How to Create Snapshots of VMs and Revert to a Snapshot
Summary: This is a great practice to do before making any changes, such as working on SSL certs, Postgres database updates, or pod and node operations. Taking a snapshot ensures that you can revert back to the original state if required. ...
Instructions
How to create a Virtual Machine (VM) snapshot.
- Log in to vSphere
- Right-click the VM
- Click Snapshots
- Take Snapshots
- Name it, description is optional
- Select what you would like to include in the snapshot. Quiesce is recommended. VM Memory takes a lot of space and time. More information is below.
Memory:
If checked, a dump of the internal state of the VM is in the snapshot. Memory snapshots take longer to create but allow reversion to a running VM state as it was when the snapshot was taken. This option is selected by default. If this option is not selected, and quiescing is not selected, the snapshot creates files which are crash-consistent, which can be used to reboot the VM.
Quiesce:
If checked, and the virtual machine is powered on when the snapshot is taken, VMware Tools is used to quiesce the file system in the VM. Quiescing a file system is a process of bringing the on-disk data of a physical or virtual computer into a state for backups. This process might include such operations as flushing dirty buffers from the operating system's in-memory cache to disk, or other higher-level application-specific tasks.
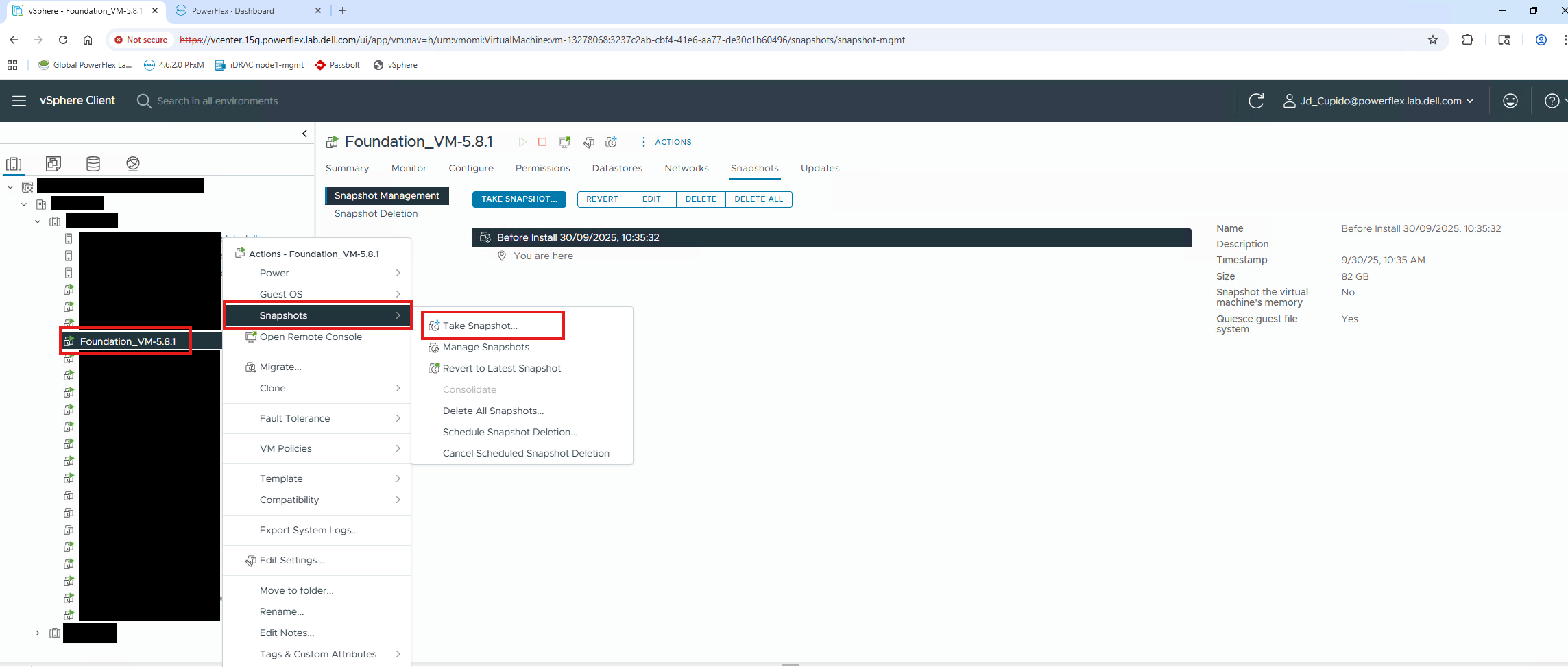
How to Revert to a Snapshot:
- Left-click on the Virtual Machine
- Click the Snapshots section
- Click snapshot required to revert to
- Click Revert

Additional Information
See Broadcom article Overview of virtual machine snapshots in vSphere 
To check the health of a PF VM after reverting to a snapshot:
kubectl get nodes systemctl status rke2-server