How To Un-Remove devices from Dell Data Security Server
Summary: This article discusses how to unremove a device from Dell Security Management Server and Dell Security Management Server Virtual.
Instructions
Affected Products:
- Dell Data Security Management Server
- Dell Data Protection | Enterprise Edition
- Dell Data Security Management Server Virtual
- Dell Data Protection | Virtual Edition
If a device is not available in the Dell Security Management Server (formerly Dell Data Protection | Enterprise Edition) or Dell Security Management Server Virtual (formerly Dell Data Protection | Virtual Edition) management console, the device may have been manually marked as removed or it could have exceeded the Device Lease Period policy, which is 30 days, by default.
Devices that are marked as removed are viewable in the Dell Security Management Server or Dell Security Management Server Virtual management console, the device entity can be updated in the database to mark the device as not removed.
Dell Data Security leverages devices that are based on their "Entity" that is mapped inside the database. These devices can become removed if they do not check into the server within the Device lease period that is defined in the server policy. The policy that controls this is the "Device Lease Period" that can be set globally for all products. When this elapses, the device is marked as "Removed" which is a flag that each entity contains in the Dell Data Security database. The following article details how to identify if a specific device has been marked as removed, and how to unremove that device.
Dell Security Management Server
Windows:
- Connect to the Dell Security Server database, using Microsoft Management Studio:
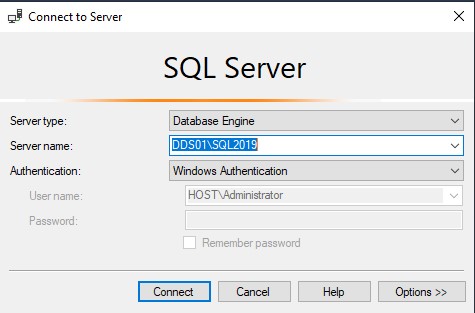 Note: In the example, the SQL Server is DDS01 with an instance named SQL2019. Windows Authentication of the logged in user is being used to access the Management Studio.
Note: In the example, the SQL Server is DDS01 with an instance named SQL2019. Windows Authentication of the logged in user is being used to access the Management Studio. - Once logged into the Management Studio, select the database from the column on the left side.
- Select the database from the column on the left side.
- Identify the endpoint using the hostname, if available.
Select * from entity where displayname like '%<HostName>%' and EntityType=5
Note: <hostname> can be a substring of the fully qualified hostname. For example, if looking for a machine with the hostname of 'DESKTOP-4I66T99.domain.com', then a substring of '%T99%' can be used to help narrow down the results.
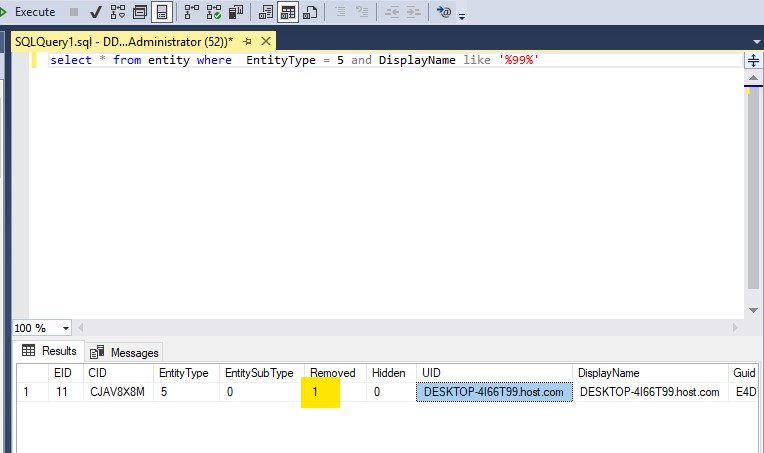 Note: The Removed flag = '1'
Note: The Removed flag = '1' - Update the removed flag with the following command:
update Entity set removed = 0 where DisplayName = '<HostName>'and Removed = 1
- This un-removes the endpoint, and it is visible in the RMC.
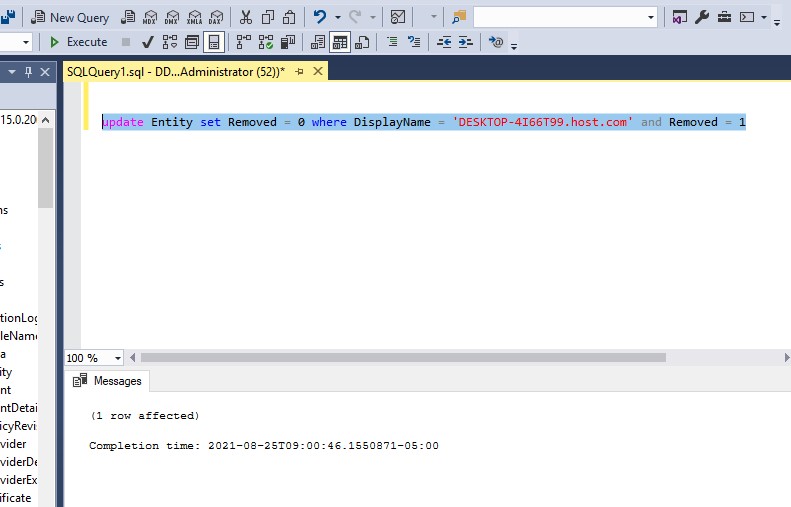
- This un-removes the endpoint, and it is visible in the RMC.
- Verify that the change has been made reselecting the machine from the Entity table and verifies the 'Removed' flag.
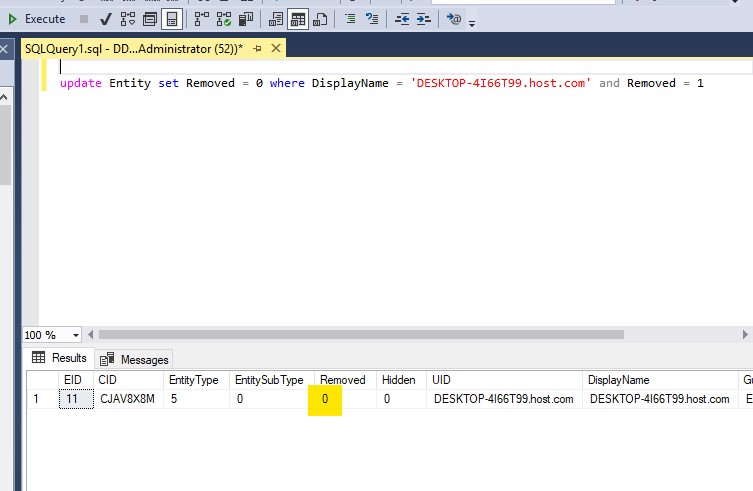
- In the Management Console, the endpoint is available now.
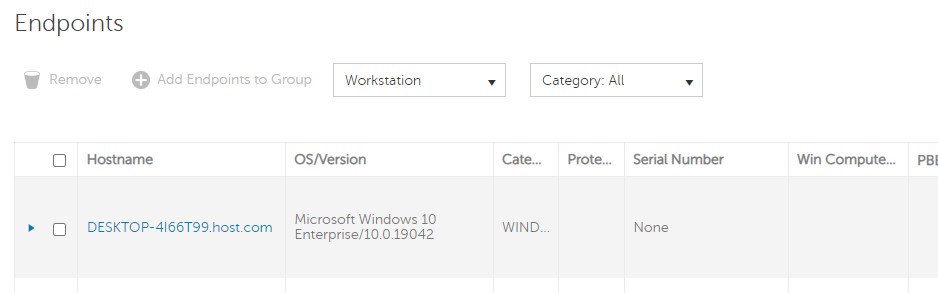
Dell Security Management Server Virtual
Dell Security Management Server Virtual using pgAdmin
- Open the pgAdmin tool and connect to the Dell Security Management Server Virtual database.
- If pgAdmin cannot connect to the database, then one step in troubleshooting this would be to verify database access on the Dell Security Management Server.
Note: For more information about Enabling Remote Database access, reference How to Enable Remote Database Access to Dell Security Management Server Virtual / Dell Data Protection Virtual Edition.
- If pgAdmin cannot connect to the database, then one step in troubleshooting this would be to verify database access on the Dell Security Management Server.
- Begin by opening a new query on the DDP database within pgAdmin.
- This can be done by selecting the database and clicking the SQL magnifying glass icon. For more information about connecting to the database with pgAdmin, see Dell Data Protection | Virtual Edition Accessing the Postgres database using pgAdmin.
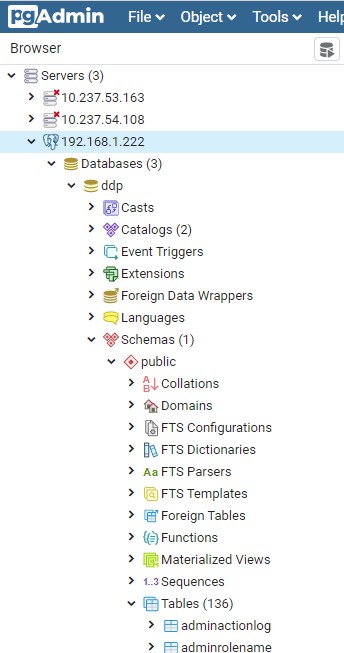
- This can be done by selecting the database and clicking the SQL magnifying glass icon. For more information about connecting to the database with pgAdmin, see Dell Data Protection | Virtual Edition Accessing the Postgres database using pgAdmin.
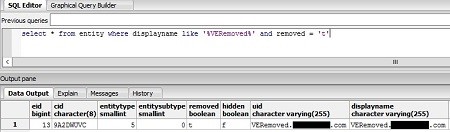
- Next, we identify the endpoint in the database and ensure that it is showing removed using this command:
- Open the Query Tool… by right-clicking the DDP database to get to the menu where Query Tool is available.
Note: Commands are case-sensitive.

select * from entity where displayname like '%<HostName>%'
- Open the Query Tool… by right-clicking the DDP database to get to the menu where Query Tool is available.
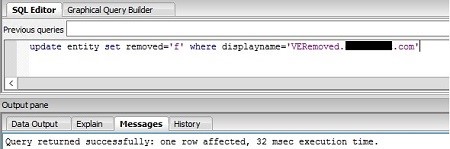
- Now, change the status of the endpoint to not removed:
update entity set removed='f' where displayname='<HostName>'
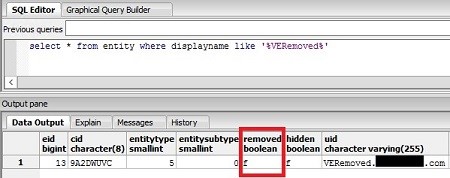
- Finally, verify that the status now shows correctly:
select * from entity where displayname like '%<HostName>%'
Dell Security Management Server Virtual using PSQL Command Line
The process to update the Dell Data Security database on a Dell Security Management Server Virtual appliance is:
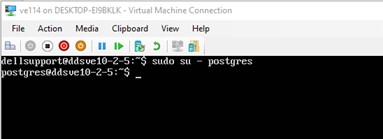
- Log in to the Dell Security Management Server Virtual appliance using the
dellsupportuser.
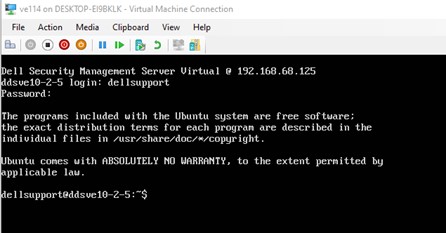
This opens a bash shell for interactive commands. - Su to the postgres user
CmD: sudo su - postgres
- Locate the endpoint to set as un-removed in the entity table in the ddp database.
Cmd: psql -d <database> -c”select * from entity where uid like ‘%<hostname identifier>%’”
Example:psql -d ddp -c”select * from entity where uid like ‘%win10%’”
Note:- Single quotes around the hostname
qto exit from the SQL command output
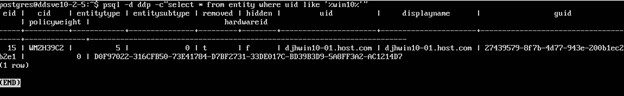
The removed field is a Boolean, and contains either t (true) or an f (false).Note: The removed field in the example is t (true). - Update the removed column in the database for the target endpoint.
Cmd: psql -d <database> -c”update <table> set <column> = <value> where uid like ‘%<hostname identifier>%’”
Example:
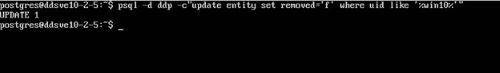
psql -d ddp -c”update entity set removed=’f’ where uid like ‘%win10%’”
- Exit from the bash shell
To contact support, reference Dell Data Security International Support Phone Numbers.
Go to TechDirect to generate a technical support request online.
For additional insights and resources, join the Dell Security Community Forum.