PowerEdge: How to Monitor Server Health from iDRAC9
Summary: This article provides general information about how to view and monitor server health from the IDRAC9/10 web interface.
This article applies to
This article does not apply to
This article is not tied to any specific product.
Not all product versions are identified in this article.
Instructions
Navigate iDRAC9 to Monitor Server Health
Table of Contents:
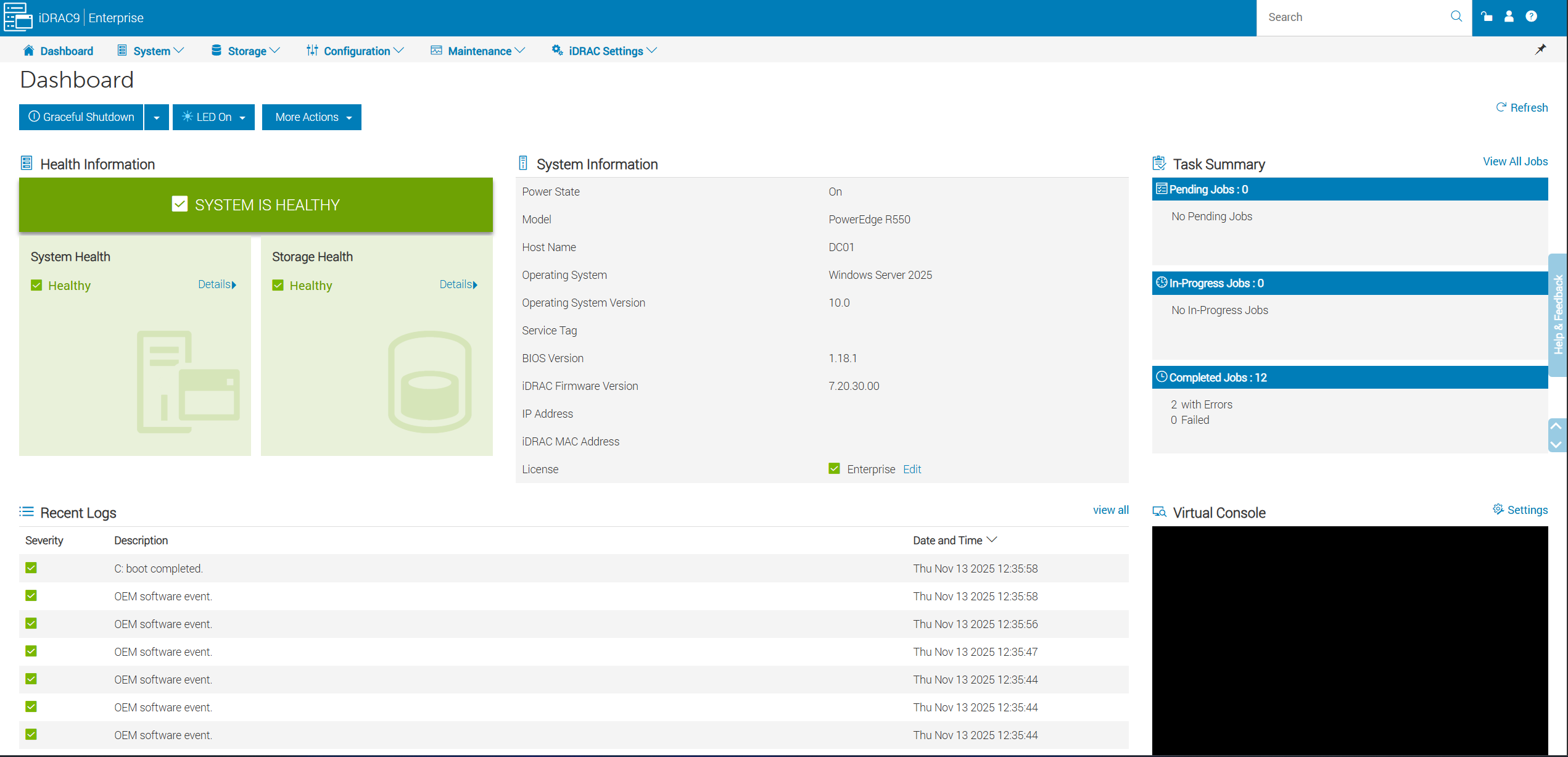
Dashboard Summary:
- Review health alerts for any warnings.
- Perform Power Actions
- Launch the Virtual Console.
- Check the Jobs in Progress.
- Read recent system logs for anomalies.
IDRAC System → Cooling:
- View the thermal profile chart.
- Inspect fan status and speeds.
- Check temperature readings for each sensor.

Figure 2: Click System -> Cooling.
-
View fan health along with the current speed. Fan speeds modulate as needed depending on inlet and component temperatures.
- Fans speed up to full speed (
100% PWM) as a response to either fan failures, temperature sensor failures or when the IDRAC goes offline.- If a fan failure is detected, the remaining fans automatically increase their speeds to compensate for the lost airflow.
- The IDRAC controls the fans making adjustments when needed, if the iDRAC goes offline for any reason the fans default to full speed.
- The IDRAC adjusts the fan speeds based on the reading from the inlet temperature sensor, if the sensor fails or stops communicating with the iDRAC the fans adjust to full speed.

- View CPU, Memory (DIMM), inlet (ambient), and exhaust temperatures as well as their warning and critical ranges
Note: If the CPU temperatures reach critical temps, the IDRAC initiates a server shutdown command.
- The IDRAC adjusts the fan speeds based on the reading from the inlet temperature sensor.
- If the inlet temperature reaches the warning or critical temperatures, the IDRAC increases the fan speeds to attempt to keep temperatures in the normal range.
- If the temperature sensor fails to communicate with the IDRAC, the fan speeds default to full speed until its back online.
Note: The inlet temperature sensor is typically located in the front/right control panel.
System Overview → Front Panel:
- Look for any alerts displayed on the front LCD panel.

Figure 5: Navigate to System -> Overview -> Front Panel.
System Overview → Memory:
- Verify total installed memory.
- Check the maximum supported memory.
- Review the memory population, and identify empty slots.
- Inspect each DIMM's health status and detailed information.

Figure 6: Click System -> Memory.
System Overview → Power:
- Check power‑supply health and input voltage.
- View current server power consumption.
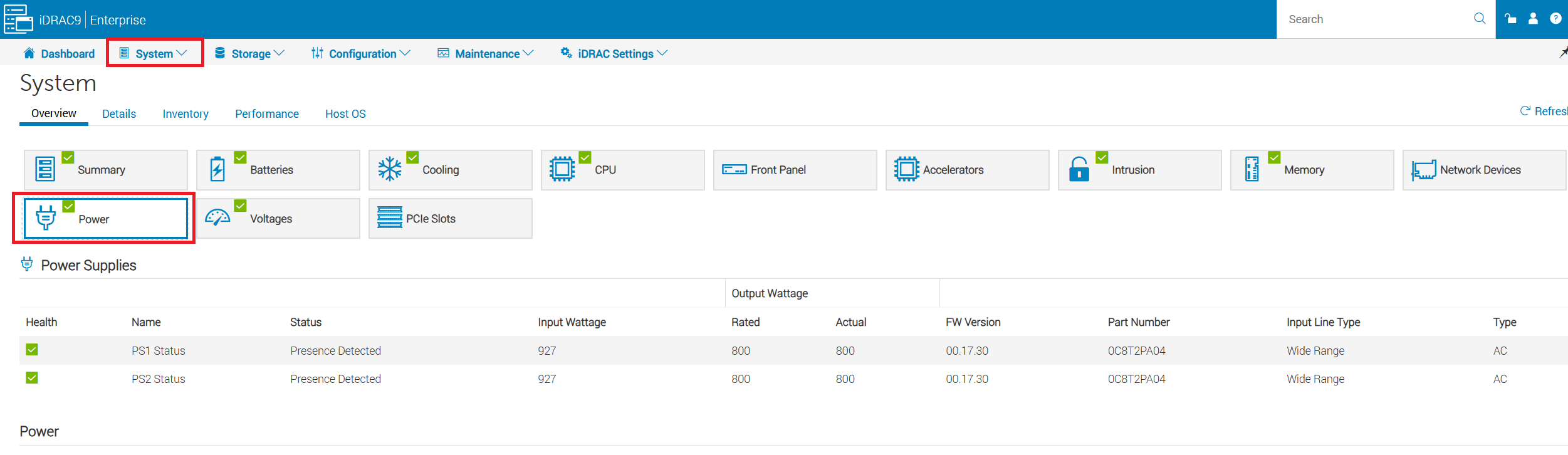
Figure 8: Go to System → Power
- View the servers total power consumption and Power Supply wattage.
Maintenance → System Update:
- Choose to update component firmware locally or over HTTPS.
- Setup automatic updates
- Use the rollback option to revert to a previous firmware version when needed.

Figure 10: Select Maintenance -> System Update Note: The rollback option is only available for firmware updated using the IDRAC and only where the firmware version supports rollback
Note: The rollback option is only available for firmware updated using the IDRAC and only where the firmware version supports rollback
Maintenance → Lifecycle Log:
- Review all events: Informational, warning, and critical
- Apply filters for keywords or specific date ranges to narrow results.

Figure 12: Click Maintenance -> Lifecycle Log
- The filter option allows filtering the log for keywords, severity, type, or specified date ranges.
Maintenance → System Event Log (SEL):
- View the history of events.
- Clear the System Event Log.

Figure 14: Navigate to Maintenance -> System Event Log
Maintenance → SupportAssist:
- Start a collection to generate a SupportAssist Report (TSR).
- Monitor the log‑collection status.
- Check server warranty details.

Figure 15: Select Maintenance -> SupportAssist
Storage → Summary:
- Assess overall storage health at a glance.
- Review recent storage events.
- Count virtual and physical disks.

Figure 16: Click Storage -> Summary
Storage → Controllers:
- View installed storage controllers.
- Perform controller‑level actions as required.
- Check health of any controller batteries.

Figure 17: Navigate to Storage -> Controllers

- Foreign Configuration - Allows you to clear any foreign configuration on single disks, or import foreign configuration of an entire array.
- For additional info, refer to - PowerEdge: How to Import a Foreign Configuration in the RAID Controller Using the System Setup Menu
- Never import foreign configuration into an online array as this can cause corruption merging old data from the foreign disk into the active array. Only import offline arrays.
- Discard Preserved Cache - The controller preserves the cache from a virtual disk if the virtual disk goes offline or is deleted because of missing physical disks. This preserved cache is preserved until you import the virtual disk or discard the cache.
- Importing foreign configuration is not possible when preserved cache is present.
Storage → Physical Disks:
- Inspect health status and detailed information for each disk.
- Perform disk actions (such as, secure erase, firmware update).
- Monitor physical disk rebuild progress.

Figure 20: Select Storage -> Physical Disks
- The disk details show information such as if the disk is in predictive failed state or show the rebuild progress if the disk is in rebuild state.
Storage → Virtual Disks:
- Review health and configuration details of each virtual disk.
- Run Consistency Checks, RAID Level Migration, capacity expansions, or assign dedicated hot spares.
- Create a new virtual disk.

Figure 22: Click Storage -> Virtual Disks
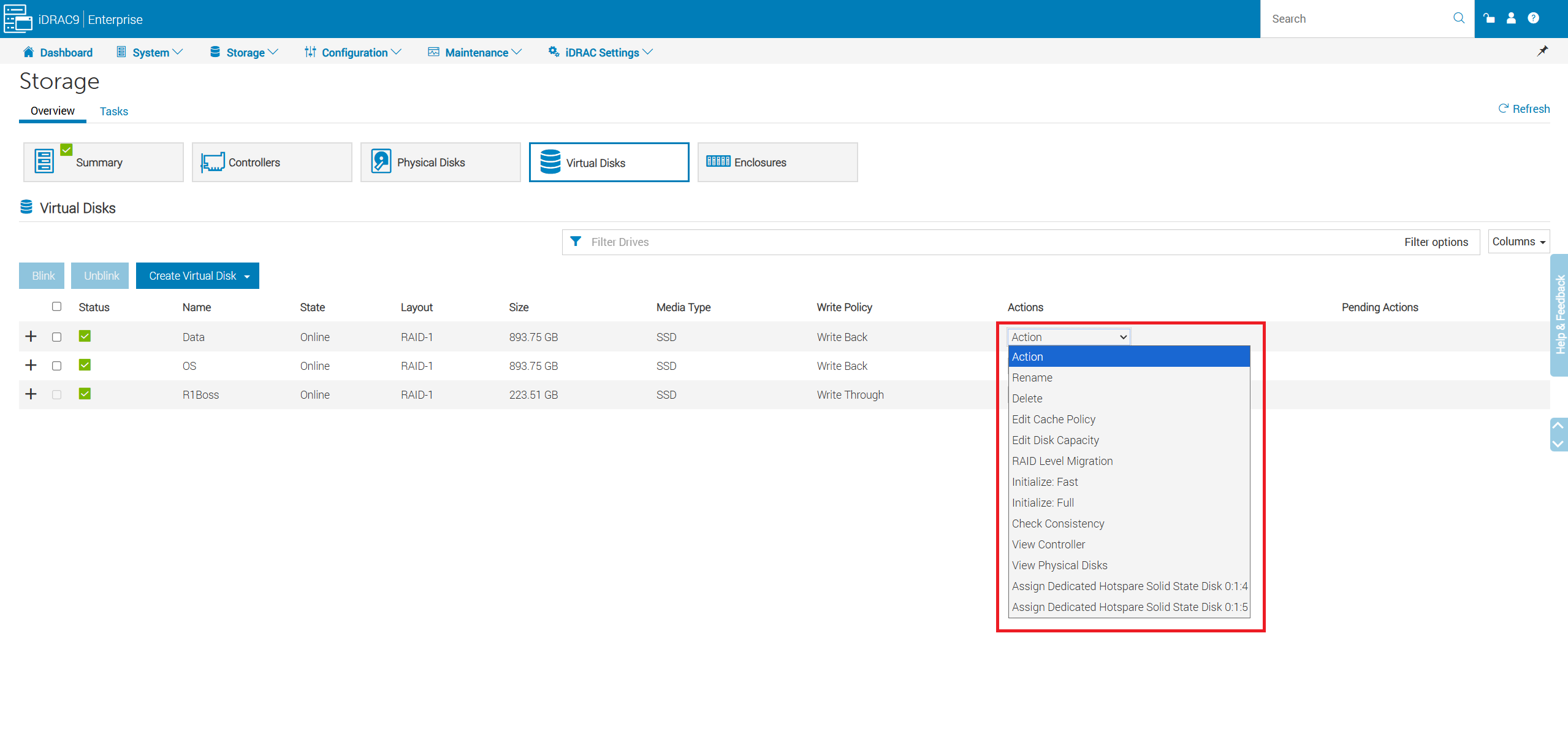
- The virtual disk actions allow you to perform tasks such as: RAID Level Migration (RLM), and Check Consistency.
- For more information about RAID Level Migration (RLM) refer to - PowerEdge: How to Reconfigure a Virtual Disk or Add More Hard Drives
- Consistency Check (CC) is a background operation that verifies and corrects the mirror or parity data for fault tolerant virtual disks. It is recommended that you periodically run a consistency check on virtual disks.
Affected Products
HS Series, iDRAC9, PowerEdge R240, PowerEdge R250, PowerEdge R260, PowerEdge R340, PowerEdge R350, PowerEdge R360, PowerEdge R440, PowerEdge R450Products
PowerEdge XR2, PowerEdge R540, PowerEdge R550, PowerEdge R640, PowerEdge R6415, PowerEdge R650, PowerEdge R650xs, PowerEdge R6515, PowerEdge R6525, PowerEdge R660, PowerEdge R660xs, PowerEdge R6615, PowerEdge R6625, PowerEdge R740, PowerEdge R740XD
, PowerEdge R740XD2, PowerEdge R7415, PowerEdge R7425, PowerEdge R750, PowerEdge R750XA, PowerEdge R7515, PowerEdge R7525, PowerEdge R760, PowerEdge R760XA, PowerEdge R760xd2, PowerEdge R760xs, PowerEdge R7615, PowerEdge R7625, PowerEdge R840, PowerEdge R860, PowerEdge R940, PowerEdge R940xa, PowerEdge R960, PowerEdge T140, PowerEdge T150, PowerEdge T160, PowerEdge T340, PowerEdge T350, PowerEdge T360, PowerEdge T440, PowerEdge T550, PowerEdge T560, PowerEdge T640, PowerEdge XR11, PowerEdge XR12
...
Article Properties
Article Number: 000391164
Article Type: How To
Last Modified: 19 Nov 2025
Version: 3
Find answers to your questions from other Dell users
Support Services
Check if your device is covered by Support Services.