Best practices for data streams sent to DDOS 8.x Data Domain
Summary: This KB article provides information about official supported stream counts for data streams sent to DDOS 8.x Data Domain
Instructions
For optimal performance, Dell Technologies recommends limits on simultaneous streams between DD and your backup servers.
A data stream, in the context of the following table, refers to a large byte stream associated with sequential file access, such as a write stream to a backup file or a read stream from a restore image. A Replication source or destination stream refers to a replication operation or a DD Boost file replication stream that is associated with a file replication operation.
| Model | RAM/NVRAM | Backup write streams | Backup read streams | Repla source streams | Repla destination streams | Mixed |
| DD6300 | 48 GB or 96 GB / 8 GB | 270 | 75 | 150 | 270 | w<=270; r<=75; ReplSrc<=150; ReplDest<=270; ReplDest+w<=270; Total<=270 |
| DD6400 | 192 GB/ 16 GB | 270 | 75 | 150 | 270 | w<=270; r<=75; ReplSrc<=150; ReplDest<=270; ReplDest+w<=270; Total<=270 |
| DD6410 | 256 GB / 16 GB | 270 | 75 | 150 | 270 | w<=270; r<=75; ReplSrc<=150; ReplDest<=270; ReplDest+w<=270; Total<=270 |
| DD6800 | 192 GB / 8 GB | 400 | 110 | 220 | 400 | w<=400; r<=110; ReplSrc<=220; ReplDest<=400; ReplDest+w<=400; Total<=400 |
| DD6900 | 288 GB / 16 GB | 400 | 110 | 220 | 400 | w<=400; r<=110; ReplSrc<=220; ReplDest<=400; ReplDest+w<=400; Total<=400 |
| DD9300 | 192 GB or 384 GB / 8 GB | 800 | 220 | 440 | 800 | w<=800; r<=220; ReplSrc<=440; ReplDest<=800; ReplDest+w<=800; Total<=800 |
| DD9400 | 576 GB / 16 GB | 800 | 220 | 440 | 800 | w<=800; r<=220; ReplSrc<=440; ReplDest<=800; ReplDest+w<=800; Total<=800 |
| DD9410 | 768 GB / 32 GB | 800 | 220 | 440 | 800 | w<=800; r<=220; ReplSrc<=440; ReplDest<=800; ReplDest+w<=800; Total<=800 |
| DD9800 | 256 GB or 768 GB / 8 GB | 1885 | 300 | 540 | 1080 | w<=1885; r<=300; ReplSrc<=540; ReplDest<=1080; ReplDest+w<=1080; Total<=1885 |
| DD9900 | 1152 GB / 16 GB | 1885 | 300 | 540 | 1080 | w<=1885; r<=300; ReplSrc<=540; ReplDest<=1080; ReplDest+w<=1080; Total<=1885 |
| DD9910 | 2048 GB / 32 GB | 1885 | 300 | 540 | 1080 | w<=1885; r<=300; ReplSrc<=540; ReplDest<=1080; ReplDest+w<=1080; Total<=1885 |
| Dell APEX Protection Storage 8 TB | 8 GB / 512 MB | 20 | 16 | 20 | 20 | w<= 20; r<= 16 ReplSrc<=20; ReplDest<=20; ReplDest+w<=20; w+r+ReplSrc <=20;Total<=20 |
| Dell APEX Protection Storage 16 TB | 16 GB / 512 MB or 24 GB / 1 GB | 45 | 30 | 45 | 45 | w<= 45; r<= 30 ReplSrc<=45; ReplDest<=45; ReplDest+w<=45; w+r+ReplSrc <=45;Total<=45 |
| Dell APEX Protection Storage 32 TB | 24 GB / 1 GB | 90 | 50 | 90 | 90 | w<= 90; r<= 50 ReplSrc<=90; ReplDest<=90; ReplDest+w<=90; w+r+ReplSrc <=90;Total<=90 |
| Dell APEX Protection Storage 48 TB | 36 GB / 1 GB | 90 | 50 | 90 | 90 | w<= 90; r<= 50 ReplSrc<=90; ReplDest<=90; ReplDest+w<=90; w+r+ReplSrc <=90;Total<=90 |
| Dell APEX Protection Storage 64 TB | 48 GB / 1 GB | 90 | 50 | 90 | 90 | w<= 90; r<= 50 ReplSrc<=90; ReplDest<=90; ReplDest+w<=90; w+r+ReplSrc <=90;Total<=90 |
| Dell APEX Protection Storage 96 TB | 64 GB / 2 GB | 180 | 50 | 90 | 180 | w<= 180; r<= 50 ReplSrc<=90; ReplDest<=180; ReplDest+w<=180; w+r+ReplSrc <=180;Total<=180 |
| DD3300 4 TB | 12 GB (virtual memory) / 512 MB | 20 | 16 | 30 | 20 | w<= 20; r<= 16 ReplSrc<=30; ReplDest<=20; ReplDest+w<=20; w+r+ReplSrc <=30;Total<=30 |
| DD3300 8 TB | 32 GB (virtual memory) / 1.536 GB | 90 | 50 | 90 | 90 | w<= 90; r<= 50 ReplSrc<=90; ReplDest<=90; ReplDest+w<=90; w+r+ReplSrc <=90;Total<=90 |
| DD3300 16 TB | 32 GB (virtual memory) / 1.536 GB | 90 | 50 | 90 | 90 | w<= 90; r<= 50 ReplSrc<=90; ReplDest<=90; ReplDest+w<=90; w+r+ReplSrc <=90;Total<=90 |
| DD3300 32 TB | 46 GB (virtual memory) / 1.536 GB | 90 | 50 | 90 | 90 | w<= 90; r<= 50 ReplSrc<=90; ReplDest<=90; ReplDest+w<=90; w+r+ReplSrc <=90;Total<=140 |
a. DirRepl, OptDup, MTreeRepl streams
Streams support on DDVE On-prem / Cloud:
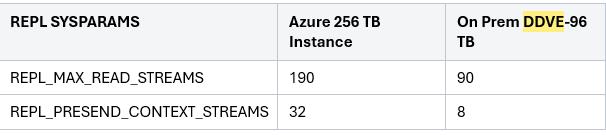
Additional Information
Background on DDR Streams
In general, a stream in this context refers to the byte-stream associated with a sequential file access. Referring to a large file being written for a backup or read for a restore (hence "write stream" and "read stream").
Also, there are two other types of streams referenced in the discussion below:
-
Managed File Replication stream -- associated with a file replication operation, also known as optdup (optimized duplication) in the Symantec NetBackup and BackupExec applications. This feature was introduced in DD OS release 4.7.
-
MTree Replication stream -- associated with a MTree replication context, while MTree replication is in progress. This feature was introduced in DD OS release 5.1
Although the use cases for these replication streams are different from the normal backup and restore operations, the stream resource utilization within the DDR is roughly equivalent to a read stream (for a source context) or a write stream (for a destination context).
The Supported Stream Count table referenced in below, represent the recommended limits for concurrent read and write streams. Exceeding these soft limits results in performance degradation (throughput and compression). Also, there is an internal hard limit that refers to the total number of streams that are supported by DDFS. The NFS server in DDFS recycles stream resources to remain under the hard limit. It is this recycling (or thrashing) of stream resources that is responsible for the steep performance decline when the hard limit is exceeded. The hard limit is 2x the soft limit. Stream thrashing occurs if the number of concurrent streams exceed the hard limit. Stream thrashing causes low (around 1mb/sec) performance, and reverse compression. When the file system detects stream thrashing, it generates the "Too many streams open" alert message.
As for replication streams, the Supported Stream Count table referenced in below use the term 'Repl streams' to refer to all types of replication streams (where applicable).
For MTree replication, the values in the Supported Stream Count table referenced in below indicates the maximum number of contexts that can be created. This is an enforced limit that cannot be exceeded. Sometimes, more MTree replication contexts are created than the read/write stream soft limit would dictate because replication utilization can be less demanding than backup and recover operations, and can oversubscribe beyond the soft limit offers greater replication density (such as in many-to-1 replication topologies).
For optdup (file replication) streams, the values in the Supported Stream Count table referenced in below are recommended limits, as described above for read and write streams counts.