Data Domain: Veeam Best Practices Limitations and Recommendations
Summary: This article contains limitations and recommendations for Data Domain with regard to Veeam 12 backup and replication user guide and other documents.
Instructions
The information below is direct from Veeam Backup & Replication Version 12 User Guide for VMware vSphere 
- We strongly recommend that you follow recommendations from this guide and also the recommendations from Veeam article kb1745 Deduplication Appliance Best Practices
- Since Veeam Backup & Replication version 12, deduplicating storage appliances use the TLS connection.
You can disable the TLS connection with a registry value for the deduplicating storage appliances that do not support the TLS connection. For more information, see Veeam article kb4429 Quantum DXi Storage With Firmware 3.x Does Not Work with Veeam Backup & Replication 12
- Use of Dell Data Domain with DD Boost does not guarantee improvement of job performance. It reduces the load on the network and improves the network throughput.
- NFS services must be enabled on Dell Data Domain. Otherwise, Veeam Backup & Replication cannot access the storage system.
- Do not enable encryption for the jobs targeted at the deduplication storage appliance. Encryption has a negative effect on the deduplication ratio. For more information, see Data Encryption
- Encryption can also affect the backup size: The size of a backup can be larger than the size of the original VM. When you enable encryption, set data processing block size to 4 MB
, and decompression on target and block alignment
(enabled by default), the size of the backup increases by 1 MB for each 4 MB data block.
This is because Veeam Backup & Replication reads blocks of 4 MB, encrypts them, adds 16 KB metadata to each data block and then aligns data blocks.
This results in that each 4 MB data block on the source becomes a 5 MB block on the target.
- When you create a backup job targeted at a Dell Data Domain backup repository, Veeam Backup & Replication offer you to switch to optimized job settings and use the 4 MB size of data block for workload.
Data processing (the Storage optimization setting). It is recommended that you use optimized job settings. Large data blocks produce a smaller metadata table that requires less memory and CPU resources to process.
For more information about storage optimization, see Data Compression and Deduplication
- Dell Data Domain does not support the reverse incremental backup method.
- You cannot use Dell Data Domain backup repositories as sources or targets for file copy jobs.
- The length of forward incremental and forever forward incremental backup chains (chains that contain one full backup and a set of subsequent incremental backups) cannot be greater than 120 restore points.
To overcome this limitation, schedule full backups (active or synthetic) to split the backup chain into shorter series. For example, to perform backups at 15-minute intervals 24 hours a day, you must schedule synthetic fulls every day. In this scenario, intervals immediately after midnight may be skipped due to duration of synthetic processing. For more information, see How Synthetic Full Backup Works
- If you connect to a Dell Data Domain backup repository over Fibre Channel, you must explicitly define a gateway server to communicate with Dell Data Domain.
As a gateway server, you must use a Microsoft Windows server that is added to the backup infrastructure and has access to the Dell Data Domain backup repository over Fibre Channel.
- During backup repository rescan, Veeam Backup & Replication detects if the hard stream limit is set for a storage unit, and displays this information in backup repository rescan statistics.
If the hard stream limit is exceeded when Veeam Backup & Replication runs tasks against the backup repository, Veeam Backup & Replication fail to create new I/O streams.
- During backup repository rescan, Veeam Backup & Replication detects if the hard stream limit is set for a storage unit, and displays this information in backup repository rescan statistics.
If the hard stream limit is exceeded when Veeam Backup & Replication runs tasks against the backup repository, Veeam Backup & Replication will fail to create new I/O streams.
Veeam article kb1745 Deduplication Appliance Best Practices 
Generic Configuration Advice
Below is general Veeam Backup & Replication configuration advice to be used when backing up to deduplicated storage.
Job-Level Settings
From Veeam article kb1745, all Vendor-documented 

Backup Job Settings
Advanced Settings
Below are the general recommendations for the Advanced Settings (Storage > Advanced):
Backup Tab
In general, deduplication devices have the lowest performance during read operations. As such, to maximize performance, the backup jobs should be write-only. Configure the backup job to use (Forward) Incremental with weekly Active full backups to achieve this.
-
Backup Mode
-
(Forward) Incremental
-
-
-
Enabled and set to weekly.
Weekly Full restore points ensure that during a restore, as few restore points must be read from as possible.
-
Maintenance Tab
-
Perform backup files health check
-
Disabled
While enabling this feature with deduplication storage is possible, it requires many read operations, which will take a long time to complete. With larger backup files on deduplicated storage, this feature could cause a backup job to spend days performing the health check, causing the job to not create new restore points.
-
-
Defragment and compact full backup file
-
Disabled
There is no need for this option when Active Fulls are being created.
-
Storage Tab
-
-
Disabled
Disabling deduplication in Veeam Backup & Replication cause the restore points to appear larger, but because Veeam does not deduplicate them, it allows the storage's deduplication function to be more effective.NOTE: Storage that uses a nondedupe zone for storing initially written files, such as ExaGrid's Landing Zone, may benefit from having Veeam's deduplication enabled to allow more restore points to be held in that rapid access state before being processed by the storage deduplication system.
-
-
-
Optimal or Dedupe-friendly
The Repository settings section of this article advises enabling a function that will cause all restore points to be decompressed before being written. As such, the compression set at the job level will only impact data compression while backup data is being transferred across the network. To reduce network congestion, either Optimal or Dedupe-friendly compression may be used. The latter will slightly reduce the effort needed to decompress before writing. Compression at the job level should rarely be disabled as it will significantly increase the amount of data that must be transferred over the network to the machine writing the data to the backup repository.
-
-
Storage optimization (Block Size)
-
4 MB
This block size, formerly called "Local target (large blocks)," will help improve performance when storing backup files on deduplication storage as it reduces the size of the backup file's internal metadata table.
-
-
-
Disabled
Data encryption has a negative effect on the deduplication ratio if you use a deduplicating storage appliance as a target. Veeam Backup & Replication uses different encryption keys for every job session. For this reason, encrypted data blocks sent to the deduplicating storage appliances appear different, even though they may contain duplicate data. If you want to achieve a higher deduplication ratio, you can disable data encryption. If you still want to use encryption, you can enable the encryption feature on the deduplicating storage appliance itself.
-
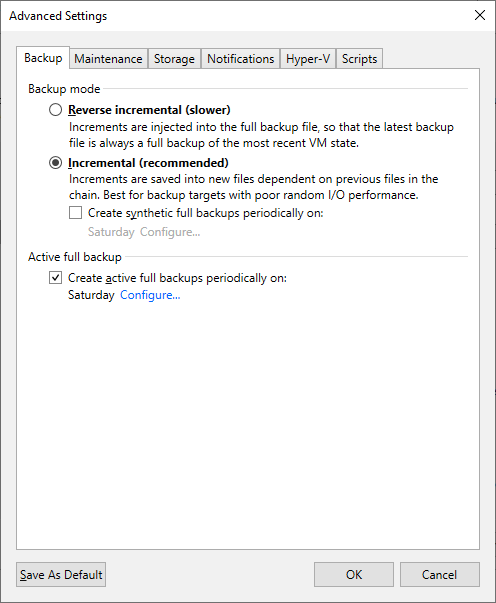
Figure 1: Enable the encryption feature on the deduplicating storage appliance.
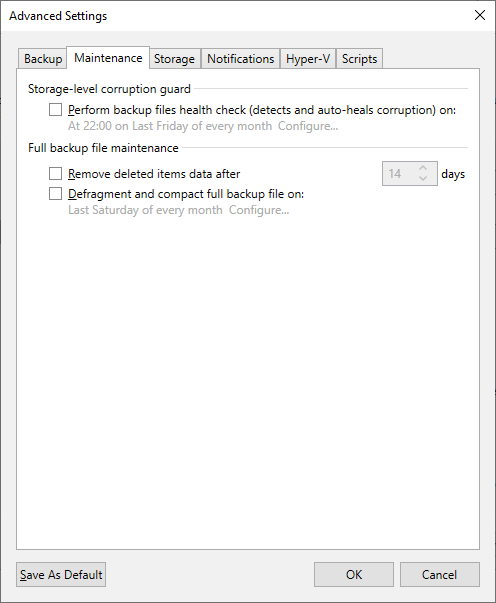
Figure 2: Set Maintenance Settings for Storage-level and Full backup
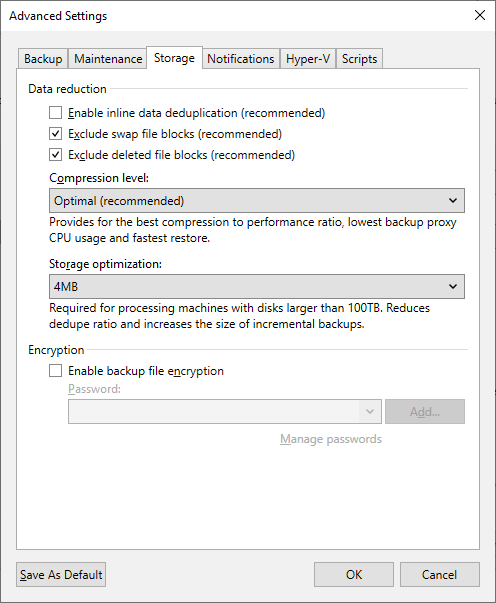
Figure 3: Set Data reduction, Compression level, and Storage optimization
From Veeam article kb1745, all Vendor-documented
 and Vendor-specific
and Vendor-specific  advice supersedes the advice below.
advice supersedes the advice below.
Backup Copy Job Settings
Backup Chain Settings
When targeting deduplicated storage, the backup copy job should be configured as follows to force the backup copy job to perform primarily write-only operations:
-
Keep certain full backups longer for archival purposes
-
Enabled and set to have at least 1 weekly
Enabling this option forces the backup copy job to enforce retention using the forward-incremental retention policy, which prevents the job from using the non-GFS retention method that involves merging the oldest increment into the full (a retention method known as Forever Forward Incremental). Forever Forward Incremental retention method is suboptimal for deduplication storage as it involves many small read and write operations to enforce retention.
-
-
Read the entire restore point from source backup instead of synthesizing it from increments
-
Enabled*
Enabling this option for local-to-local backup copy jobs being written to deduplication storage that does not support block cloning forces the job to perform strictly write-only operations to create the GFS full. Thereby avoiding unnecessarily taxing synthetic GFS full creation processing that involves creating the GFS full restore point by reading from previous restore points stored on the deduplication storage.
*This option should be disabled if:-
The backup copy job is transferring backups across a low-speed connection. Specifically, a link so slow that transferring the entire full to the destination would be slower than the job creating a full synthetically using data already present on the deduplication storage.
Some offsite connections may be fast enough to perform the full transfer faster than the synthetic creation process. It comes down to comparing the network throughput vs. the read+write speed of the deduplication storage. For example, if the connection used to reach the backup copy destination is 100 Mbps (12.5 MB/s), and the deduplication storage can create a synthetic full at 40 MB/s, the option should be disabled. However, if the connection is 500 Mbps (62.5 MB/s), that is faster than the deduplication storage in this example, so reading the entire restore point across the network would be quicker. -
The target deduplication appliance backup repository uses block cloning functionality.
Block cloning is available with integrated deduplication appliances (HPE StoreOnce Catalyst, Exagrid, Data Domain DDboost, and Quantum DXi)
-
-
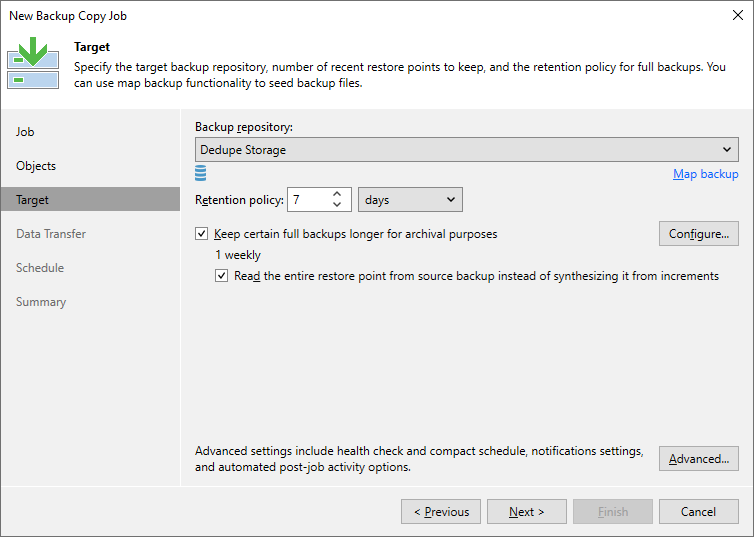
Figure 4: Specifiy the target backup repository, recent restore points, and retention policy.
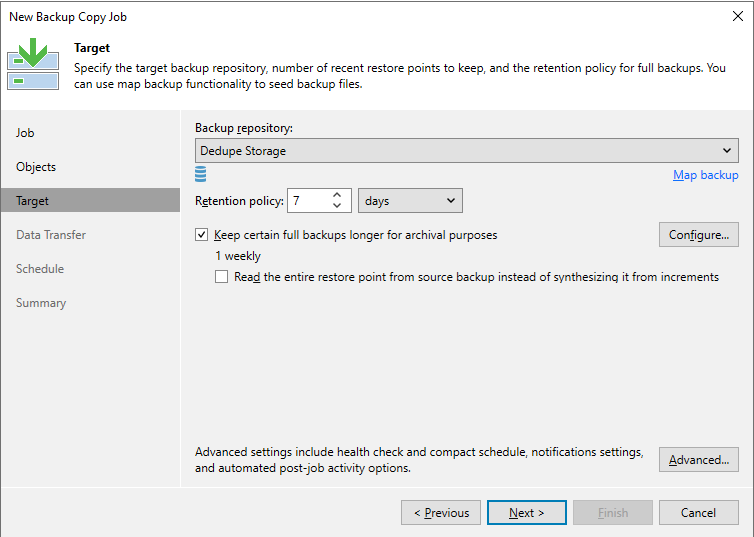
Figure 5: Remove option to read the entire restore point from source backup.
Advanced Settings
Below are the general recommendations for the Advanced Settings (Target > Advanced):
Maintenance Tab
-
Perform backup files health check
-
Disabled
While enabling this feature with deduplication storage is possible, it requires many read operations, which will take a very long time to complete. With larger backup files on deduplicated storage, this feature could cause a backup job to spend days performing the health check, causing the job to not create new restore points.
-
-
Defragment and compact full backup file
-
Disabled
There is no need for this option when Active Fulls are being created.
-
Storage Tab
-
-
Disabled
Disabling deduplication in Veeam Backup & Replication will cause the restore points to appear larger, but because Veeam does not deduplicate them, it allows the storage's deduplication function to be more effective.NOTE: Storage that uses a nondedupe zone for storing initially written files, such as ExaGrid's Landing Zone, may benefit from having Veeam's deduplication enabled to allow more restore points to be held in that rapid access state before being processed by the storage deduplication system.
-
-
-
Auto
The Repository settings section of this article advises enabling a function that will cause all restore points to be decompressed before being written. As such, the compression set at the job level will only impact data compression while backup data is being transferred across the network.
-
-
-
Disabled
Data encryption has a negative effect on the deduplication ratio if you use a deduplicating storage appliance as a target. Veeam Backup & Replication uses different encryption keys for every job session. For this reason, encrypted data blocks sent to the deduplicating storage appliances appear as different though they may contain duplicate data. If you want to achieve a higher deduplication ratio, you can disable data encryption. If you still want to use encryption, you can enable the encryption feature on the deduplicating storage appliance itself.
-
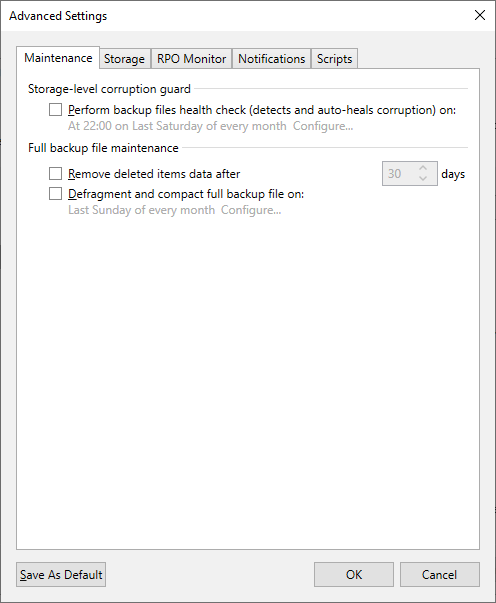
Figure 6: Set Maintenance Settings for Target Storage-level and Full backup
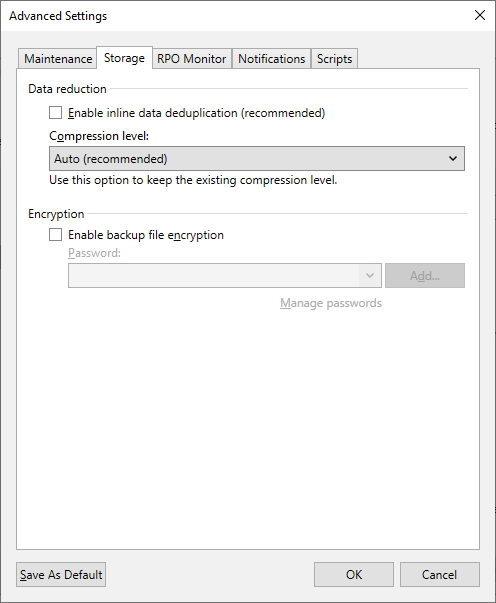
Figure 7: Set Target Data reduction, Compression level, and Storage optimization
Backup Repository Settings
From Veeam article kb1745, all Vendor-documented 

When creating a new Backup Repository 


The settings below are general advice for deduplication storage.
Storage Compatibility Settings 
Below are the general recommendations for the Storage Compatibility Settings (Repository > Advanced):
-
Align backup file data blocks
-
Enabled for deduplication storage that uses fixed block length deduplication or deduplication storage capable of block cloning.
-
Disabled for deduplication storage that uses variable length deduplication.
-
-
Decompress backup file data blocks before storing
-
Enabled for all deduplication storage that does not have a nondedupe landing zone.
Writing backup files to the deduplication storage that are uncompressed and undeduplicated by Veeam will allow the deduplication mechanisms within the storage to operate efficiently.
-
-
This repository is backed by rotated drives
-
Disabled
-
-
Use per-machine backup files
-
Enabled
-
Additional Information
Data Domain Boost Veeam All Simple Support Matrix
Data Domain Backup Software Veeam All Simple Support Matrix
Dell Data Domain Supported Features
The DD Boost technology offers a set of features for advanced data processing. Veeam Backup & Replication supports the following features:
- Distributed Segment Processing
- Advanced Load Balancing and Link Failover
- Virtual Synthetics In addition to these technologies, Veeam Backup & Replication supports in-flight data encryption and per storage unit streams.
Distributed Segment Processing
Distributed Segment Processing lets Dell Data Domain "distribute" the deduplication process and perform a part of data deduplication operations on the gateway server side. Without Distributed Segment Processing, Dell Data Domain performs deduplication on the Dell Data Domain storage system. The gateway server sends unfiltered data blocks to Dell Data Domain over the network. Data segmentation, filtering and compression operations are performed on the target side, before data is written to disk. With Distributed Segment Processing, operations on data segmentation, filtering and compression are performed on the gateway server side. The gateway server sends only unique data blocks to Dell Data Domain. As a result, the load on the network reduces and the network throughput improves.
Advanced Load Balancing and Link Failover
Advanced Load Balancing and Link Failover allow you to balance data transfer load and route VM data traffic to a working link in case of network outage problems. Without Advanced Load Balancing, every gateway server connects to Data Domain on a dedicated Ethernet link. Such configuration does not provide an ability to balance the data transfer load across the links. If a network error occurs during the data transfer process, the backup job fails and needs to be restarted. Advanced Load Balancing allows you to aggregate several Ethernet links into one interface group. As a result, Dell Data Domain automatically balances the traffic load coming from several gateway servers united in one group. If some link in the group goes down, Dell Data Domain automatically performs link failover, and the backup traffic is routed to a working link.
Virtual Synthetics
Veeam Backup & Replication supports Virtual Synthetic Fulls by Dell Data Domain. Virtual Synthetic Fulls let you synthesize a full backup on the target backup storage without physically copying data from source datastores. To construct a full backup file, Dell Data Domain uses pointers to existing data segments on the target backup storage. Virtual Synthetic Fulls reduce the workload on the network and backup infrastructure components and increase the backup job performance.
In-Flight Data Encryption
Veeam Backup & Replication supports in-flight encryption introduced in Dell Data Domain Boost 3.0. If necessary, you can enable data encryption at the backup repository level. Veeam Backup & Replication will leverage the Dell Data Domain technology to encrypt data transported between the DD Boost library and Da ta Domain system.
Per Storage Unit Streams
Veeam Backup & Replication supports per storage unit streams on Dell Data Domain. The maximum number of parallel tasks that can be targeted at the backup repository (the Limit maximum concurrent tasks to N setting) is applied to the storage unit, not the whole Dell Data Domain system.
Accelerated Restore of Entire VM
To speed up entire VM restore on Dell Data Domain, Veeam Backup & Replication uses the mechanism of sequential data reading from backups and parallel VM disks restore. Dell Data Domain storage systems are optimized for sequential I/O operations. However, data blocks of VM disks in backup files are stored not sequentially, but in the random order. If data blocks of VM disks are read at random, the restore performance from backups on Dell Data Domain degrades. To accelerate the restore process, Veeam Backup & Replication creates a map of data blocks in backup files. It uses the created map to read data blocks of VM disks from backup files sequentially, as they reside on disk. Veeam Backup & Replication writes data blocks to target in the order in which they come from the target Veeam Data Mover, restoring several VM disks in parallel. This accelerated restore mechanism is enabled by default, and is used for the entire VM restore scenario.
How Accelerated Restore Works
Entire VM restore from backups on Dell Data Domain is performed in the following way:
- Veeam Backup & Replication opens all backup files in the backup chain, reads metadata from these backup files and caches this metadata on the backup proxy that is assigned for the restore task.
- Veeam Backup & Replication uses the cached metadata to build a map of data blocks. The map contains references to VM data blocks, sorted by VM disks.
- Every VM disks is processed in a separate task. For every task, Veeam Backup & Replication starts a separate Veeam Data Mover on the backup proxy. Veeam Data Movers read data blocks of VM disks from the backup repository sequentially, as these blocks reside on disk, and put read data blocks to the buffer on the backup proxy.
- Data blocks are written to target in the order in which they come from the target Veeam Data Mover.
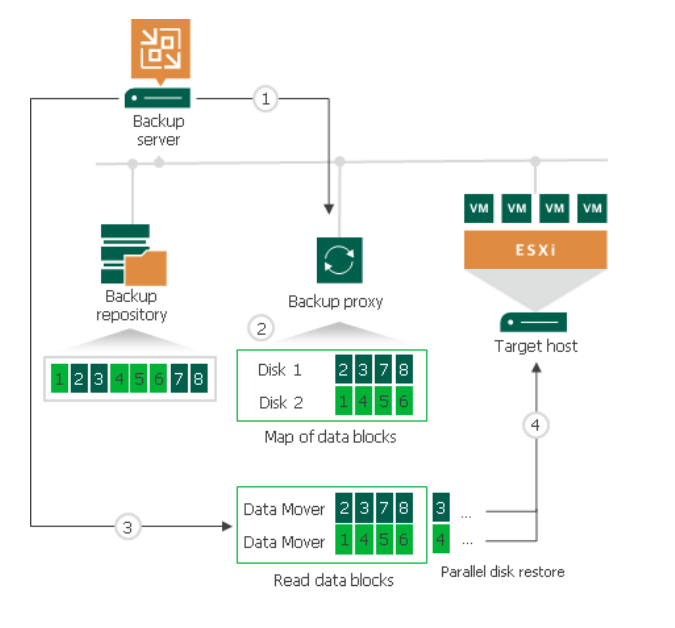
Figure 8: Workflow of how Accelerated Restore works
Backup Proxy for Accelerated Restore
Veeam Backup & Replication restores all disks of a VM through one backup proxy. If you instruct Veeam Backup & Replication to select a backup proxy for the restore task automatically, it picks the least loaded backup proxy in the backup infrastructure. If you assign a backup proxy explicitly, Veeam Backup & Replication uses the selected backup proxy. For every VM disk, Veeam Backup & Replication starts a separate Veeam Data Mover on the backup proxy. For example, if you restore a VM with 10 disks, Veeam Backup & Replication starts 10 Veeam Data Movers on the backup proxy. The backup proxy assigned for the entire VM restore task must have enough RAM resources to be able to restore VM disks in parallel. For every VM disk, 200 MB of RAM is required. The total amount of required RAM resources is calculated by the following formula: Total amount of RAM = Number of VM disks * 200 MB Before starting the restore process, Veeam Backup & Replication checks the amount of RAM resources on the backup proxy. If the backup proxy does not have enough RAM resources, Veeam Backup & Replication displays a warning in the job session details and automatically fails over to a regular VM disks processing mode (data of VM disks is read at random and VM disks are restored sequentially).
Limitations for Accelerated Restore
The accelerated restore of entire VM has the following limitations:
- Accelerated restore works on Dell Data Domain systems with DD Boost.
- If you restore a VM with dynamically expanding disks, the restore process may be slow.
- If you restore a VM using the Network transport mode, the number of VM disks restored in parallel cannot exceed the number of allowed connections to an ESXi host.
- If Dell Data Domain is added as an extent to a scale-out backup repository, you must set the backup file placement policy to Locality. If the backup file placement policy is set to Performance, parallel VM disk restore will be disabled.
Storage Appliances and Tapes
Storage appliances that are used to store backup data in filer (CIFS/NFS) or block device mode (iSCSI/FC/SAS) are not supported if the backup data is offloaded to tapes and is no longer stored directly on the filer/block device (Hierarchical Storage Management with Tape tier). To offload data to tapes, make sure that: • All of the backup data is stored on the appliance altogether (that is, all of the backup chains are stored on the appliance as a whole and not scattered across multiple devices) and only copies are stored on tapes. • These appliances emulate a tape system (VTL) as an access protocol for.
Dell Data Domain
- Dell Data Domain must meet software and hardware requirements. For more information, see System Requirements.
- The DD Boost license must be installed on the Dell Data Domain system, DD Boost must be enabled and configured.
- The gateway server that you plan to use for work with Dell Data Domain must be added to the backup infrastructure. If the Dell Data Domain storage system does not meet these requirements, you can add it as a SMB (CIFS) folder. In this case, Veeam Backup & Replication will not use the DD Boost technology to work with Dell Data Domain. For more information, see Dell Data Domain.
Step 1. Launch New Backup Repository Wizard
To launch the New Backup Repository wizard, do the following:
- Open the Backup Infrastructure view.
- In the inventory pane, right-click the Backup Repositories node and select Add Backup Repository. Alternatively, you can click Add Repository on the ribbon.
- In the Add Backup Repository window, select Deduplicating Storage Appliance and the type of the backup repository you want to add.
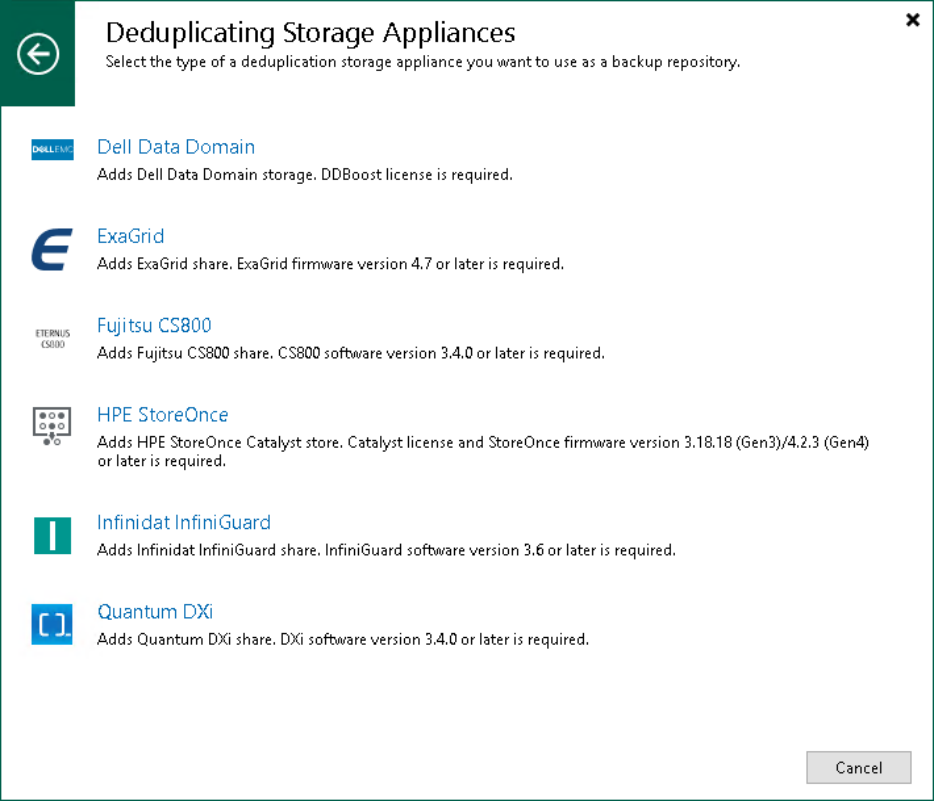
Figure 9: Launch new backup repository Wizard.
Step 2. Specify Backup Repository Name and Description.
At the Name step of the wizard, specify a name and description for the backup repository:
- In the Name field, specify a name for the backup repository.
- In the Description field, provide a description for future reference.
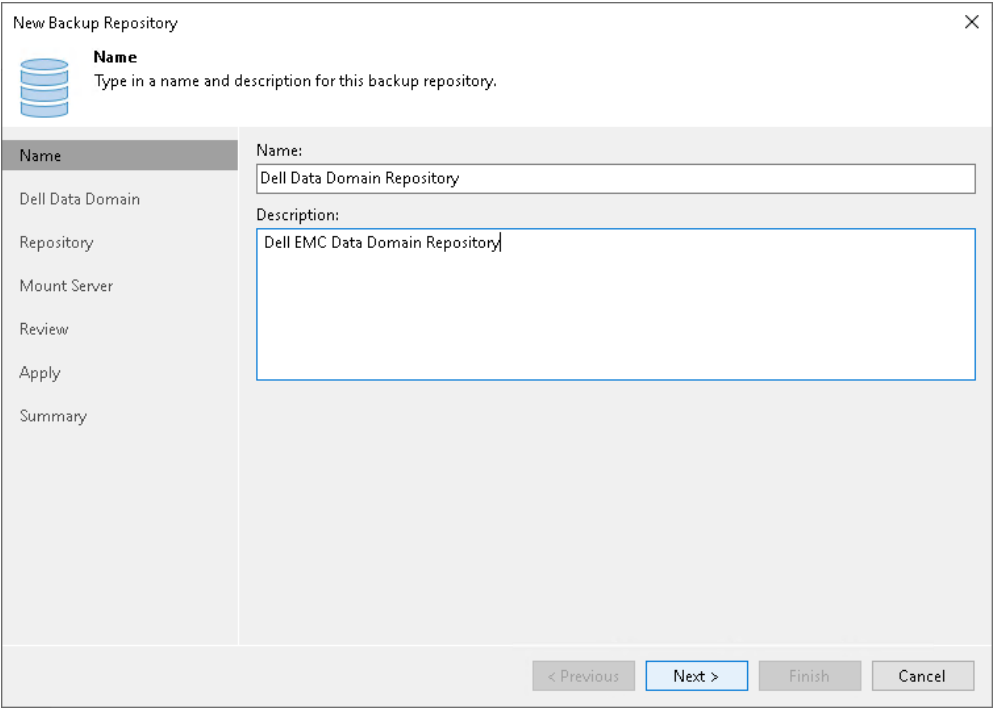
Figure 10: Specify the backup repository name and description.
Step 3. Specify Server Settings
Options that you can specify at the Server step of the wizard depend on the type of backup repository you are adding.
Dell Data Domain
To configure settings for Dell Data Domain:
- Specify connection settings for Dell Data Domain:
- If Dell Data Domain works over TCP, in the Type in Data Domain server name field, enter a full DNS name, or IPv4 or IPv6 address of the Dell Data Domain server.
 .
.
- If Dell Data Domain works over Fibre Channel, select the Use Fibre Channel (FC) connectivity check box. In the Type in Data Domain server name field, enter a name of the Data Domain Fibre Channel server. To get the Data Domain Fibre Channel server name, in Data Domain System Manager, open the Data Management > DD Boost > Fibre Channel tab.
- In the Credentials field, specify credentials of the user account to connect to the Dell Data Domain server or Dell Data Domain Fibre Channel server.

To connect to the Dell Data Domain server, you must use credentials for the DD Boost User.
To specify the DD Boost User account settings, in Data Domain System Manager, open the Data Management > DD Boost Settings tab.
- To use in-flight encryption between the backup proxy and Dell Data Domain, select the Enable DDBoost encryption check box and choose the encryption level - Medium or High.
- In the Gateway server field, specify which gateway server you want to use:
- If you want Veeam Backup & Replication to select a gateway server automatically, leave Automatic selection.
- If you want to select servers that can be used as gateway servers explicitly, click Choose next to the Gateway server field. In the Gateway Server window, click Use the following gateway servers only and select servers. The servers must have a direct access to the Dell Data Domain appliance and must be located as close to the appliance as possible. Veeam Backup & Replication will choose the most suitable server.

IMPORTANT
If you connect to Dell Data Domain over Fibre Channel, you must explicitly define the gateway servers to communicate with Dell Data Domain. The servers you select must be added to the backup infrastructure and must have access to the Dell Data Domain appliance over Fibre Channel.
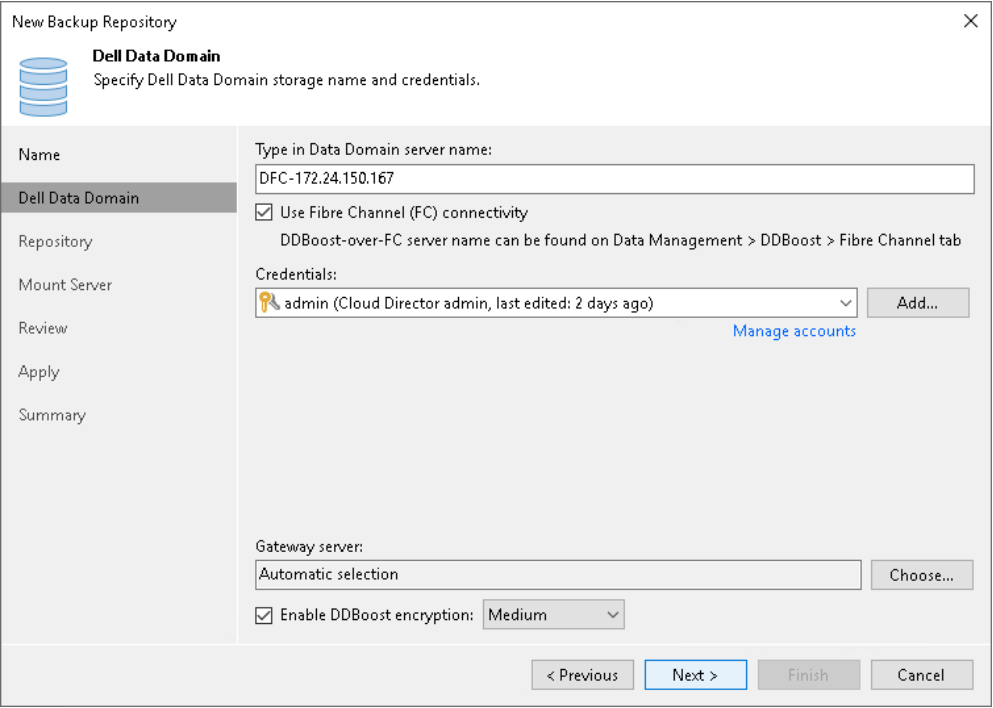
Figure 11: Using Fibre channel
Preconfigured Advanced Settings
Depending on the type of deduplicating storage appliance you use, Veeam Backup & Replication automatically sets advanced settings to the following ones:
Dell Data Domain
- The Align backup file data blocks option is disabled and cannot be changed.
- The Decompress backup data blocks before storing option is enabled.
- The This repository is backed by rotated hard drives option is disabled and cannot be changed.
- The Use per-machine backup files option is enabled.
Limitations for Performance Tier
Consider the following limitations for performance tier:
- The same limitations that are specific for certain types of backup repositories apply to the performance extents.
For example, if you add Dell Data Domain as a performance extent to the scale-out backup repository, you will not be able to create a backup chain longer than 120 points in this scale-out backup repository.
Ports
On backup infrastructure components, Veeam Backup & Replication automatically creates firewall rules for the required ports. These rules allow communication between the components.
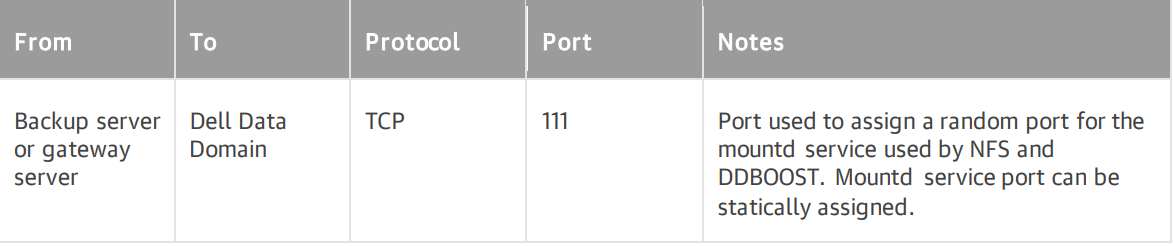
Figure 12: Automated firewall rules for TCP111
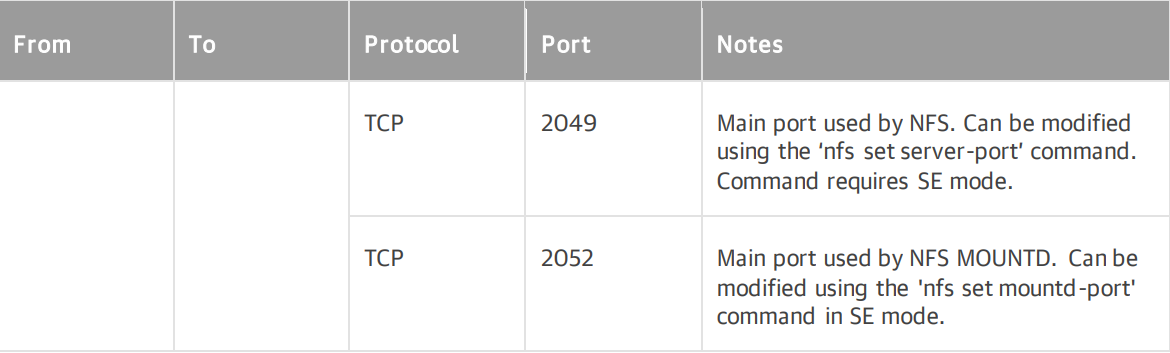
Figure 13: Automated firewall rules for TCPport2049 and 2052
Additional knowledge based articles for Veeam:
- Dell article 194977, Veeam Backup & Replication with PowerProtect DataDomain
- Dell article 197234, Data Domain Boost: The backups from VEEAM 11 or 11a running on Windows 2016 or 2019 to Data Domain using DDBOOST over IP may fail and Veeam may stop responding
Data Domain articles for using ifgroups for ddboost: