VMware: Debugging ESXi MCE PSOD
Summary: How to debug the ESXi Machine Check Exception (MCE) purple diagnostic screen (PSOD) with an example.
Instructions
ESXi servers may stop with a purple diagnostic screen (PSOD) due to Machine Check Exception (MCE) errors. MCE errors are due to hardware issues.
The MCE purple diagnostic screen displays multiple items. Out of these, the MCi_STATUS register is useful in debugging the issue.
Register Details:
- The
MCi_STATUSregister consists of information about the machine check error. - The register is displayed next to the "
S:" As shown in the example below:
MC: PCPU18 B:13 S:0xfe20004000011166 M:0x7246040086 A:0x38c989b100 5
Bits and their significance:
| 63 | 62 | 61 | 60 | 59 | 58 | 57 | 53-56 | 38-52 | 32-37 | 16-31 | 0-15 |
| VALID flag - If set, then information is valid. | OVERFLOW flag - If set, then may indicate multiple MCEs occurred close to each other. | UNC flag- If set, then CPU could not correct the error. | EN flag | MISCV flag - If set, then MISC register contains more information. | ADDRV - If set, then the ADDR register contains where the error occurred. | PCC flag- If set, then it means that the processor may have been corrupted. | Architectural if bit 11 is set, else "other information." | Architectural if bit 10 is set, else "other information." | Other information | Model-specific error code for CPU | Machine check error code |
To debug the error, the low 16 bits of the MCi_STATUS register are important. These bits indicate a simple or compound error.
Option 1: Using Automatic Tool
VMware Purple Diagnostic Screen (PSOD) Error Reader

Option 2: Using Manual Steps
- Simple errors are quick to debug
0000 0000 0000 0000 -- No Error reported to this bank of error-reporting registers. 0000 0000 0000 0001 -- Unclassified - Error has not been classified. 0000 0000 0000 0010 -- Parity error in internal microcode ROM. 0000 0000 0000 0011 -- External error-BINIT# from another processor caused this processor MCE. Happens only if BINIT# observation enabled during power on. 0000 0000 0000 0100 -- Functional redundancy check master/slave error. 0000 0000 0000 0101 -- Internal parity error. 0000 0000 0000 0110 -- SMM handler tried to execute outside the ranges specified by SMRR. 0000 0100 0000 0000 -- Internal timer error. 0000 1110 0000 1011 -- I/O error. 0000 01xx xxxx xxxx -- Internal unclassified error. Atleast one X must be equal to 1.
- Compound errors
000F 0000 0000 11LL - Generic Cache Hierarchy error.
000F 0000 0001 TTLL - {TT}TLB{LL}_ERR. TLB errors.
000F 0000 1MMM CCCC - {MMM}_Channel{CCCC}_ERR - Memory controller errors.
000F 0001 RRRR TTLL - {TT}CACHE{LL}_{RRRR}_ERR - Cache Hierarchy errors.
000F 1PPT RRRR IILL - BUS{LL}_{PP}_{RRRR}_{II}_T_ERR - Bus and Interconnect errors.
- F - Form flag
0 – Normal Filtering 1 – Corrected Filtering
Filtering means that some or all the subsequent corrections to this entry in this structure are not posted.
- TT - Applies to 2 and 4 above.
Indicates type of transaction:
00 - Instruction 01 - Data 10 - Generic
- LL - Applies to 1, 2, 4 and 5 above.
This indicates the level in the memory hierarchy where the error occurred.
00 - Level 0 - L0 01 - Level 1 - L1 10 - Level 2 - L2 11 - Generic – LG (It is shown only when processor cannot determine the hierarchy level)
- RRRR - Indicates the type of action associated with the error. The actions are:
0000 - Generic Error - ERR 0001 - Generic Read - RD 0010 - Generic Write - WR 0011 - Data Read - DRD 0100 - Data Write - DWR 0101 - Instruction Fetch - IRD 0110 - Prefetch - PREFETCH 0111 - Eviction - EVICT 1000 - Snoop - SNOOP
- PP (Participation) - Describes the role of the local processor in the error.
00 - SRC - Local processor originated request 01 - RES - Local processor responded to request 10 - OBS - Local processor observed error as third party 11 - Generic
- T (Time-out) - 1 = Request timed out.
- II (Memory or I/O)
00 - M - Memory Access 10 - IO - I/O 01 - Reserved 11 - Other transaction
- Memory Controller errors - Defined by MMM and CCCC subfields above
- MMM - Memory error
000 - GEN - Generic undefined request 001 - RD - Memory read error 010 - WR - Memory write error 011 - AC - Address/Command error 100 - MS - Memory Scrubbing error 101-111 - Reserved
- CCCC - Channel with the error
0000-1110 - CHN - Channel number 1111 - Channel not specified
Here is an example of how to analyze an MCE purple diagnostic screenshot:
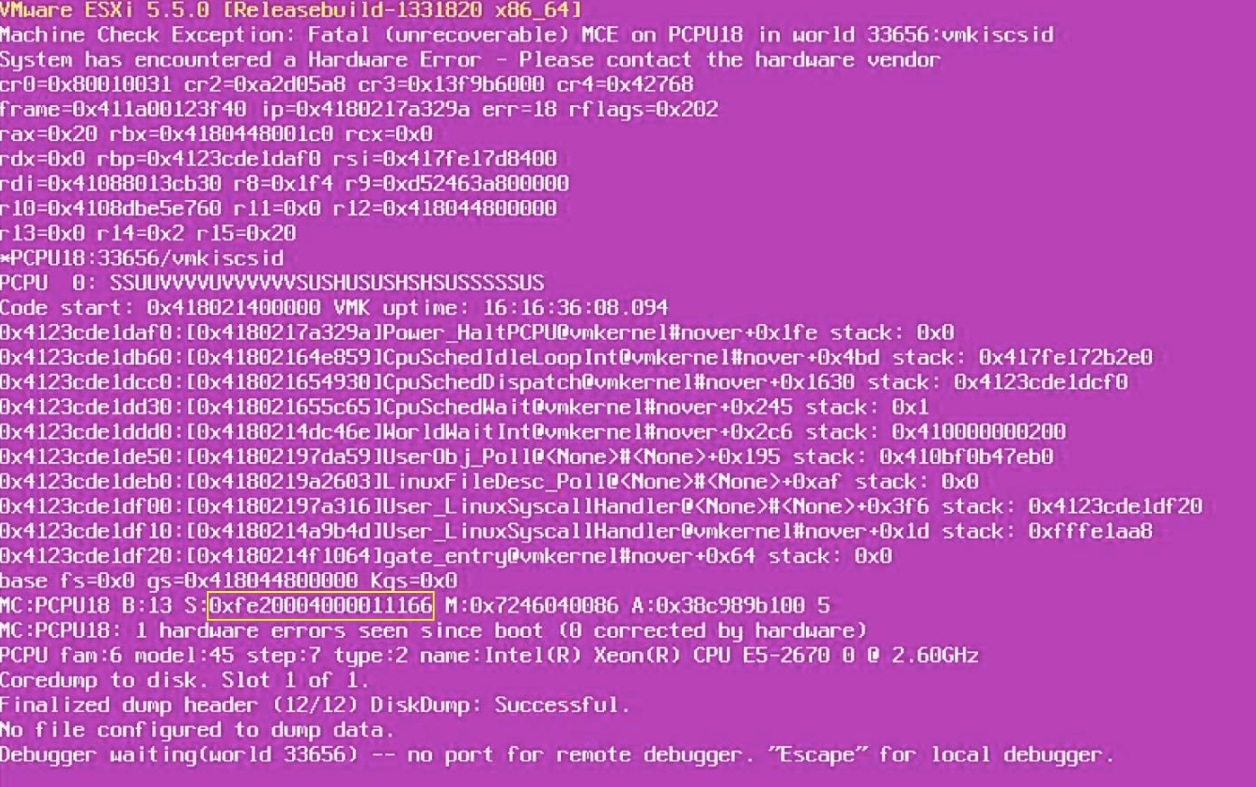
- Write down the
MCi_STATUSregister value. Here it is:
0xfe20004000011166.
- Convert it to binary:
1111 1110 0010 0000 0000 0000 0100 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 0001 0001 0110 0110
- Take the lower 16 bits of the
MCi_STATUSregister:
0001 0001 0110 0110
Compare it with the compound errors. In this case, this appears to be a cache hierarchy error (type 4).
- Apply the values:
F = 1 RRRR = 0110 – Prefetch TT = 01 – Transaction type - Data LL = 10 – Level 2 cache
Conclusion:
- It looks like the purple diagnostic screen occurred while there was a prefetch operation on some data in the L2 cache of the processor.
- Thus, this could be an issue with the L2 cache on the processor.
- Therefore, the CPU should be replaced first and then check if the issue is resolved. In case the issue comes up again, the motherboard could be replaced.