PowerProtect: How to perform SQL Self-Service restore
Summary: This article shows the steps required to perform a self-service SQL restore with the PowerProtect Data Manager (PPDM) SQL module.
This article applies to
This article does not apply to
This article is not tied to any specific product.
Not all product versions are identified in this article.
Instructions
Connect to the SQL server where data must be restored.


PowerProtect DD System: Select the DD where the backup is stored.
SQL Server Host: Select the source SQL server where the database to be restore was protected.
SQL Server Instance: Select the SQL server instance that contains the database to be restored.
Select the Database to be restore and backup date.
Restore to SQL Server: Define SQL target SQL server where the database is restored and the Database name where the data must be restored.
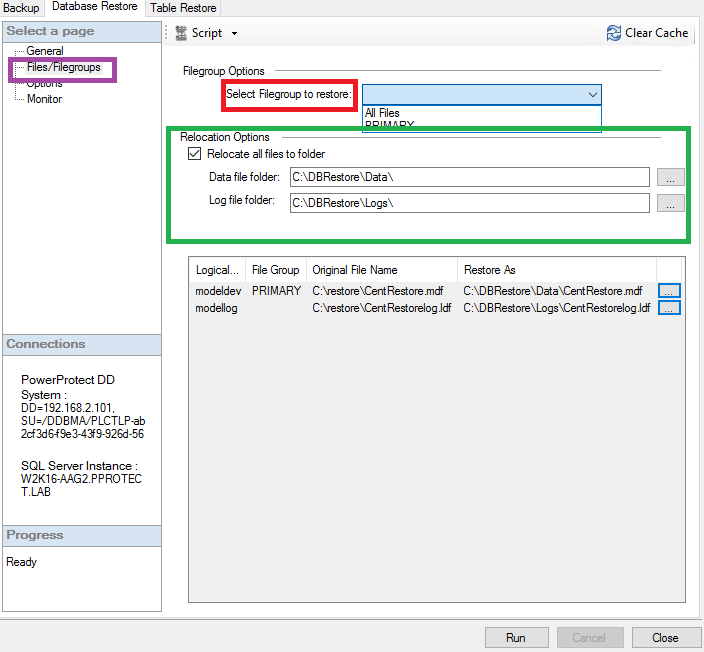
Filegroup Options: Define which file groups must be restored.
Relocation options: Define the relocation path where the database data and logs are to be restored.
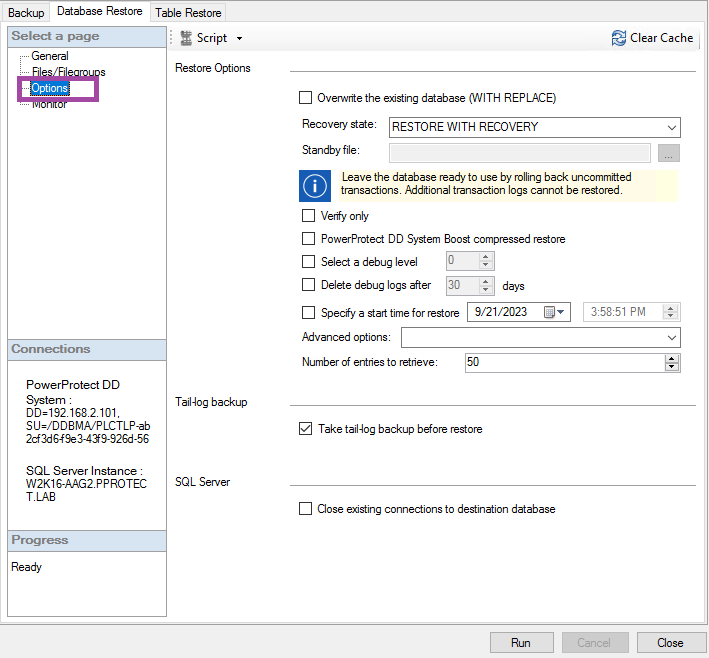
Overwrite existing database: The database is overwritten only if the database name is unchanged.
Recovery State:

- Open SQL management studio as administrator user:
- Open SMS plug-in:

- From the Data Base Restore tab, General section, configure the restore settings:

PowerProtect DD System: Select the DD where the backup is stored.
SQL Server Host: Select the source SQL server where the database to be restore was protected.
SQL Server Instance: Select the SQL server instance that contains the database to be restored.
Select the Database to be restore and backup date.
Restore to SQL Server: Define SQL target SQL server where the database is restored and the Database name where the data must be restored.
- Under the FIle/FileGroups options, define the following settings:

Filegroup Options: Define which file groups must be restored.
Relocation options: Define the relocation path where the database data and logs are to be restored.
- Under the options section, define optional available options for the restore to be performed:

Overwrite existing database: The database is overwritten only if the database name is unchanged.
Recovery State:
● RESTORE WITH RECOVERY: To leave the database in the ready-to-use state by rolling back uncommitted transactions, and disable the ability to restore the most recent or additional transaction logs.
● RESTORE WITH NORECOVERY: Leave the database in the non-operational state by not rolling back uncommitted transactions. Enables restoring the most recent or additional transaction logs.
● RESTORE WITH STANDBY: Enable the ability to undo committed transactions, save the undo actions in a standby file that enables you to reverse the restore effects, and put the database in the read-only mode. If you select this option, specify the Standby file field. To do this, select the button to the right of the field, browse for, and then select the file.
● RESTORE WITH NORECOVERY: Leave the database in the non-operational state by not rolling back uncommitted transactions. Enables restoring the most recent or additional transaction logs.
● RESTORE WITH STANDBY: Enable the ability to undo committed transactions, save the undo actions in a standby file that enables you to reverse the restore effects, and put the database in the read-only mode. If you select this option, specify the Standby file field. To do this, select the button to the right of the field, browse for, and then select the file.
Verify Only: Perform a verify only operation.
PowerProtect DD System Boost compressed restore: To compress the restore contents and transport them from the DD Replicator to the application host.
Select Debug level: Set the debug level for troubleshooting purposes.
Delete debug logs after: Define the number of days to maintain the debug level before been deleted.
Specify a start time for restore: Restore all the backups that were performed during or after a specified start time, and up to the time of the backup that is being restored.
Number of entries to retrieve: Edit the number of save sets or versions that the Microsoft application agent cache retrieves.
Take tail-log backup before restore: To perform a tail-log backup of the data before performing a restore operation.
Close existing connections to destination database: To ensure exclusive access to the database during the restore operation if multiple connections exist.
PowerProtect DD System Boost compressed restore: To compress the restore contents and transport them from the DD Replicator to the application host.
Select Debug level: Set the debug level for troubleshooting purposes.
Delete debug logs after: Define the number of days to maintain the debug level before been deleted.
Specify a start time for restore: Restore all the backups that were performed during or after a specified start time, and up to the time of the backup that is being restored.
Number of entries to retrieve: Edit the number of save sets or versions that the Microsoft application agent cache retrieves.
Take tail-log backup before restore: To perform a tail-log backup of the data before performing a restore operation.
Close existing connections to destination database: To ensure exclusive access to the database during the restore operation if multiple connections exist.
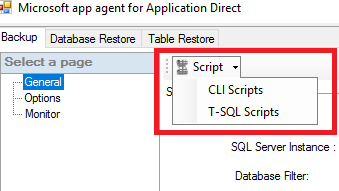
- On top of the SMS plug-in, we have Scripts generator tool that allows us to select between two script types:

- CLI Scripts: PPDM SQL module command-line scripts to be run on the command line.
- T-SQL Scripts: T-SQL scripts that can be run from an SQL server.

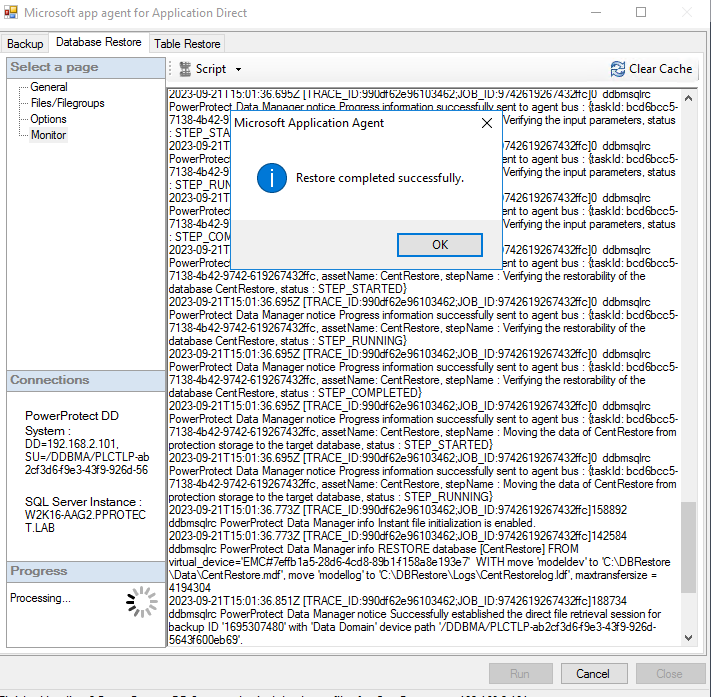
- Under the Monitor section, monitor the restore operation:

Additional Information
Article Properties
Article Number: 000217890
Article Type: How To
Last Modified: 04 Jan 2024
Version: 2
Find answers to your questions from other Dell users
Support Services
Check if your device is covered by Support Services.