ECS (Elastic Cloud Storage) provides a hyperscale, geo-distributed, software-defined cloud storage platform that is perfect for unstructured data, Big Data applications and Data Lakes. Deployed as a software-only solution or as a turnkey appliance, ECS offers all the cost advantages of public cloud running on commodity infrastructure while featuring enterprise reliability, availability and serviceability.
The new version of ECS headlines many new features and enhancements. Here is a “Top Ten” list of the most significant improvements and changes in ECS, version 2.0:
1. Built-in Element Management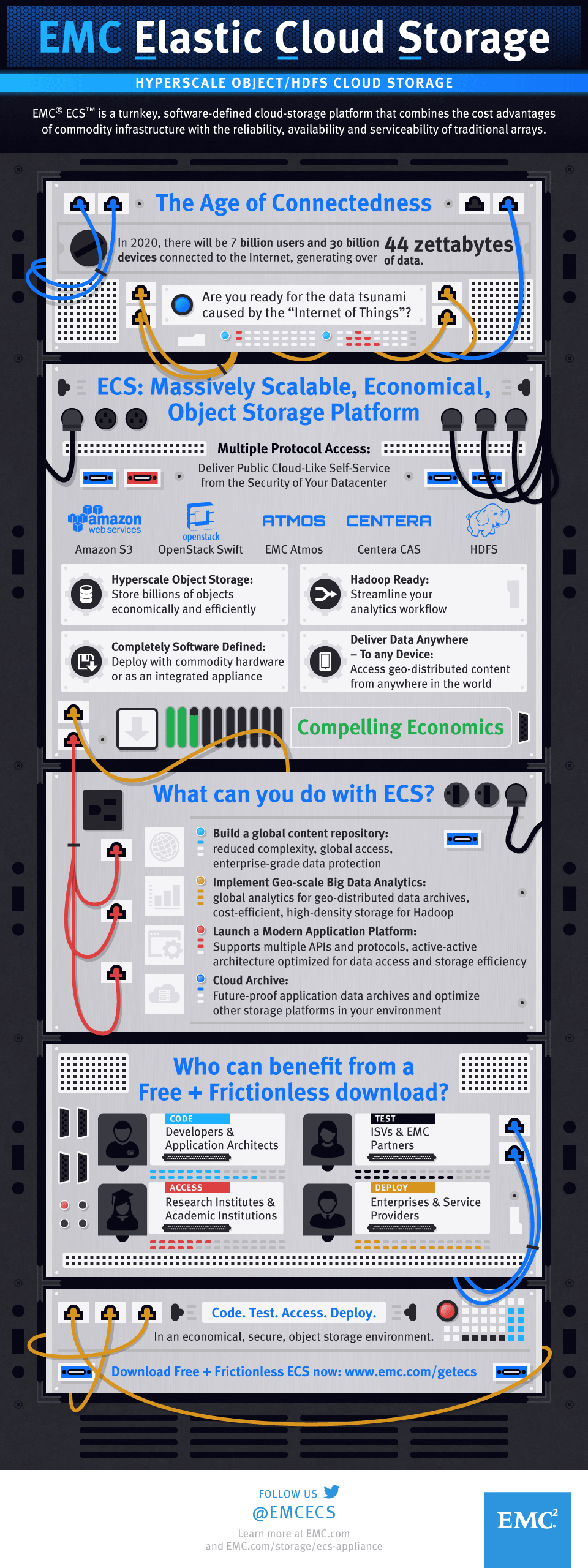
Any storage array requires strong element management capabilities to manage the infrastructure and its lifecycle. Until last release of ECS, the element management functionality of ECS was delivered via ViPR Controller. This meant that each installment of ECS would require a minimum of 3 additional VMs to run the ECS Appliance.
In ECS 2.0, all of the element management functionality is part of the ECS software itself and there is no requirement for additional ViPR Controller to manage ECS. The user interface for managing ECS is on each node and the administrator can hit any of the ECS nodes to get access to it. The improved interface is easy and simple to use with lot of enhanced functionality.
For customers who want a single pane of glass for management of their storage infrastructure, ECS will be able to plug into ViPR Controller like any other array that ViPR Controller manages and provide one single northbound interface for administrators for storage management.
2. Better UI, simplified management and operations
One of the fundamental changes in 2.0 release is the introduction of self-service UI and management built into the ECS software itself. ECS offers a simpler and more intuitive UI that allows administrators to easy deploy and manage their Appliance’s lifecycle.
In addition, based on the feedback from 1.x customers, a lot of the terminologies have been simplified, better-named or even removed. For example, a “tenant” is now the same as a “namespace”, so you don’t need two different variables. ECS 2.0 has simplified the multi-tenancy model and number of roles involved for managing the ECS. All of these operations managed by the UI are consuming a standard set of REST APIs that can be consumed directly if the customer chooses to use another user experience for managing their storage environment.
3. Improved Monitoring and Diagnosis in ECS UI
The new UI has lots of new information that will assist in monitoring, diagnosis and performance analysis, with drill downs and charts to make the analysis easier to visualize.
To start with, administrator can get information on
- Capacity utilization for disks,nodes and storage pools.
- Granular information on bandwidth, IOPs, latency and network utilization in different categories such as erasure coding, geo-caching, metadata, user data etc.
Other enhancements include detailed reports on replication groups
- Bandwidth for ingress/egress
- Progress of replication, details about chunks that are being cached and replicated etc.
In case of site failure or disaster, Administrators are able to get details on duration of recovery and amount of data to be recovered.
All this information will be stored for 7 days. For a longer period of data, the Customer can use ViPR SRM (with a new Solution Pack) or their own software that accesses ECS via REST API as all of the monitoring and diagnostics data is available through REST APIs.
4. Rack-level Awareness for better HA
ECS 2.0 brings rack-level awareness to the software so that when data has to be
distributed across disks and nodes, ECS software can spread the data across different racks for increased high-availability and redundancy. Each disk, node, rack and DCs are considered fault domains in ECS and data is distributed in a way to maximize the data availability.
5. Geo-replication: Unsealed chunk replication means better RPO
For geo-replication cases before ECS 2.0, ECS software wrote an object to chunks (of size 128MB), it waited for the chunk to get filled up, and then replicated the chunk to a remote site in an asynchronous process. Although this strategy is more efficient, the drawback is that if an entire site or a rack goes down, there could be many chunks with less than 128MB of data that have not been replicated. To reduce the risk of data loss, the software now starts streaming the data to remote Data center and the replication process kicks off as soon as a chunk receives new data. This feature will help with an improved RPO.
6. Geo-caching for better performance in multi-sites & Overall performance Improvements
In a multi-site environment, the data were always accessed from the primary site where it was originally written. This meant that every time customers in other sites accessed the data, it involved cost for WAN bandwidth as well as slower performance caused by WAN latency.
ECS 2.0 solves the above problem by the use of geo-caching the data at the secondary site on the local disk so that customers can access the data locally without a WAN transfer. This is more applicable to scenarios where the number of sites is greater than 2.
EMC 2.0 has stepped up the game in object performance when compared to earlier object platforms. Performance comparing ECS Appliance to ATMOS:
*Small Objects: write 6X faster – read 2X faster
*Large Objects: write 5X faster – read 9X faster
7. Temporary Site Failover
Temporary site failures like network drops are pretty common in data centers. ECS 2.0 has smart temporary site failures and failback features that allow applications to access its data even when the primary site is unavailable or unreachable. The delta writes can go to the secondary site. ECS software will also automatically re-sync the sites and reconcile the data when all the sites are operational and connected to each other again. Any conflicts that arise, get resolved leveraging the algorithms built into the software layer.
8. Metering and Auditing
One of the common requirements for running a large-scale multi-tenant distributed storage environment is to have very detailed metering. ECS 2.0 provides key statistics for individual buckets and tenants. This includes capacity, object count, objects created, objects deleted and bandwidth consumption (inbound as well as outbound bandwidth). The design and implementation is done in a way that it will satisfy the requirements of large scale services providers either in a single managed customer or a multi-tenant shared environment.
The new software also enables auditing for buckets, which allows administrators to view activities regarding creation, update, and deletion of buckets, and any changes in bucket ownership. This is especially important for environments that have to be governed by specific regulations. The events can be accessed through the UI or the REST API.
9. Quotas
ECS 2.0 software now allows administrators to set soft or hard quotas for buckets and tenants. This allows for administrators to set guard rails on consumption by application thus creating a sandbox without impacting other application users.
Alerts are raised and writes can be blocked after the set limit if the administrator chooses so. The administrator can also set up policies that can lock a specific bucket or a user if in case their application workload is causing other tenants to be impacted.
10. Free & Frictionless Download of ECS Software
Today, EMC announced the “Free and Frictionless” version of ECS. There is now a free download of ECS software for development and testing purposes with unlimited capacity and perpetual licensing. ECS made a bet on Docker even before it was GA and every single ECS Appliance ships with Docker in it. Now, we are making the same software containerized for broader audience. This allows developers, partners and customers to use and develop for ECS, while enjoying access to a large developer community. ECS is downloaded as a docker container, and installation can be done manually or automated through Puppet or Vagrant to run the software on one or more VMs/ bare metal servers. Stay tuned for information in EMC Pulse blog, the ECS Twitter account, and the EMC Community Network.
That’s ECS 2.0 in a nutshell. Of course, there will be more blog posts and white papers coming out soon as well. Customers, partners and developers have helped shaped the 2.0 version. We will continue to solicit more feedback on additional features should be added to the platform. If you have any request for features, please let us know and we will incorporate that in our roadmap.