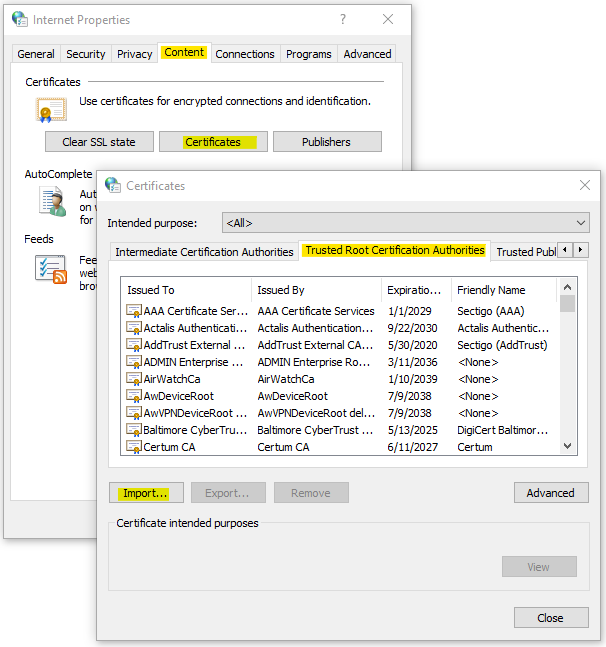
Scenario #3: Third-party CA signed the certificate.
-
If a third-party CA-signed certificate is showing as invalid, it could be due to several reasons. Here are a few things that you can check:
-
Expiration Date: Ensure that the certificate is still valid and has not expired. Check the expiration date of the certificate to ensure it is still valid.
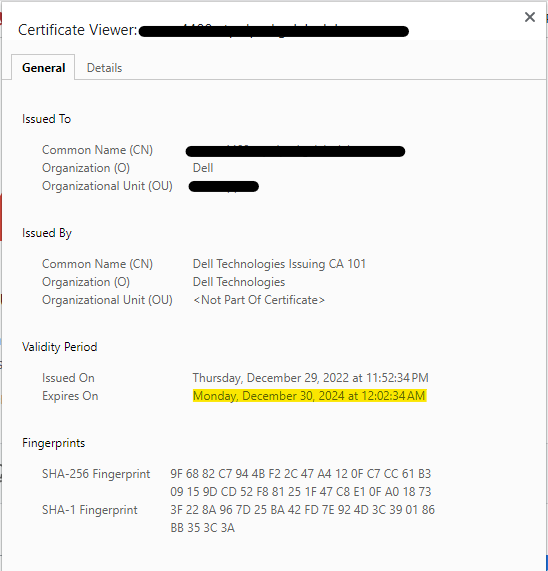
-
Certificate Chain: Check if the certificate chain is complete and correctly installed on the server. A certificate chain includes the SSL certificate, intermediate certificates, and root certificate. Ensure that all certificates in the chain are valid and installed correctly.

-
Domain Name Mismatch: Ensure that the domain name on the certificate (Subject Alternative Name) matches the domain name of the server you are trying to access. If there is a mismatch, the certificate shows as invalid.
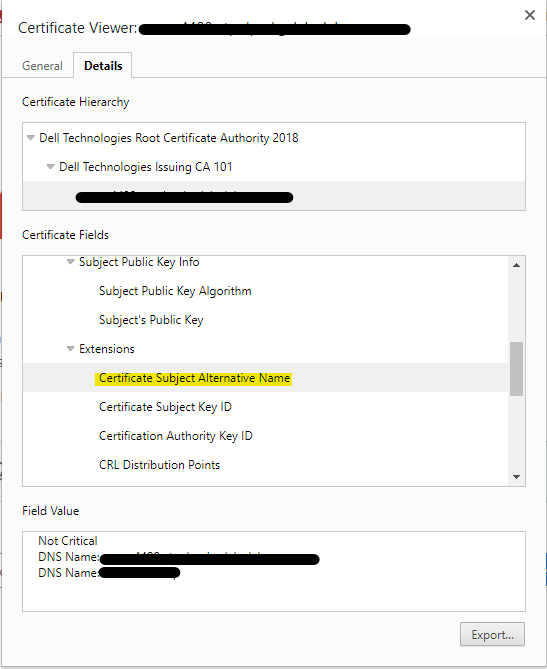
-
Certificate Revocation: Check if the certificate has been revoked by the issuing CA. A revoked certificate shows as invalid.
-
Certificate Authority: Ensure that the CA that issued the certificate is trusted by your browser or device. If the CA is not trusted, the certificate shows as invalid.
-
If you still have issues after checking the above, you want to contact the support team of the CA that issued the certificate for further assistance.