Alienware x14 R2, x16 R1, and x16 R2 Laptop CPU Performance Behavior
Summary: This article provides information about the CPU Performance behavior on Alienware x14 R2 and Alienware x16 R1 and x16 R2 laptops.
Instructions
Affected Products:
Alienware x14 R2 Laptop (With Raptor Lake (RPL))
Alienware x16 R1 Laptop (With Raptor Lake (RPL))
Alienware x16 R2 Laptop (With Meteor Lake (MTL))
This article is intended to provide guidance to verify whether the laptop is:
- Performing as expected
- Alienware feature: Thermal Event (TCC) Offset Slider
- Describes the difference between each Alienware Command Center (AWCC) operating mode
- Frequently asked questions (FAQ) mostly about high Central processing unit (CPU) temperature problem
Five operating modes are provided for customers to select in the Alienware Command Center application. Fan acoustic level and laptop performance are the main difference between each mode.
The five modes are:
- Full Speed Mode has been re-named Overdrive Mode: The fan spins at full speed to support the CPU operating at turbo frequency for a longer time. The fan noise is noticeable and can be heard.
- Performance Mode: The fan spins aggressively to support the CPU operating at turbo frequency for a longer time. The fan noise is noticeable and can be heard.
- Balanced Mode: The fan spins in a moderate manner. The noise from the fan is less noticeable, but the period for the CPU to operate at turbo frequency is shorter.
- Battery Saver Mode: The fan spins in a moderate manner. The noise from the fan is less noticeable, but the Graphics processing unit (GPU) and GPU performance is limited for better skin comfort and battery life.
- Quiet Mode: The fan runs in a quieter level than in Balanced Mode. The noise from the fan is less noticeable, but the period for the CPU to operate at turbo frequency would be lower and shorter.
- Regardless of operating modes, the CPU temperature can exceed 100°C (212°F). (109°C (228.2°F) for MTL.) Then trigger a TCC under heavy loading. When TCC is activated, the CPU Power Limit 1 (PL1) frequency decreases a couple of hundred MHz to weaken the rising temperature. It allows the laptops thermal control mechanism to find the best thermal performance balance.
- You may be concerned about such high CPU temperatures in operation, but it is a general design feature of all gaming laptops.
In general, the CPU frequency keeps higher than Intel CPUs high frequency under Performance Mode and Balanced Mode.
| CPU module name | # of cores | # of physical big cores | # Threads | Processor Base frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i5-13420H | 8 | 4 | 12 | 2.1 GHz |
| i7-13620H | 10 | 6 | 16 | 2.4 GHz |
| i7-13700H | 14 | 6 | 20 | 2.4 GHz |
| i9-13900HK | 14 | 6 | 20 | 2.6 GHz |
| Core Ultra 7-155H | 14 | 6 | 20 | 1.4 GHz |
| Core Ultra 9-185H | 14 | 6 | 20 | 2.3 GHz |
- Verify using the integrated ePSA diagnostics that the laptop has an overheating issue.
- Change the operating thermal mode to Performance Mode. (See: How to Change AWCC Operating Mode)
- Set the test environment conditions (See: Test Environment Definition (Ambient Temperature 28°C (82.4°F) and plug in the AC adapter.
- Use Dell SupportAssist to stress the CPU. (See: SOP for Stress CPU in Dell SupportAssist)
- Choose the FUSION tab on the AWCC home page to monitor CPU Frequency and CPU temperature.
| AWCC Operating Mode | Processor | CPU Clock (During the first five minutes Alienware SupportAssist CPU Stress Test) |
CPU Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance Mode | MTL Intel Core Ultra 9-185H | 3100 MHz ~ 5100 MHz | May be up to 110°C (230°F) |
| MTL Intel Core Ultra 7-155H | 3000 MHz ~ 4800 MHz | ||
| RPL i9-13900HK (AWx16 R1, RTX 4080 or 4090) |
3600 MHz ~ 5000 MHz | May be up to 100°C (212°F) | |
| RPL i9-13900HK (AWx16 R1, RTX 4060 or 4070) |
3600 MHz ~ 4900 MHz | ||
| RPL i7-13700H (AWx16 R1, RTX 4080 or 4090) |
3600 MHz ~ 5000 MHz | ||
| RPL i7-13700H (AWx16 R1, RTX 4060 or 4070) |
3600 MHz ~ 4900 MHz | ||
| RPL i7-13620H (AWx14 R2, RTX 4050 or 4060) |
3600 MHz ~ 4500 MHz | ||
| RPL i5-13420H (AWx14 R2, RTX 3050, 4050 or 4060) |
3600 MHz ~ 4500 MHz |
On Alienware x14 R2 and x16 R1 i5, i7, and i9 RPL configurations, it allows you to customize your own CPU TCC triggering point setting. (Within the offset range 0°C~15°C (32°F~59°F), the default is 0.) It means that the CPU Tj(max) can be 85°C~100°C (185°F~212°F). However, on Alienware x16 R2 Core Ultra 7 and 9 MTL configurations, it allows you to customize your own CPU TCC triggering point setting. (Within the offset range 0°C~15°C (32°F~59°F), the default is 0.) It means that the CPU Tj(max) can be 95°C~110°C (203°F~230°F).
Intel states the following: Regardless of the AWCC operating modes, the CPU temperature can exceed 100°C (212°F), then trigger TCC under heavy loading. When a TCC event occurs, the CPU Power Limit 1 (PL1) frequency decreases a couple of hundred MHz to weaken the rising temperature. It allows the laptop thermal control mechanism to find the best thermal performance balance.
Although it is a general design of all gaming laptops, you may still be concerned about such high CPU temperatures. This is mainly because of third-party tools such as HWiNFO. These third-party tools show a warning message and the CPU temperature in red when the CPU Temperature is greater than 90°C (194°F).
The CPU TCC Offset Slider provides you with more authority to adjust the CPU thermal event algorithm.
See TCC Offset Slider SOP in this document for SOP to set it in the BIOS setup menu.
Why does the laptops Diagnostic Tool post "High CPU temperature" when the laptop is in idle mode?
The laptop is never truly idle, even if the laptop reports that it is idle. There are still some background tasks operating in high CPU frequency. Which induces a high CPU temperature peak value (within 1 second) then drops down to a lower average temperature.
Does the CPU get damaged when the CPU temperature reaches 100°C (212°F)?
No, the CPU operates well under the Intel CPU specification: RPL: Tj(max)=100°C (212°F) and MTL: Tj(max)=110°C (230°F)
(Statement from Intel) Processor supplies a method (Digital Thermal Sensor or DTS) to report real time die temperature below, equal to, or above Tj(max). While the die should not run above Tj (max), a temperature value above Tj(max) may occur occasionally under normal operation. (Tj(max))
Does the CPU overheat when some tools report "CPU overheat/100°C" (212°F) or "Thermal throttling/TCC"?
No, the CPU operates well under the Intel CPU specification: RPL: Tj(max)=100°C (212°F) and MTL: Tj(max)=110°C (230°F)
For new generations of processors, when the CPU operates with max frequency. The thermal throttling or thermal event is often triggered to find a balance between thermal comfort and performance by dynamically adjusting the CPU power. You can neglect the warning messages if the CPU operates at boost frequency. Where the boost frequency is higher than the CPU base frequency, as defined by the processor manufacturers such as Intel.
Why does the diagnostic tool on the laptop post "high CPU temperature" in gaming applications or graphic stress applications?
Some Games and Graphics stress applications that combine with heavy CPU loading to cause high CPU temperatures.
Is the CPU peak temperature under Balanced Mode lower than under Performance Mode?
No, under Balanced Mode, the CPU can still boost to its highest frequency within a short period and induce high peak temperature.
The CPU high peak temperature is designed to strive for the best performance, no matter at Performance Mode, Balanced Mode, Quiet Mode, or Battery Savor Mode.
Is it expected behavior if the single-core CPU (including P-Cores) reaches 100°C (212°F) and other cores do not?
Yes, there is favor code in the Intel RPL and MTL CPU functions. The CPU uses the most efficient P-core to work, to cause efficient code with higher temperatures.
Is the feature "CPU TCC Offset Slider" only at Alienware x14 R2, x16 R1, and x16 R2?
No, they are among several Alienware gaming laptops to have the CPU TCC Offset Slider feature.
How to Change AWCC Operating Mode
-
Open the AWCC application (References version 6.x)
-
Select the DASHBOARD tab.
-
Select the operating mode from the Performance or Thermal menu.
SOP for Stress CPU in Dell SupportAssist
-
Open My Alienware.
-
Select SUPPORT.
-
Select the Troubleshooting tab.
-
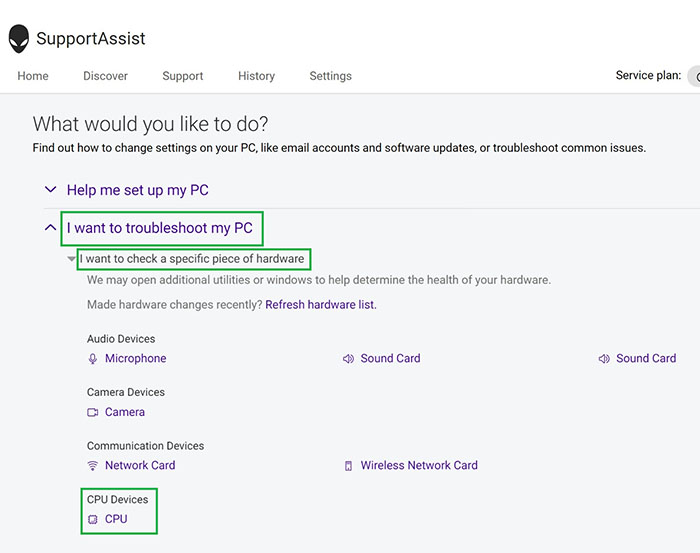
Select I want to troubleshoot my PC.
-
Select I want to check a specific piece of hardware.
-
Select CPU.
-
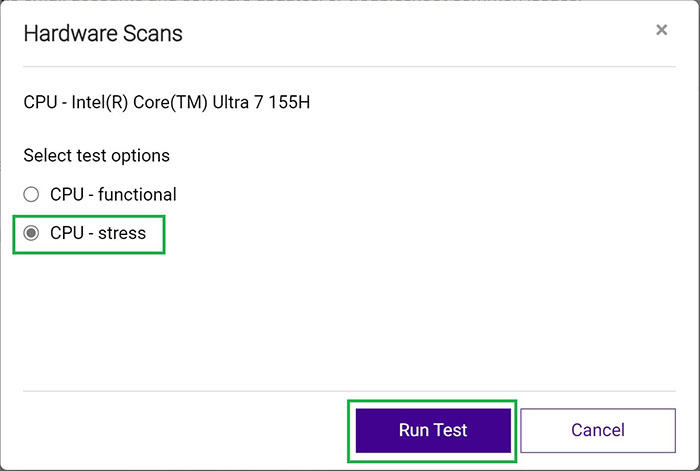
Select CPU Stress Test.
-
Click Run Test.
Test Environment Definition (Ambient Temperature 28°C (82.4°F))
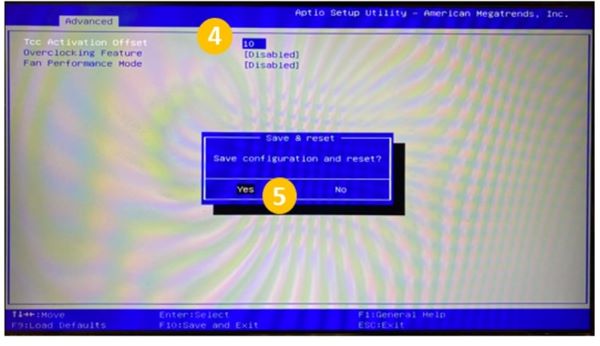
TCC Offset Slider SOP
-
Press the F2 key to enter the BIOS User Interface during booting through the splash screen.
-
Choose the Advanced tab. (Use the arrow keys to navigate.)
-
Select Performance Options.
-
Input the value of TCC Activation offset (in the selected field add number from 0~15 (0°C~15°C (32°F~59°F))).
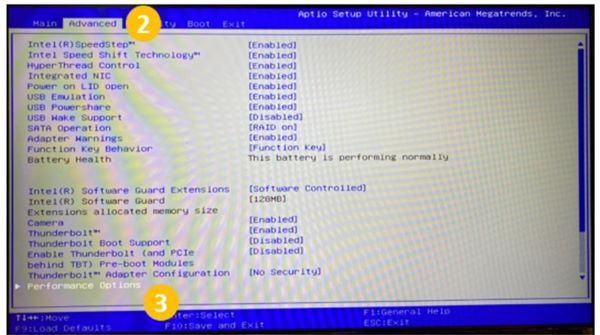
-
Press the F10 key to save the changes and reboot.