RAID Made Simple: Complete Guide for Dell Systems
Summary: Complete guide to RAID on supported Dell computers. Learn RAID 0 vs RAID 1, setup steps, supported models, troubleshooting tips & FAQs for supported Dell systems.
Instructions
Are you looking to boost your Dell system's storage performance or add data protection? RAID might be exactly what you need. This comprehensive guide walks you through everything about RAID on supported Dell systems—from the basics to troubleshooting common issues.
Understanding RAID: What It Is and Why It Matters
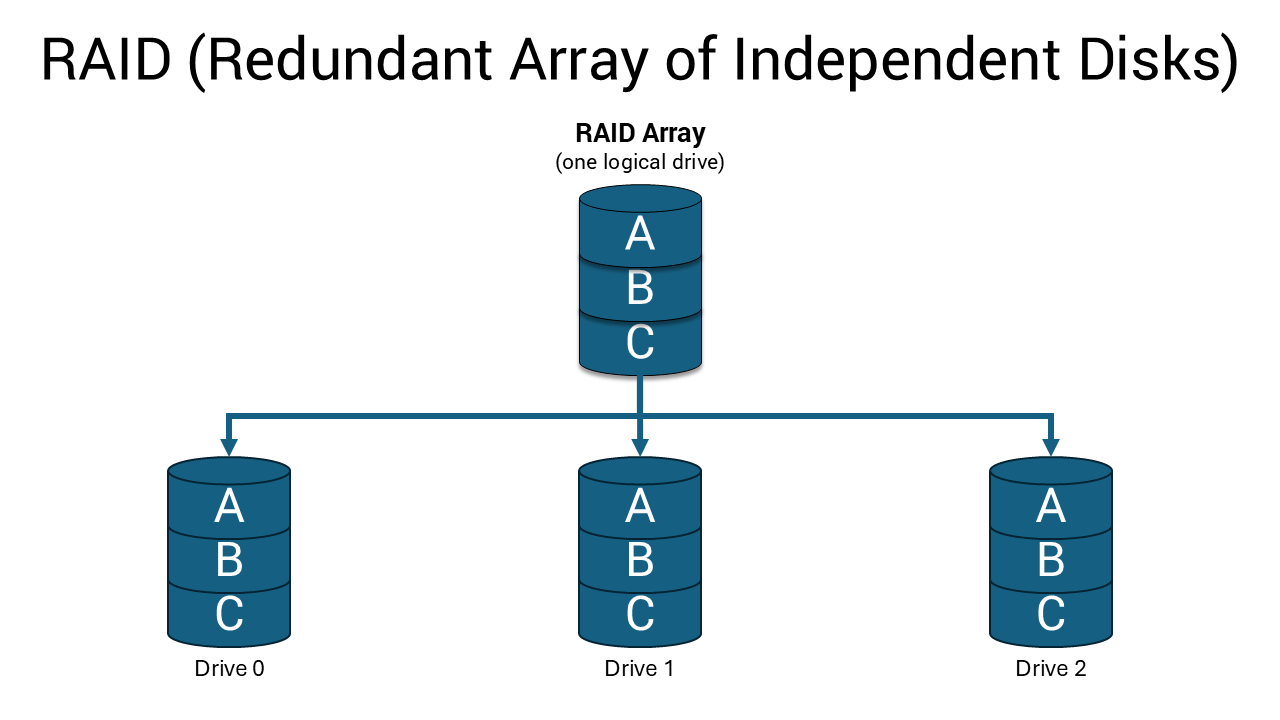
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) combines multiple storage drives into a single logical unit. Think of it as teamwork for your storage drives—they work together to either speed up your system, protect your data, or both.
When you set up RAID, your computer treats multiple physical drives as one drive. This setup can dramatically improve performance, provide data backup protection, or deliver both benefits depending on which RAID level you choose.
Tutorial on Introduction of RAID concepts
Duration: 00:01:27 (hh:mm:ss)
When available, closed caption (subtitles) language settings can be chosen using the CC icon on this video player.
Why Choose RAID for Your Dell System?
RAID offers several compelling advantages:
- Performance boost: RAID 0 can significantly speed up file transfers and application loading times by splitting data across multiple drives.
- Data protection: RAID 1 creates an exact copy of your data on a second drive, so you're protected if one drive fails.
- Improved reliability: With RAID 1, your system keeps running even when one drive stops working.
- Enterprise capabilities: Higher-end Dell workstations support advanced RAID levels for professional applications.
RAID Types Explained: Finding the Right Fit
Dell systems support different RAID configurations depending on the model and target use case.
Understanding RAID Levels
Duration: 00:03:34 (hh:mm:ss)
When available, closed caption (subtitles) language settings can be chosen using the CC icon on this video player.
RAID 0: Maximum Performance
RAID 0 stripes (distributes evenly) your data across two or more drives, allowing them to work simultaneously. When you save a file, pieces go to different drives at the same time, making read and write operations much faster. However, any I/O operations with block sizes larger than the stripe size splits the I/O and become constrained by the slowest of the drives.
Benefits:
- Significantly faster data transfer speeds
- Maximum use of available drive space
- Ideal for performance-intensive applications
Considerations:
- No data protection—if one drive fails, you lose everything
- Performance variability can be problematic for applications that are latency sensitive, particularly with small random write operations

RAID 1: Complete Data Protection
RAID 1 (mirroring) creates an identical copy of everything on two drives. Every file you save gets written to both drives simultaneously, creating a perfect mirror. All I/O operations must be performed identically to both drives, thus variations in drive performance when the models are different result in the I/O operations completing only as fast as the slowest drive.
Benefits:
- Complete data redundancy—if one drive fails, your data remains safe
- System continues running normally with just one working drive
- Perfect for important documents, business data, and irreplaceable files
Considerations:
- Uses only half of your total drive capacity for storage
- Performance limited by the slower drive in mismatched pairs

Advanced RAID Levels
Some Dell workstations may support additional RAID configurations:
- RAID 5: Requires at least three drives, provides fault tolerance of one drive failure with distributed parity
- RAID 10: Combines RAID 0 and 1 benefits but needs four drives minimum
- RAID 6: Offers dual parity protection for mission-critical applications, can handle two simultaneous drive failures
These advanced levels are typically found on Dell Precision workstations with dedicated RAID controllers.

Tutorial on Understanding Parity
Duration: 00:03:34 (hh:mm:ss)
When available, closed caption (subtitles) language settings can be chosen using the CC icon on this video player.
Important RAID Limitations
Intel Optane Compatibility: RAID is not supported on Intel Optane configurations across Dell systems.
Drive Matching Requirements: For optimal performance when configuring drives as a RAID volume, Dell Technologies recommends drive models that are identical. Care must be taken to match not only the drive vendor, capacity, and class, but also the specific model.
Choosing the Right RAID for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate RAID configuration depends on your priorities and how you use your Dell system.
Choose RAID 0 When You Need:
- Maximum performance for gaming or content creation
- Fast file transfers for large media files
- Quick application loading and system responsiveness
- Full use of your drive capacity
Best for: Content creators, developers, and users with separate backup strategies.
Choose RAID 1 When You Need:
- Data protection for important files
- System reliability for business use
- Peace of mind knowing your data is safe
- Continued operation if a drive fails
Best for: Business users, professionals with critical data, and anyone who values data security over maximum performance.
System Requirements and Compatibility
Before setting up RAID, verify that your specific Dell model supports it:
- Check Dell Support: Visit Dell Manuals and enter your service tag or express service code
- Review system specifications: Look for RAID support in the technical specifications
- Verify drive requirements: Ensure you have the appropriate number and type of drives
Hardware Requirements:
- Two or more identical drives (same capacity, model, and preferably manufacturer)
- Available drive bays or M.2 slots
- BIOS/UEFI support for RAID configuration
- Compatible RAID controller (built-in or add-in card)
What is a RAID Controller?
A RAID controller manages multiple hard drives, making them work together as one logical drive.
Types of RAID Controller
Two types of RAID controller:
Hardware-based RAID
Uses a dedicated physical controller to manage hard drive.
- Offers high speed and reliability
- Can work independently from the system's processor
- Often built into the motherboard or as a separate card
Software-based RAID
Uses the system's processor and memory to manage RAID.
- No special hardware required
- Cost-effective, but may reduce overall system performance
- Slower than hardware RAID
Setting Up RAID: Step-by-Step Instructions
RAID setup procedures vary depending on your Dell system model and controller type.
Before You Begin
Warning: Setting up RAID will erase all data on the drives involved. Back up any important data before proceeding.
- Ensure you have two or more identical drives installed in your Dell system
- Verify all drives are properly connected with SATA data and power cables
- Have your Windows installation media ready
Standard Intel-Based Systems
Configure SATA Mode in BIOS/UEFI:
- Restart your computer and press F2 during startup to enter BIOS/UEFI setup
- Navigate to Storage or System Configuration settings
- Find the SATA Operation mode and change it from AHCI to RAID
- Save changes and exit UEFI setup (typically F10)
- Restart the computer
Create RAID Array (Legacy BIOS Systems):
- Press Ctrl + I during startup when you see the Intel Rapid Storage Technology prompt
- Select "Create RAID Volume" from the menu
- Enter a name for your RAID volume
- Choose RAID level (RAID 0 for performance, RAID 1 for protection)
- Select the drives to include in the array
- Set stripe size (128KB recommended for most users)
- Confirm configuration and wait for completion
Create RAID Array (UEFI Systems):
- Press F12 during startup at the Dell splash screen
- Select "Device Configuration" from the pre-boot menu
- Choose "Create RAID Volume" and press Enter
- Select RAID level using + key to toggle options
- Mark drives by highlighting and pressing Enter, then typing "X"
- Select "Create Volume" and confirm the configuration
- Wait for array creation to complete
AMD-Based Precision Workstations
For systems like the Precision T7875 Tower with AMD processors:
- Enter BIOS setup by pressing F2 during startup
- Navigate to storage configuration settings
- Enable RAID mode for the appropriate controller
- Save and restart the system
- Use AMD RAIDXpert2 utility to create and manage RAID arrays
- Follow the on-screen prompts to configure your desired RAID level
Systems with Dedicated RAID Controllers
For Precision workstations with Broadcom MegaRAID controllers:
- Access RAID BIOS using the appropriate key combination (typically Ctrl + H)
- Use the MegaRAID configuration utility to create virtual drives
- Configure RAID level, stripe size, and other parameters
- Initialize the virtual drive and proceed with OS installation
Install Your Operating System
- Insert Windows installation media and restart the computer
- Boot from installation media (press F12 to select boot device)
- Proceed with Windows installation normally
- Select your RAID volume when prompted to choose a drive
- Complete installation as usual
Monitoring and Maintaining Your RAID Array
Regular monitoring keeps your RAID array running smoothly and alerts you to potential issues.
Install Management Software
- Intel Rapid Storage Technology: For Intel-based systems, download and install the Intel RST application from Dell Support. This software provides real-time monitoring, performance statistics, and automatic notifications.
- AMD RAIDXpert2: For AMD-based systems, use the AMD RAIDXpert2 utility for comprehensive RAID management and monitoring.
- MegaRAID Storage Manager: For systems with dedicated Broadcom controllers, install the appropriate management software for advanced monitoring capabilities.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
- Monitor drive health: Check management software monthly for warning signs or error messages.
- Keep drivers updated: Install driver updates as they become available to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
- Plan for drive replacement: Consider proactively replacing drives every 3-5 years to prevent simultaneous failures in RAID 1 configurations.
- Maintain separate backups: Even with RAID 1 protection, maintain backups of critical data on external drives or cloud storage.
Troubleshooting Common RAID Issues
Even with proper setup, you might encounter issues with your RAID configuration.
RAID Array Not Detected
Symptoms: BIOS doesn't show RAID options, or Windows doesn't detect the array.
Solutions:
- Check drive connections: Ensure all SATA data and power cables are securely connected
- Verify RAID mode: Confirm BIOS is set to RAID mode, not AHCI
- Update BIOS: Download and install the latest BIOS version from Dell Support
- Check drive compatibility: Ensure drives are identical models with matching performance characteristics
Degraded RAID 1 Array
Symptoms: System warns about drive failure or degraded array status.
Solutions:
- Identify the failed drive: Use your RAID management software to check drive status
- Replace the failed drive: Install an identical drive in the same location
- Rebuild the array: The system should automatically start rebuilding the mirror
- Monitor the rebuild process: This can take several hours depending on drive capacity
Poor RAID 0 Performance
Symptoms: Expected performance boost isn't noticeable.
Solutions:
- Verify drive matching: Ensure both drives are identical models to avoid performance constraints from the slowest drive
- Check stripe size: 128KB works well for most applications
- Update storage drivers: Download latest drivers from Dell Support
- Monitor application workload: RAID 0 performance benefits vary depending on I/O block sizes and access patterns
Boot Issues After RAID Setup
Symptoms: Computer won't boot or shows "No operating system found."
Solutions:
- Check boot order: Ensure RAID volume is first in boot priority
- Verify RAID mode: Confirm SATA Operation is still set to RAID mode
- Check array status: Use F12 > Device Configuration (UEFI) or management software to verify array health
- Repair boot files: Use Windows installation media to access repair tools
- Reinstall Windows: If other solutions fail, a clean installation might be necessary
Model-Specific Instructions and Additional Resources
While this guide covers general RAID setup procedures, your specific Dell model might have unique requirements or additional features. For detailed, model-specific instructions:
- Visit Dell Support at support.dell.com
- Enter your service tag or select your model
- Download your system's user manual from the manuals & documents section
- Check for model-specific RAID guides in the support articles
Your user manual contains detailed instructions, exact BIOS menu locations, and any special considerations for your particular Dell system.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which Dell systems support RAID?
Answer: RAID support varies significantly by model and is not available on all Dell systems. For example, OptiPlex 7010 does not support RAID while OptiPlex 9010 does, even though they share similar chipsets. Generally, higher-end business systems like specific OptiPlex models, Precision workstations, and servers include RAID support. Mobile workstations like the Precision 5570 support RAID with multiple drive configurations. Always check your specific model's specifications on Dell Support.
2. Can I convert my existing single drive to RAID without losing data?
Answer: No, setting up RAID requires formatting the drives involved, which erases all existing data. You must back up your data to an external drive or cloud storage before configuring RAID. After setting up the RAID array, you can restore your data from the backup. This limitation exists because RAID fundamentally changes how data is stored and accessed across the drives.
3. What happens if one drive fails in RAID 1?
Answer: In RAID 1, if one drive fails, your system continues running normally using the remaining drive. You'll receive warnings about the degraded array status, but all your data remains accessible. You should replace the failed drive as soon as possible with an identical model and allow the system to rebuild the mirror. During rebuilding, your data is vulnerable because there's only one copy, so avoid intensive disk operations until the rebuild completes.
4. Why do I need identical drives for RAID?
Answer: Dell Technologies strongly recommends identical drive models for optimal RAID performance. In RAID 0, mismatched drives can cause I/O operations to be constrained by the slowest drive, leading to variable latencies. In RAID 1, all operations must complete on both drives, so performance is limited to the slowest drive in the array. Using identical drives ensures consistent performance and eliminates compatibility issues.
5. Can I use RAID with Intel Optane memory?
Answer: No, RAID is not supported on Intel Optane configurations. If you have an Intel Optane-equipped system, you cannot configure the storage drives in a RAID array. This is a hardware limitation that applies across Dell systems.
6. What RAID levels does my Dell system support?
Answer: Most Dell consumer and business systems support RAID 0 and RAID 1. Higher-end Precision workstations may support additional levels like RAID 5 and RAID 10, especially when equipped with dedicated RAID controllers. The exact RAID levels available depend on your specific model and hardware configuration. Check your system's documentation for definitive information about your model's capabilities.
7. How do I know if my RAID array is healthy?
Answer: Use the appropriate management software for your system: Intel Rapid Storage Technology for Intel-based systems, AMD RAIDXpert2 for AMD systems, or MegaRAID Storage Manager for systems with dedicated controllers. These applications provide real-time monitoring of drive health, performance metrics, and alert notifications. You can also check array status through BIOS/UEFI setup or the F12 Device Configuration menu on UEFI systems.
8. Can I use RAID with NVMe SSD drives?
Answer: Yes, some current Dell systems support RAID configurations with NVMe SSD drives. The Precision 5570, for example, supports RAID with multiple drive configurations including NVMe drives. NVMe RAID can provide excellent performance benefits, especially in RAID 0 configurations. However, ensure your system's M.2 slots and chipset support NVMe RAID before attempting configuration.
9. What should I do if my system doesn't have RAID options in BIOS?
Answer: Some Dell models, like the OptiPlex 7010, do not include RAID support in their BIOS by design. This is a hardware limitation that cannot be overcome with software updates. If RAID functionality is critical for your needs, you may need to upgrade to a different Dell model that supports RAID or consider an external RAID solution.
10. My Dell system has multiple drive bays or slots - does this mean it supports RAID?
Answer: No, having multiple drive bays or M.2 slots does not guarantee RAID support. RAID functionality requires specific BIOS/UEFI support and compatible storage controllers, which vary by model. For example, the Precision 5680 has multiple drive M.2 slots but no RAID support in its BIOS by design, while the similar Precision 5570 includes full RAID functionality. Many Dell systems can accommodate multiple drives for separate storage volumes without RAID capabilities. Always verify RAID support in your system's specifications on Dell Support before purchasing additional drives for RAID configuration.
11. How long does it take to rebuild a RAID 1 array?
Answer: RAID 1 rebuild time depends on drive capacity and system performance. For modern drives, expect several hours for the rebuild process. A 1TB drive might take 2-4 hours, while larger drives can take 8-12 hours or more. During rebuild, system performance may be reduced, and the array is vulnerable since only one copy of data exists. Avoid intensive disk operations and ensure the system remains powered on until rebuild completion.